

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (04): 489-496.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.333
Special Issue: 老年人群健康最新文章合集; 营养最新文章合集; 老年问题最新文章合集
• Original Research·Methods and Tools • Previous Articles Next Articles
Development,Reliability and Validity of a Concise,Prediction Model-based Nutritional Risk Assessment Scale for Nursing Home-dwelling Older People
Peking University School of Nursing,Beijing 100083,China
*Corresponding author:XIE Hong,Associate professor,Master supervisor;E-mail:xh6959@163.com
Received:2021-05-15
Revised:2021-11-13
Published:2022-02-05
Online:2022-01-29
通讯作者:
谢红
CLC Number:
ZHU Dan, XIE Hong.
Development,Reliability and Validity of a Concise,Prediction Model-based Nutritional Risk Assessment Scale for Nursing Home-dwelling Older People [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(04): 489-496.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.333
| 自变量 | b(95%CI) | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI(kg/m2,以≥23为参照) | |||||
| <19.0 | 6.075(5.172,6.977) | 0.460 | 174.080 | <0.001 | |
| 19.0~20.9 | 3.922(3.186,4.659) | 0.376 | 109.017 | <0.001 | |
| 21.0~22.9 | 2.141(1.486,2.796) | 0.334 | 41.057 | <0.001 | |
| 近3个月体质量变化(以<1 kg为参照) | |||||
| >3 kg | 4.852(3.542,6.161) | 0.668 | 52.718 | <0.001 | |
| 不知道 | 3.943(3.377,4.508) | 0.288 | 186.886 | <0.001 | |
| 1~3 kg | 2.456(1.855,3.057) | 0.307 | 64.112 | <0.001 | |
| 活动能力(以独立活动为参照) | |||||
| 卧床 | 4.310(3.510,5.110) | 0.408 | 111.499 | <0.001 | |
| 依赖工具 | 1.446(1.006,1.887) | 0.225 | 41.389 | <0.001 | |
| 牙齿状况(以正常为参照) | |||||
| 全或半口缺牙 | 3.959(3.371,4.547) | 0.300 | 174.336 | <0.001 | |
| 佩戴义齿 | 1.357(0.892,1.821) | 0.237 | 32.705 | <0.001 | |
| 神经精神疾病(以无认知障碍或抑郁为参照) | |||||
| 重度认知障碍或抑郁 | 4.639(3.745,5.532) | 0.456 | 103.566 | <0.001 | |
| 轻度认知障碍或抑郁 | 2.367(1.712,3.023) | 0.335 | 50.079 | <0.001 | |
| 疾病种数(种,以0~3为参照) | |||||
| >3 | 1.355(0.771,1.939) | 0.298 | 20.714 | <0.001 | |
| 药物种数(种,以0~3为参照) | |||||
| >3 | 1.283(0.780,1.786) | 0.257 | 24.984 | <0.001 | |
| 户外独立活动时间(h,以≥1为参照) | |||||
| <1 | 1.638(1.154,2.123) | 0.247 | 43.959 | <0.001 | |
| 进食能力(以自行进食为参照) | |||||
| 喂食 | 2.795(1.991,3.598) | 0.410 | 46.500 | <0.001 | |
| 自行进食稍困难 | 1.093(0.299,1.888) | 0.405 | 7.275 | 0.007 | |
| 小腿围(cm,以≥31为参照) | |||||
| <31 | 1.208(0.791,1.625) | 0.213 | 32.210 | <0.001 | |
