中国全科医学 ›› 2026, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (09): 1137-1145.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2025.0169
孙沁瑜1,2,3, 邓毅凡1,2,3, 杨天笑3, 方震1,3, 纪军1,3, 何胜虎1,3, 张晶1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-22
修回日期:2025-11-17
出版日期:2026-03-20
发布日期:2026-01-28
通讯作者:
张晶
作者贡献:
孙沁瑜进行研究的构思、设计以及文章撰写;邓毅凡、杨天笑、方震进行数据的收集、整理与统计学分析;纪军、何胜虎负责文章的修订;张晶负责文章的质量控制及审校,对文章整体负责,监督管理。
基金资助:
SUN Qinyu1,2,3, DENG Yifan1,2,3, YANG Tianxiao3, FANG Zhen1,3, JI Jun1,3, HE Shenghu1,3, ZHANG Jing1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2025-05-22
Revised:2025-11-17
Published:2026-03-20
Online:2026-01-28
Contact:
ZHANG Jing
摘要: 背景 既往发现,糖化血红蛋白和载脂蛋白A-1比值(HbA1c/ApoA-1)、三酰甘油葡萄糖-体质指数(TyG-BMI)与冠状动脉疾病的发生、发展相关,但与冠状动脉钙化(CAC)严重程度的相关性并不明确。 目的 探讨HbA1c/ApoA-1、TyG-BMI及两者联合与CAC严重程度的相关性。 方法 纳入2024年于扬州大学附属苏北人民医院行冠状动脉CT血管造影(CTA)的441例患者进行回顾性分析,将入组患者分为无/轻度钙化组[冠状动脉钙化积分(CACS)=0~99分,223例]和中/重度钙化组(CACS≥100分,218例)。收集患者的临床数据,计算HbA1c/ApoA-1、TyG-BMI。采用单因素和多因素Logistic回归分析探讨中/重度CAC的危险因素,将HbA1c/ApoA-1、TyG-BMI分别作为连续变量和分类变量进行分析。采用非线性趋势限制性立方样条(RCS)曲线探讨HbA1c/ApoA-1、TyG-BMI与CACS的关系。绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评估HbA1c/ApoA-1、TyG-BMI及联合对中/重度CAC的预测价值。对性别、年龄、高血压、2型糖尿病、吸烟史和酗酒史进行亚组分析,采用似然比检验进行交互检验。 结果 患者中位年龄70.0(62.0,75.0)岁,男276例、女165例。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,空腹血糖(OR=1.018,95%CI=1.009~1.028)、脂蛋白a(OR=1.001,95%CI=1.001~1.002)、HbA1c/ApoA-1(OR=1.158,95%CI=1.059~1.267)、TyG-BMI(OR=1.013,95%CI=1.006~1.020)升高为中/重度CAC的危险因素(P<0.05)。分别将HbA1c/ApoA-1、TyG-BMI作为连续变量和分类变量进行多因素Logistic回归分析,HbA1c/ApoA-1分组[Q1组111例(HbA1c/ApoA-1≤182.69),Q2组109例(182.69<HbA1c/ApoA-1≤207.06),Q3组106例(207.06<HbA1c/ApoA-1 ≤231.24)和Q4组115例(HbA1c/ApoA-1>231.24)]Q2、Q3、Q4组为中/重度CAC的危险因素(P<0.05)。TyG-BMI分组[Q1组112例(TyG-BMI≤0.17),Q2组108例(0.17<TyG-BMI≤4.23),Q3组110例(4.23<TyG-BMI≤5.36)和Q4组111例(TyG-BMI>5.36)]Q3、Q4组为中/重度CAC的危险因素(P<0.05)。ROC曲线结果显示空腹血糖、脂蛋白a、HbA1c/ApoA-1和TyG-BMI预测中/重度CAC的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.675(95%CI=0.625~0.725)、0.609(95%CI=0.557~0.661)、0.672(95%CI=0.622~0.732)、0.693(95%CI=0.644~0.742),HbA1c/ApoA-1与TyG-BMI联合预测的AUC为0.728(95%CI=0.682~0.775)。非线性RCS曲线结果表明,HbA1c/ApoA-1与CACS非线性相关(P非线性=0.007),TyG-BMI与CACS线性相关(P非线性=0.636)。 结论 HbA1c/ApoA-1、TyG-BMI及两者联合与CAC严重程度具有显著的相关性,对严重CAC具有一定预测价值,值得临床推广应用。
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(男/女) | 年龄[M(P25,P75),岁] | 高血压[例(%)] | 2型糖尿病[例(%)] | 吸烟史[例(%)] | 酗酒史[例(%)] | 入院收缩压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无/轻度钙化组 | 223 | 130/93 | 69.0(61.0,75.0) | 134(60.1) | 38(17.0) | 48(21.5) | 34(15.2) | 136(125,148) |