Table 1 Ordinal,multinominal Logistic regression analysis of factors related to nutrition status in nursing home-dwelling older people
| 自变量 | b(95%CI) | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI(kg/m2,以≥23为参照) | |||||
| <19.0 | 6.075(5.172,6.977) | 0.460 | 174.080 | <0.001 | |
| 19.0~20.9 | 3.922(3.186,4.659) | 0.376 | 109.017 | <0.001 | |
| 21.0~22.9 | 2.141(1.486,2.796) | 0.334 | 41.057 | <0.001 | |
| 近3个月体质量变化(以<1 kg为参照) | |||||
| >3 kg | 4.852(3.542,6.161) | 0.668 | 52.718 | <0.001 | |
| 不知道 | 3.943(3.377,4.508) | 0.288 | 186.886 | <0.001 | |
| 1~3 kg | 2.456(1.855,3.057) | 0.307 | 64.112 | <0.001 | |
| 活动能力(以独立活动为参照) | |||||
| 卧床 | 4.310(3.510,5.110) | 0.408 | 111.499 | <0.001 | |
| 依赖工具 | 1.446(1.006,1.887) | 0.225 | 41.389 | <0.001 | |
| 牙齿状况(以正常为参照) | |||||
| 全或半口缺牙 | 3.959(3.371,4.547) | 0.300 | 174.336 | <0.001 | |
| 佩戴义齿 | 1.357(0.892,1.821) | 0.237 | 32.705 | <0.001 | |
| 神经精神疾病(以无认知障碍或抑郁为参照) | |||||
| 重度认知障碍或抑郁 | 4.639(3.745,5.532) | 0.456 | 103.566 | <0.001 | |
| 轻度认知障碍或抑郁 | 2.367(1.712,3.023) | 0.335 | 50.079 | <0.001 | |
| 疾病种数(种,以0~3为参照) | |||||
| >3 | 1.355(0.771,1.939) | 0.298 | 20.714 | <0.001 | |
| 药物种数(种,以0~3为参照) | |||||
| >3 | 1.283(0.780,1.786) | 0.257 | 24.984 | <0.001 | |
| 户外独立活动时间(h,以≥1为参照) | |||||
| <1 | 1.638(1.154,2.123) | 0.247 | 43.959 | <0.001 | |
| 进食能力(以自行进食为参照) | |||||
| 喂食 | 2.795(1.991,3.598) | 0.410 | 46.500 | <0.001 | |
| 自行进食稍困难 | 1.093(0.299,1.888) | 0.405 | 7.275 | 0.007 | |
| 小腿围(cm,以≥31为参照) | |||||
| <31 | 1.208(0.791,1.625) | 0.213 | 32.210 | <0.001 | |
| 项目 | Logistic回归模型 | 决策树模型 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 良好 | 风险 | 不良 | 良好 | 风险 | 不良 | |
| AUC | 0.962a | 0.942a | 0.989a | 0.914a | 0.868a | 0.968a |
| 灵敏度 | 0.826 | 0.902 | 0.819 | 0.729 | 0.828 | 0.862 |
| 特异度 | 0.931 | 0.814 | 0.986 | 0.909 | 0.771 | 0.918 |
| 约登指数 | 0.758 | 0.716 | 0.805 | 0.638 | 0.589 | 0.780 |
Table 2 The AUC,sensitivity,specificity and Youden index of Logistic regression model and decision tree model for predicting nutrition status in nursing home-dwelling older people
| 项目 | Logistic回归模型 | 决策树模型 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 良好 | 风险 | 不良 | 良好 | 风险 | 不良 | |
| AUC | 0.962a | 0.942a | 0.989a | 0.914a | 0.868a | 0.968a |
| 灵敏度 | 0.826 | 0.902 | 0.819 | 0.729 | 0.828 | 0.862 |
| 特异度 | 0.931 | 0.814 | 0.986 | 0.909 | 0.771 | 0.918 |
| 约登指数 | 0.758 | 0.716 | 0.805 | 0.638 | 0.589 | 0.780 |
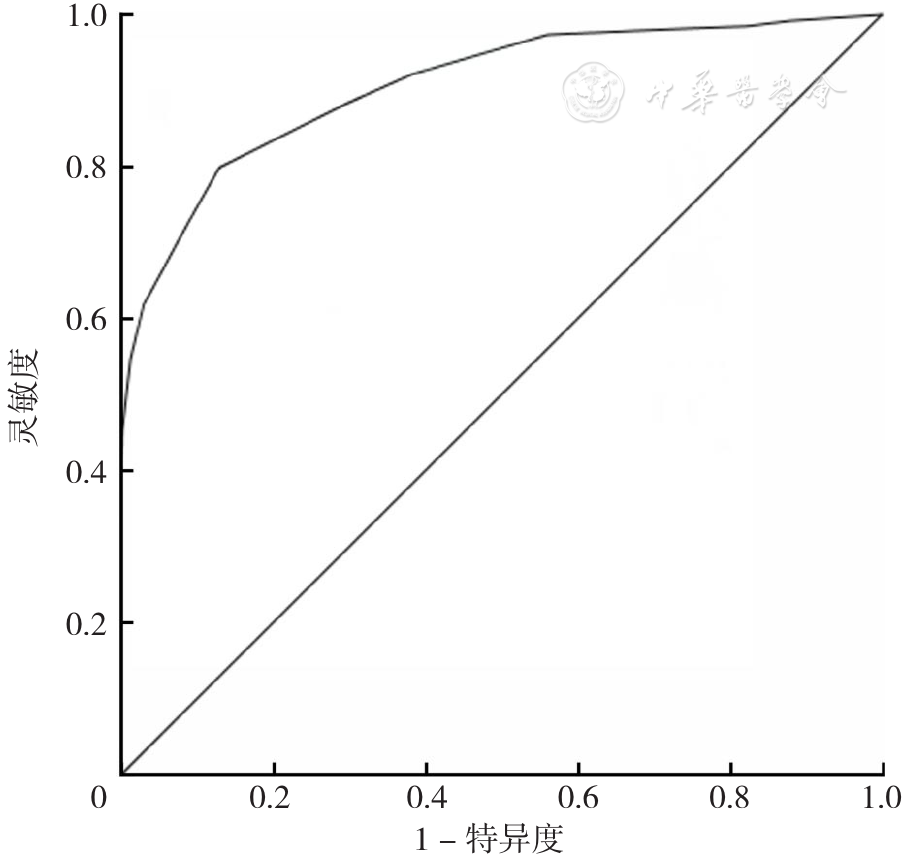
Figure 2 ROC curve of the predictive performance for nutritional risk/malnutrition of the concise Nutritional Risk Assessment Scale for Nursing Home-dwelling Older People
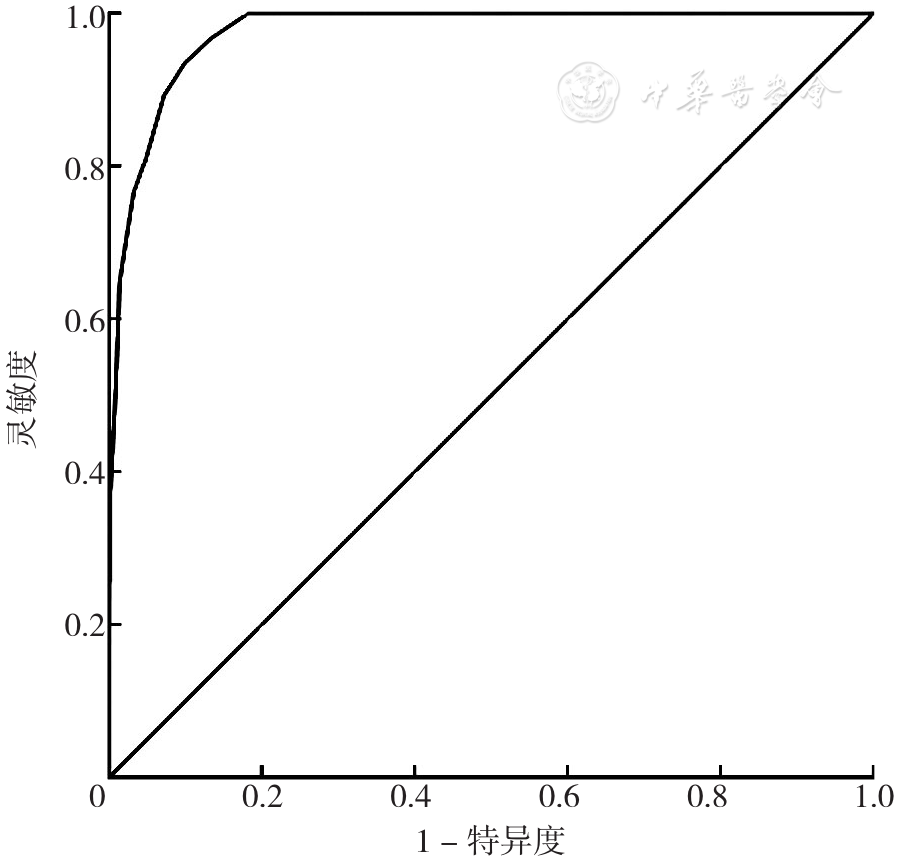
Figure 3 ROC curve of the predictive performance for malnutrition of the concise Nutritional Risk Assessment Scale for Nursing Home-dwelling Older People
| 项目 | 赋值(分) | 项目 | 赋值(分) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI(kg/m2) | 神经精神疾病 | ||||
| <19.0 | 3 | 重度认知障碍或抑郁 | 2 | ||
| 19.0~20.9 | 2 | 轻度认知障碍或抑郁 | 1 | ||
| 21.0~22.9 | 1 | 无认知障碍或抑郁 | 0 | ||
| ≥23.0 | 0 | 疾病种数(种) | |||
| 近3个月体质量变化 | >3 | 0.5 | |||
| >3 kg | 2 | 0~3 | 0 | ||
| 不知道 | 2 | 药物种数(种) | |||
| 1~3 kg | 1 | >3 | 0.5 | ||
| <1 kg | 0 | 0~3 | 0 | ||
| 活动能力 | 户外独立活动时间(h) | ||||
| 卧床 | 2 | <1 | 1 | ||
| 依赖工具 | 1 | ≥1 | 0 | ||
| 独立活动 | 0 | 进食能力 | |||
| 牙齿状况 | 喂食 | 1 | |||
| 全或半口缺牙 | 2 | 自行进食稍困难 | 0.5 | ||
| 佩戴义齿 | 1 | 自行进食 | 0 | ||
| 正常 | 0 | 小腿围(cm) | |||
| <31 | 0.5 | ||||
| ≥31 | 0 | ||||
Table 3 The concise Nutritional Risk Assessment Scale for Nursing Home-dwelling Older People
| 项目 | 赋值(分) | 项目 | 赋值(分) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI(kg/m2) | 神经精神疾病 | ||||
| <19.0 | 3 | 重度认知障碍或抑郁 | 2 | ||
| 19.0~20.9 | 2 | 轻度认知障碍或抑郁 | 1 | ||
| 21.0~22.9 | 1 | 无认知障碍或抑郁 | 0 | ||
| ≥23.0 | 0 | 疾病种数(种) | |||
| 近3个月体质量变化 | >3 | 0.5 | |||
| >3 kg | 2 | 0~3 | 0 | ||
| 不知道 | 2 | 药物种数(种) | |||
| 1~3 kg | 1 | >3 | 0.5 | ||
| <1 kg | 0 | 0~3 | 0 | ||
| 活动能力 | 户外独立活动时间(h) | ||||
| 卧床 | 2 | <1 | 1 | ||
| 依赖工具 | 1 | ≥1 | 0 | ||
| 独立活动 | 0 | 进食能力 | |||
| 牙齿状况 | 喂食 | 1 | |||
| 全或半口缺牙 | 2 | 自行进食稍困难 | 0.5 | ||
| 佩戴义齿 | 1 | 自行进食 | 0 | ||
| 正常 | 0 | 小腿围(cm) | |||
| <31 | 0.5 | ||||
| ≥31 | 0 | ||||
| 条目 | 因子1 | 因子2 | 因子3 | 因子4 | 因子5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 活动能力 | 0.858 | 0.001 | 0.045 | 0.087 | 0.107 |
| 户外独立活动时间 | 0.752 | 0.083 | 0.093 | -0.035 | -0.140 |
| 进食能力 | 0.776 | 0.004 | 0.078 | 0.214 | -0.017 |
| 疾病种数 | 0.022 | 0.841 | -0.030 | -0.132 | -0.031 |
| 药物种数 | 0.058 | 0.797 | -0.006 | 0.226 | 0.003 |
| BMI | 0.048 | -0.013 | 0.874 | -0.115 | 0.055 |
| 小腿围 | 0.151 | -0.027 | 0.705 | 0.308 | -0.093 |
| 神经精神疾病 | 0.035 | 0.004 | 0.062 | 0.857 | 0.152 |
| 牙齿状况 | 0.341 | 0.124 | 0.057 | 0.517 | -0.257 |
| 近3个月体质量变化 | -0.025 | -0.014 | -0.013 | 0.036 | 0.959 |