| 中/重度钙化组 | 218 | 146/72 | 70.0(64.0,75.0) | 164(75.2) | 69(31.7) | 62(28.4) | 39(17.9) | 135(125,151) |
| Z(χ2)值 | 3.544a | -1.208 | 11.531a | 12.807a | 2.816a | 0.558a | -0.096 | |
| P值 | 0.060 | 0.227 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.093 | 0.455 | 0.923 | |
| 组别 | 入院舒张压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] | 左心室射血分数[M(P25,P75),%] | 空腹血糖[M(P25,P75),mg/dL] | HbA1c[M(P25,P75),%] | 三酰甘油[M(P25,P75),mg/dL] | |||
| 无/轻度钙化组 | 79(70,86) | 56.0(49.0,60.0) | 95.495(84.234,111.343) | 6.229(5.600,6.333) | 95.656(78.827,148.798) | |||
| 中/重度钙化组 | 78.0(70,86) | 53.0(48.0,57.0) | 111.441(94.144,128.063) | 6.333(5.900,6.333) | 132.412(98.534,203.932) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.120 | -2.671 | -6.354 | -3.043 | -4.941 | |||
| P值 | 0.904 | 0.008 | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | |||
| 组别 | 总胆固醇[M(P25,P75),mg/dL] | 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇[M(P25,P75),mg/dL] | 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇[M(P25,P75),mg/dL] | 脂蛋白a[M(P25,P75),g/L] | ApoA-1[M(P25,P75),g/L] | |||
| 无/轻度钙化组 | 157.200(132.058,179.429) | 43.310(35.770,53.365) | 93.754(75.987,114.076) | 166.700(87.800,240.840) | 1.260(1.115,1.500) | |||
| 中/重度钙化组 | 152.746(126.451,174.692) | 41.764(34.416,49.788) | 90.488(68.446,116.300) | 211.550(130.650,340.325) | 1.210(1.040,1.368) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -1.554 | -1.521 | -1.160 | -3.956 | -3.476 | |||
| P值 | 0.120 | 0.128 | 0.246 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| 组别 | 载脂蛋白B[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 载脂蛋白A-1/载脂蛋白B[M(P25,P75)] | 丙氨酸氨基转移酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 碱性磷酸酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | |||
| 无/轻度钙化组 | 0.800(0.680,0.975) | 1.584(1.300,1.900) | 22.500(16.150,27.914) | 24.000(20.000,27.706) | 77.000(63.500,90.000) | |||
| 中/重度钙化组 | 0.800(0.630,0.950) | 1.500(1.300,1.900) | 20.800(15.0,28.0) | 23.900(19.000,28.000) | 79.000(64.250,91.000) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -1.034 | -0.594 | -0.841 | -0.147 | -0.810 | |||
| P值 | 0.301 | 0.553 | 0.400 | 0.884 | 0.418 | |||
| 组别 | 白蛋白[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 尿酸[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 肌酐[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | HbA1c/ApoA-1[M(P25,P75)] | TyG-BMI[M(P25,P75)] | |||
| 无/轻度钙化组 | 3.925(3.740,4.205) | 341.700(281.000,387.050) | 75.800(62.300,84.541) | 3.653(0.155,4.762) | 194.949(171.698,217.205) | |||