Table 4 The distribution map of factor loading of the concise Nutritional Risk Assessment Scale for Nursing Home-dwelling Older People
| 条目 | 因子1 | 因子2 | 因子3 | 因子4 | 因子5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 活动能力 | 0.858 | 0.001 | 0.045 | 0.087 | 0.107 |
| 户外独立活动时间 | 0.752 | 0.083 | 0.093 | -0.035 | -0.140 |
| 进食能力 | 0.776 | 0.004 | 0.078 | 0.214 | -0.017 |
| 疾病种数 | 0.022 | 0.841 | -0.030 | -0.132 | -0.031 |
| 药物种数 | 0.058 | 0.797 | -0.006 | 0.226 | 0.003 |
| BMI | 0.048 | -0.013 | 0.874 | -0.115 | 0.055 |
| 小腿围 | 0.151 | -0.027 | 0.705 | 0.308 | -0.093 |
| 神经精神疾病 | 0.035 | 0.004 | 0.062 | 0.857 | 0.152 |
| 牙齿状况 | 0.341 | 0.124 | 0.057 | 0.517 | -0.257 |
| 近3个月体质量变化 | -0.025 | -0.014 | -0.013 | 0.036 | 0.959 |
| 项目 | 预测营养不良风险/营养不良 | 预测营养不良 |
|---|---|---|
| AUC | 0.907a | 0.976a |
| 灵敏度 | 0.799 | 0.809 |
| 特异度 | 0.870 | 0.953 |
| 约登指数 | 0.670 | 0.761 |
Table 5 Sensitivity,specificity,Youden index and AUC of the concise Nutritional Risk Assessment Scale for Nursing Home-dwelling Older People
| 项目 | 预测营养不良风险/营养不良 | 预测营养不良 |
|---|---|---|
| AUC | 0.907a | 0.976a |
| 灵敏度 | 0.799 | 0.809 |
| 特异度 | 0.870 | 0.953 |
| 约登指数 | 0.670 | 0.761 |
| [1] | 国家统计局. 中华人民共和国2019年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[EB/OL]. [2021-02-28]. . |
| [2] | POLONEN S, TIIHONEN M, HARTIKAINEN S,et al. Individually tailored dietary counseling among old home care clients-effects on nutritional status[J]. J Nutr Health Aging,2017,21(5):567-572. DOI:10.1007/s12603-016-0815-x. |
| [3] | 国务院办公厅. 国民营养计划(2017—2030)[EB/OL]. (2017-07-13)[2021-02-28]. . |
| [4] | 石汉平,李薇,齐玉梅,等. 营养筛查与评估[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2014. |
| [5] | 朱丹,曾平,韩凤,等. 京津地区养老机构《老年人营养不良风险评估》应用效果评价研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2020,23(24):3081-3085. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2020.00.217. |
| [6] | LEE J H, JEONG S N, CHOI S H. Predictive data mining for diagnosing periodontal disease:the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys(KNHANESⅤ andⅥ) from 2010 to 2015[J]. J Public Health Dent,2019,79(1):44-52. DOI:10.1111/jphd.12293. |
| [7] | 徐欣怡,许勤,花红霞,等. 基于预测模型的消化道肿瘤术后疲劳风险筛查评分量表的构建与应用[J]. 中国全科医学,2020,23(14):1819-1826,1832. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.793. |
| [8] | MUÑOZ D B, MARTÍNEZ D L I J, ROMERO-SALDAÑA M,et al. Development of predictive models for nutritional assessment in the elderly[J]. Public Health Nutr,2021,24(3):449-456. DOI:10.1017/S1368980020002153. |