| 中/重度钙化组 | 3.925(3.643,4.228) | 338.050(281.625,405.750) | 77.750(65.050,87.200) | 4.732(3.720,5.769) | 222.309(193.761,250.083) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.535 | -0.478 | -0.789 | -6.257 | -7.002 | |||
| P值 | 0.593 | 0.633 | 0.430 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
表1 两组基线资料对比
Table 1 Comparison of general data of patients in 2 groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(男/女) | 年龄[M(P25,P75),岁] | 高血压[例(%)] | 2型糖尿病[例(%)] | 吸烟史[例(%)] | 酗酒史[例(%)] | 入院收缩压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无/轻度钙化组 | 223 | 130/93 | 69.0(61.0,75.0) | 134(60.1) | 38(17.0) | 48(21.5) | 34(15.2) | 136(125,148) |
| 中/重度钙化组 | 218 | 146/72 | 70.0(64.0,75.0) | 164(75.2) | 69(31.7) | 62(28.4) | 39(17.9) | 135(125,151) |
| Z(χ2)值 | 3.544a | -1.208 | 11.531a | 12.807a | 2.816a | 0.558a | -0.096 | |
| P值 | 0.060 | 0.227 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.093 | 0.455 | 0.923 | |
| 组别 | 入院舒张压[M(P25,P75),mmHg] | 左心室射血分数[M(P25,P75),%] | 空腹血糖[M(P25,P75),mg/dL] | HbA1c[M(P25,P75),%] | 三酰甘油[M(P25,P75),mg/dL] | |||
| 无/轻度钙化组 | 79(70,86) | 56.0(49.0,60.0) | 95.495(84.234,111.343) | 6.229(5.600,6.333) | 95.656(78.827,148.798) | |||
| 中/重度钙化组 | 78.0(70,86) | 53.0(48.0,57.0) | 111.441(94.144,128.063) | 6.333(5.900,6.333) | 132.412(98.534,203.932) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.120 | -2.671 | -6.354 | -3.043 | -4.941 | |||
| P值 | 0.904 | 0.008 | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | |||
| 组别 | 总胆固醇[M(P25,P75),mg/dL] | 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇[M(P25,P75),mg/dL] | 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇[M(P25,P75),mg/dL] | 脂蛋白a[M(P25,P75),g/L] | ApoA-1[M(P25,P75),g/L] | |||
| 无/轻度钙化组 | 157.200(132.058,179.429) | 43.310(35.770,53.365) | 93.754(75.987,114.076) | 166.700(87.800,240.840) | 1.260(1.115,1.500) | |||
| 中/重度钙化组 | 152.746(126.451,174.692) | 41.764(34.416,49.788) | 90.488(68.446,116.300) | 211.550(130.650,340.325) | 1.210(1.040,1.368) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -1.554 | -1.521 | -1.160 | -3.956 | -3.476 | |||
| P值 | 0.120 | 0.128 | 0.246 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| 组别 | 载脂蛋白B[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 载脂蛋白A-1/载脂蛋白B[M(P25,P75)] | 丙氨酸氨基转移酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 碱性磷酸酶[M(P25,P75),U/L] | |||
| 无/轻度钙化组 | 0.800(0.680,0.975) | 1.584(1.300,1.900) | 22.500(16.150,27.914) | 24.000(20.000,27.706) | 77.000(63.500,90.000) | |||