| [9] | NURSAL T Z, NOYAN T, TARIM A,et al. A New weighted scoring system for subjective global assessment[J]. Nutrition,2005,21(6):666-671. DOI:10.1016/j.nut.2004.08.027. |
| [10] | 林红,孙国珍,张海锋,等. 心力衰竭患者微型营养评价量表的改良及其信效度检验[J]. 中华护理杂志,2017,52(2):150-153. DOI:10.3761/j.issn.0254-1796.2017.02.004. |
| [11] | 李语薇. 新生儿营养风险筛查工具的构建与临床应用研究[D]. 重庆:重庆医科大学,2017. |
| [12] | 陆丽娜. 住院儿童营养筛查工具的建立、评估和应用[D]. 上海:上海交通大学,2016. |
| [13] | 杨青,王国蓉,江宾,等. 基于决策树的肿瘤患者难免性压疮风险预测模型研究[J]. 护理学杂志,2019,34(13):4-7. DOI:10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2019.13.004. |
| [14] | 郭丽娜,许欣筑,林淑娴. 基于决策树的医院内感染预后影响因素模型的分析[J]. 现代预防医学,2015,42(14):2647-2650. |
| [15] | 章轶立,魏戌,聂佩芸,等. 基于SMOTE算法和决策树的绝经后骨质疏松性骨折分类模型建构[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(1):1-5. |
| [16] | 李峥,刘宇,李巍,等. 护理学研究方法[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2018. |
| [17] | 傅华,段广才,黄国伟. 预防医学[M]. 6版. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2013. |
| [18] | 吴明隆. 问卷统计分析实务:SPSS操作与应用[M]. 重庆:重庆大学出版社,2010. |
| [19] | 国务院办公厅. 关于加快发展养老服务业的若干意见[EB/OL]. (2013-09-13)[2021-06-20]. . |
| [20] | 孙建琴. 中国五城市老年人营养不良风险评估初步结果[EB/OL]. (2013-08-28)[2021-02-28]. . |
| [21] | LEIJ-HALFWERK S, VERWIJS M H, VAN HOUDT S,et al. Prevalence of protein-energy malnutrition risk in European older adults in community,residential and hospital settings,according to 22 malnutrition screening tools validated for use in adults ≥65 years:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Maturitas,2019,126:80-89. DOI:10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.05.006. |
| [22] | AGARWAL E, MARSHALL S, MILLER M,et al. Optimising nutrition in residential aged care:a narrative review[J]. Maturitas,2016,92:70-78. DOI:10.1016/j.maturitas.2016.06.013. |
| [23] | 中华医学会肠外肠内营养学分会老年营养支持学组. 中国老年患者肠外肠内营养应用指南(2020)[J]. 中华老年医学杂志,2020,39(2):119-132. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2020.02.002. |
| [24] | CEDERHOLM T, BARAZZONI R, AUSTIN P,et al. ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition[J]. Clin Nutr,2017,36(1):49-64. DOI:10.1016/j.clnu.2016.09.004. |
| [25] | JENSEN G L, CEDERHOLM T, CORREIA M,et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition:a consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community[J]. J Parenter Enteral Nutr,2019,43(1):32-40. DOI:10.1002/jpen.1440. |