| 中/重度钙化组 | 0.800(0.630,0.950) | 1.500(1.300,1.900) | 20.800(15.0,28.0) | 23.900(19.000,28.000) | 79.000(64.250,91.000) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -1.034 | -0.594 | -0.841 | -0.147 | -0.810 | |||
| P值 | 0.301 | 0.553 | 0.400 | 0.884 | 0.418 | |||
| 组别 | 白蛋白[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 尿酸[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 肌酐[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | HbA1c/ApoA-1[M(P25,P75)] | TyG-BMI[M(P25,P75)] | |||
| 无/轻度钙化组 | 3.925(3.740,4.205) | 341.700(281.000,387.050) | 75.800(62.300,84.541) | 3.653(0.155,4.762) | 194.949(171.698,217.205) | |||
| 中/重度钙化组 | 3.925(3.643,4.228) | 338.050(281.625,405.750) | 77.750(65.050,87.200) | 4.732(3.720,5.769) | 222.309(193.761,250.083) | |||
| Z(χ2)值 | -0.535 | -0.478 | -0.789 | -6.257 | -7.002 | |||
| P值 | 0.593 | 0.633 | 0.430 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 自变量 | β | SE | Z值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高血压 | 0.702 | 0.208 | 3.371 | <0.001 | 2.017(1.341~3.033) |
| 2型糖尿病 | 0.813 | 0.230 | 3.534 | <0.001 | 2.255(1.436~3.539) |
| 左心室射血分数 | -0.021 | 0.014 | -1.529 | 0.126 | 0.979(0.953~1.006) |
| 空腹血糖 | 0.026 | 0.004 | 5.960 | <0.001 | 1.026(1.017~1.035) |
| HbA1c | 0.435 | 0.122 | 3.571 | <0.001 | 1.545(1.217~1.962) |
| 三酰甘油 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 4.267 | <0.001 | 1.005(1.003~1.007) |
| 脂蛋白a | 0.001 | 0.000 | 2.842 | 0.004 | 1.001(1.001~1.002) |
| ApoA-1 | -1.274 | 0.370 | -3.443 | <0.001 | 0.280(0.135~0.578) |
| HbA1c/ApoA-1 | 0.202 | 0.040 | 5.110 | <0.001 | 1.224(1.133~1.322) |
| TyG-BMI | 0.020 | 0.003 | 6.647 | <0.001 | 1.020(1.014~1.026) |
表2 中/重度CAC危险因素的单因素Logistic回归分析
Table 2 Univariable Logistic regression analysis of risk factors for moderate-to-severe CAC
| 自变量 | β | SE | Z值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高血压 | 0.702 | 0.208 | 3.371 | <0.001 | 2.017(1.341~3.033) |
| 2型糖尿病 | 0.813 | 0.230 | 3.534 | <0.001 | 2.255(1.436~3.539) |
| 左心室射血分数 | -0.021 | 0.014 | -1.529 | 0.126 | 0.979(0.953~1.006) |
| 空腹血糖 | 0.026 | 0.004 | 5.960 | <0.001 | 1.026(1.017~1.035) |
| HbA1c | 0.435 | 0.122 | 3.571 | <0.001 | 1.545(1.217~1.962) |
| 三酰甘油 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 4.267 | <0.001 | 1.005(1.003~1.007) |
| 脂蛋白a | 0.001 | 0.000 | 2.842 | 0.004 | 1.001(1.001~1.002) |
| ApoA-1 | -1.274 | 0.370 | -3.443 | <0.001 | 0.280(0.135~0.578) |
| HbA1c/ApoA-1 | 0.202 | 0.040 | 5.110 | <0.001 | 1.224(1.133~1.322) |
| TyG-BMI | 0.020 | 0.003 | 6.647 | <0.001 | 1.020(1.014~1.026) |
| 自变量 | β | SE | Z值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高血压 | 0.407 | 0.245 | 1.663 | 0.096 | 1.503(0.930~2.430) |