| [26] | ROBERTS H C, LIM S, COX N J,et al. The challenge of managing undernutrition in older people with frailty[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(4):808. DOI:10.3390/nu11040808. |
| [27] | VISVANATHAN R, YU S. Australian and New Zealand Society for Geriatric Medicine position statement abstract:undernutrition and the older person[J]. Australas J Ageing,2017,36(1):75. DOI:10.1111/ajag.12344. |
| [28] | WINTER J E, MACINNIS R J, WATTANAPENPAIBOON N,et al. BMI and all-cause mortality in older adults:a meta-analysis[J]. Am J Clin Nutr,2014,99(4):875-890. |
| [29] | GUYONNET S, ROLLAND Y. Screening for malnutrition in older people[J]. Clin Liver Dis,2015,19(3):429. DOI:10.1016/j.cger.2015.04.009. |
| [30] | 张文彤. SPSS统计分析基础教程[M]. 3版. 北京:高等教育出版社,2017. |
| [1] | FENG Xiaoyu, LI Wanling, LYU Siman, NI Cuiping, WANG Haocheng, LIU Yu. International Research Status and Hot Spot Analysis of InterRAI HC Based on Bibliometrics [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(34): 4351-4358. |
| [2] | GU Hanxin, LIU Yang, LIU Yuanli. Falls Prevention Intervention for Community-dwelling Older Adults from the Perspective of Policy Tools: an International Comparative Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(34): 4231-4238. |
| [3] | WANG Yue, CHEN Qing, LIU Lurong. Detection Rate of Depression and Its Influencing Factors in Chinese Elderly: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(34): 4329-4335. |
| [4] | YU Xinyan, ZHAO Jun, ZHAO Xiaoye, JIANG Qingru, CHEN Yatian, WANG Yan, ZHANG Haicheng. Application of Mobile Smart Healthcare in the Prevention and Control of Cardiovascular Diseases in Elderly Patients with Chronic Diseases in Primary Care [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(33): 4167-4172. |
| [5] | XIN Gongkai, CONG Xin, YUAN Lei, CHENG Yuetong, NI Cuiping, ZHANG Weiwei, ZHANG Pingping, LIU Yu. Research Progress on Comprehensive Assessment Tools for the Elderly with Dementia [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(33): 4103-4109. |
| [6] | ZHANG Shuai, LI Qin, LI Dongfeng, XIAO Jinping, LI Yunpeng. A Prospective Cohort Study of Solid Fuels Use and Risk of Hypertension in Chinese Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(32): 4001-4006. |
| [7] | JIAN Qiufeng, XU Ronghua, YAO Qian, ZHOU Yuanyuan. A Meta-analysis of the Prevalence and Influencing Factors of Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment in Chinese Elderly Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(32): 4070-4079. |