| 2型糖尿病 | 0.509 | 0.310 | 1.644 | 0.100 | 1.663(0.907~3.051) |
| 空腹血糖 | 0.018 | 0.005 | 3.947 | <0.001 | 1.018(1.009~1.028) |
| HbA1c | -0.041 | 0.152 | -0.269 | 0.788 | 0.960(0.712~1.294) |
| 三酰甘油 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 1.681 | 0.093 | 1.002(1.000~1.005) |
| 脂蛋白a | 0.001 | 0.001 | 2.852 | 0.004 | 1.001(1.001~1.002) |
| ApoA-1 | -0.771 | 0.433 | -1.782 | 0.075 | 0.463(0.198~1.080) |
| HbA1c/ApoA-1 | 0.147 | 0.046 | 3.199 | 0.001 | 1.158(1.059~1.267) |
| TyG-BMI | 0.013 | 0.004 | 3.547 | <0.001 | 1.013(1.006~1.020) |
表3 中/重度CAC危险因素的多因素Logistic回归分析
Table 3 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of risk factors for moderate-to-severe CAC
| 自变量 | β | SE | Z值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高血压 | 0.407 | 0.245 | 1.663 | 0.096 | 1.503(0.930~2.430) |
| 2型糖尿病 | 0.509 | 0.310 | 1.644 | 0.100 | 1.663(0.907~3.051) |
| 空腹血糖 | 0.018 | 0.005 | 3.947 | <0.001 | 1.018(1.009~1.028) |
| HbA1c | -0.041 | 0.152 | -0.269 | 0.788 | 0.960(0.712~1.294) |
| 三酰甘油 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 1.681 | 0.093 | 1.002(1.000~1.005) |
| 脂蛋白a | 0.001 | 0.001 | 2.852 | 0.004 | 1.001(1.001~1.002) |
| ApoA-1 | -0.771 | 0.433 | -1.782 | 0.075 | 0.463(0.198~1.080) |
| HbA1c/ApoA-1 | 0.147 | 0.046 | 3.199 | 0.001 | 1.158(1.059~1.267) |
| TyG-BMI | 0.013 | 0.004 | 3.547 | <0.001 | 1.013(1.006~1.020) |
| 变量 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |
| HbA1c/ApoA-1 | 1.224(1.133~1.322) | <0.001 | 1.188(1.095~1.290) | <0.001 | 1.180(1.085~1.284) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c/ApoA-1四分位分组(以Q1组为参照) | ||||||
| Q2组 | 0.938(0.539~1.633) | 0.821 | 0.758(0.421~1.366) | 0.357 | 0.804(0.438~1.475) | 0.481 |
| Q3组 | 2.287(1.332~3.928) | 0.003 | 1.877(1.066~3.307) | 0.029 | 1.856(1.031~3.344) | 0.039 |
| Q4组 | 4.444(2.528~7.810) | <0.001 | 3.302(1.824~5.977) | <0.001 | 3.043(1.651~5.610) | <0.001 |
表4 HbA1c/ApoA-1和中/重度CAC的相关性
Table 4 Correlation between HbA1c/ApoA-1 and moderate-to-severe CAC
| 变量 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |
| HbA1c/ApoA-1 | 1.224(1.133~1.322) | <0.001 | 1.188(1.095~1.290) | <0.001 | 1.180(1.085~1.284) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c/ApoA-1四分位分组(以Q1组为参照) | ||||||
| Q2组 | 0.938(0.539~1.633) | 0.821 | 0.758(0.421~1.366) | 0.357 | 0.804(0.438~1.475) | 0.481 |
| Q3组 | 2.287(1.332~3.928) | 0.003 | 1.877(1.066~3.307) | 0.029 | 1.856(1.031~3.344) | 0.039 |
| Q4组 | 4.444(2.528~7.810) | <0.001 | 3.302(1.824~5.977) | <0.001 | 3.043(1.651~5.610) | <0.001 |