| [8] | CHEN Xi, ZHANG Juan, LI Lin, ZHANG Jiaqi, WU Yaoli, GUO Hui, WANG Chaoqun. Association between Physical Activity and Risk of All-cause Mortality in Middle-aged and Elderly People in China: a Prospective Cohort Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(31): 3890-3895. |
| [9] | ZHANG Peng, GAO Ying, YANG Hongxi, WAN Chunxiao. Association between Serum Uric Acid Level and the Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease among the Elderly in Longevity Areas of China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(31): 3884-3889. |
| [10] | DUAN Yanqin, PENG Ying, LIU Shenglan, LIU Haijiao, YANG Huiqiong, HU Haiqing. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Potentially Inappropriate Medication among Elderly Outpatients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(31): 3902-3907. |
| [11] | ZHANG Ming, XU Jing, SUN Zhenhua, ZHAO Wenhao, MA Yingqian, ZHANG Jianqiao, SHEN Haiping. Improvement of Nutritional Status of Elderly Patients with Severe Obstruction Esophageal Carcinoma by Image-guided Photodynamic Therapy [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(30): 3780-3784. |
| [12] | PAN Yaojia, WANG Weiqiang, YI Weizhuo, GAO Bing, FU Fanglin, HAN Zheng, SUN Meng, DONG Yaqin, GU Huaicong. Relationship between Triglyceride-glucose Index and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Middle-aged Obese Residents of Different Genders [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(29): 3628-3635. |
| [13] | WANG Zhen, SHEN Guoqi, LI Yanan, ZHU Yinghua, QIU Hang, ZHENG Di, XU Tongda, LI Wenhua. Development and Validation of a Risk Prediction Model for Contrast-induced Acute Kidney Injury after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(29): 3650-3656. |
| [14] | ZHOU Sijing, LUO Bangan, CAO Hui, ZHANG Xi, WANG Dongxin. Epidemiological Characteristics of Dementia and Its Correlation with Multimorbidity among Residents Aged 65 and Above [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(29): 3616-3621. |
| [15] | WANG Xiaoran, ZHANG Dan. Influence of Multimorbidity on Anxiety Symptoms among Chinese Elderly People: a Propensity Score-matched Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(29): 3622-3627. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||