| 变量 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |
| TyG-BMI | 1.020(1.014~1.026) | <0.001 | 1.017(1.011~1.023) | <0.001 | 1.017(1.010~1.023) | <0.001 |
| TyG-BMI四分位分组(以Q1组为参照) | ||||||
| Q2组 | 2.374(1.352~4.169) | 0.003 | 1.929(1.072~3.472) | 0.028 | 1.840(1.009~3.354) | 0.047 |
| Q3组 | 2.912(1.653~5.130) | <0.001 | 2.194(1.205~3.998) | 0.010 | 2.125(1.153~3.915) | 0.016 |
| Q4组 | 6.709(3.749~12.007) | <0.001 | 4.967(2.695~9.155) | <0.001 | 4.750(2.544~8.869) | <0.001 |
表5 TyG-BMI和中/重度CAC的相关性
Table 5 Correlation between TyG-BMI and moderate-to-severe CAC
| 变量 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |
| TyG-BMI | 1.020(1.014~1.026) | <0.001 | 1.017(1.011~1.023) | <0.001 | 1.017(1.010~1.023) | <0.001 |
| TyG-BMI四分位分组(以Q1组为参照) | ||||||
| Q2组 | 2.374(1.352~4.169) | 0.003 | 1.929(1.072~3.472) | 0.028 | 1.840(1.009~3.354) | 0.047 |
| Q3组 | 2.912(1.653~5.130) | <0.001 | 2.194(1.205~3.998) | 0.010 | 2.125(1.153~3.915) | 0.016 |
| Q4组 | 6.709(3.749~12.007) | <0.001 | 4.967(2.695~9.155) | <0.001 | 4.750(2.544~8.869) | <0.001 |
| 变量 | AUC(95%CI) | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 最佳截断值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 空腹血糖 | 0.675(0.625~0.725) | 0.543 | 0.729 | 96.486 mg/dL |
| 脂蛋白a | 0.609(0.557~0.661) | 0.753 | 0.445 | 242.200 g/L |
| HbA1c/ApoA-1 | 0.672(0.622~0.723) | 0.570 | 0.729 | 3.834 |
| TyG-BMI | 0.693(0.644~0.742) | 0.758 | 0.560 | 218.134 |
| 联合指标 | 0.728(0.682~0.775) | 0.704 | 0.642 |
表6 影响因素对中/重度CAC的预测价值
Table 6 Predictive value of influencing factors for moderate to severe CAC
| 变量 | AUC(95%CI) | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 最佳截断值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 空腹血糖 | 0.675(0.625~0.725) | 0.543 | 0.729 | 96.486 mg/dL |
| 脂蛋白a | 0.609(0.557~0.661) | 0.753 | 0.445 | 242.200 g/L |
| HbA1c/ApoA-1 | 0.672(0.622~0.723) | 0.570 | 0.729 | 3.834 |
| TyG-BMI | 0.693(0.644~0.742) | 0.758 | 0.560 | 218.134 |
| 联合指标 | 0.728(0.682~0.775) | 0.704 | 0.642 |
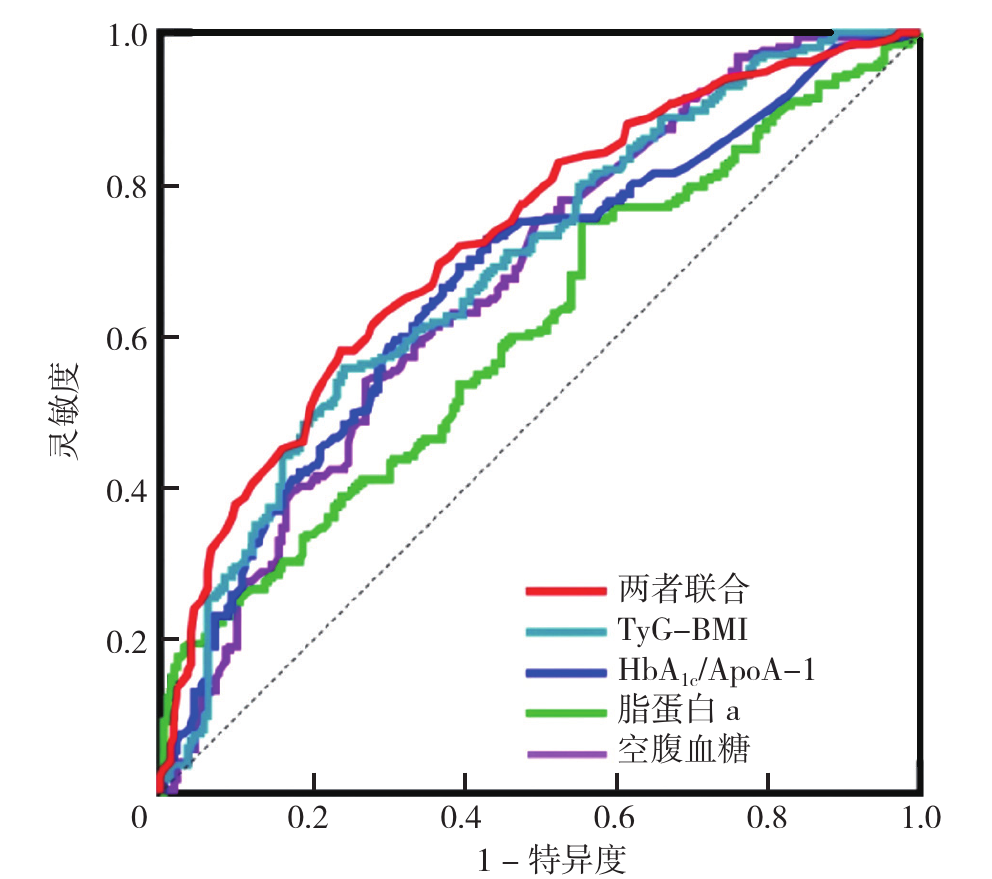
图1 空腹血糖、脂蛋白a、HbA1c/ApoA-1、TyG-BMI及HbA1c/ApoA-1与TyG-BMI联合预测中/重度CAC的ROC曲线注:HbA1c=糖化血红蛋白,ApoA-1=载脂蛋白A-1,TyG-BMI=三酰甘油葡萄糖-体质指数;联合指标为HbA1c/ApoA-1和TyG-BMI联合。
Figure 1 ROC curves of fasting blood glucose, lipoprotein a, HbA1c/ApoA-1, TyG-BMI and the combined prediction of HbA1c/ApoA-1 and TyG-BMI for moderate/severe CAC
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
中国高血压防治指南修订委员会,高血压联盟(中国),中国医疗保健国际交流促进会高血压分会,等. 中国高血压防治指南(2024年修订版)[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2024, 32(7): 603-700. DOI: 10.16439/j.issn.1673-7245.2024.07.002.
|
| [11] |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2021, 13(4): 315-409. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20210221-095.
|
| [12] |
戴承晔, 邓毅凡, 何胜虎, 等.单核细胞计数/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇及促甲状腺激素对绝经期女性急性冠脉综合征患者预测价值及与冠状动脉病变相关性研究[J].中国全科医学, 2024, 27(33): 4132-4138. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0094.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [1] | 盛鲁光, 刘丹丹, 刘维斌, 鲁郡, 雷涛, 陈清光, 陆灏, 徐碧林. 短期饮食干预对肥胖合并糖代谢异常患者的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2026, 29(03): 373-379. |
| [2] | 中国医药教育协会心血管内科专业委员会, 中国医疗保健国际交流促进会心血管健康医学分会. 青年冠状动脉疾病的早期筛查和预防专家共识[J]. 中国全科医学, 2026, 29(02): 137-147. |
| [3] | 张姝, 程钰, 吴寿岭, 陈朔华, 吴云涛. 非糖尿病人群累积血浆致动脉粥样硬化指数暴露对新发心血管疾病影响的队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(36): 4558-4565. |
| [4] | 王碧优, 高鹰, 尤俊方, 刘莉, 张卿, 苏海燕. 心血管疾病风险人群脂质比值与炎症指标的典型相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(33): 4132-4139. |
| [5] | 阳坚, 吴传安, 周海蓉, 田峰, 迟春花. 三酰甘油葡萄糖-体质指数对2型糖尿病合并代谢相关脂肪性肝病的诊断价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(32): 4075-4081. |
| [6] | 廖姣姣, 王照宇, 李兆基, 赵威, 詹思延, 王鹏, 陶立元. 非高密度脂蛋白胆固醇动态变化对颈动脉内中膜增厚的预测价值:一项双向性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(31): 3932-3941. |
| [7] | 向心月, 张冰青, 欧阳煜钦, 汤文娟, 冯文焕. 短期内科门诊减重对肥胖患者动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病风险的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3229-3239. |
| [8] | 韩冰, 杜淑珍, 孟晓雪, 张璐, 陈梓娴, 滕凤玲. 心力衰竭患者血浆骨膜蛋白水平与心肌纤维化的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2979-2984. |
| [9] | 高海钧, 任佳禹, 王若琳, 周慧亚, 曲鹏. 内皮细胞损伤及其功能障碍在动脉粥样硬化中作用的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2697-2704. |
| [10] | 褚田雨, 顾艳. 颈动脉钙化特征在评估斑块稳定性及临床事件中的作用[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2247-2252. |
| [11] | 吕露露, 祝万洁, 肖明洋, 李祎珂, 张娟. 原发性高血压患者血压昼夜节律与血浆氧化的低密度脂蛋白/β2-糖蛋白I复合物及颈动脉粥样硬化的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2228-2233. |
| [12] | 程璐, 秦存, 柏品清, 王健英, 任亚萍, 胡晓娟, 张宝军, 张磊, 周一心. 儿童中医体质与血脂代谢的相关性:基于浦东新区儿童青少年生长发育及健康队列[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(06): 751-755. |
| [13] | 陈玲, 徐锐, 程新春, 张占英, 徐红. 基于NOD样受体3炎性小体通路对利拉鲁肽在氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导内皮细胞损伤的作用机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(05): 601-606. |
| [14] | 杨红, 刘成, 刘森, 邵琪琪, 夭元昊, 付真彦. 残余胆固醇与进展为主要不良心血管事件的非罪犯病变易损斑块的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(03): 299-304. |
| [15] | 任小乔, 王盼, 吴昊, 纪勇, 石志鸿. 脑血管病急性期血尿酸/血肌酐比值与脑血管事件复发及死亡的关系:一项前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 175-182. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





