中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (17): 2176-2182.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0609
所属专题: 神经退行性病变最新文章合集; 阿尔茨海默病最新文章合集
• 综述与专论 • 上一篇
李晓晓1, 白艳杰2,*( ), 王岩1, 张雍闯1, 陈淑颖1, 陈丽敏1
), 王岩1, 张雍闯1, 陈淑颖1, 陈丽敏1
收稿日期:2022-06-26
修回日期:2022-10-08
出版日期:2023-06-15
发布日期:2022-10-13
通讯作者:
白艳杰
基金资助:
LI Xiaoxiao1, BAI Yanjie2,*( ), WANG Yan1, ZHANG Yongchuang1, CHEN Shuying1, CHEN Limin1
), WANG Yan1, ZHANG Yongchuang1, CHEN Shuying1, CHEN Limin1
Received:2022-06-26
Revised:2022-10-08
Published:2023-06-15
Online:2022-10-13
Contact:
BAI Yanjie
摘要: 脑卒中后认知障碍(PSCI)是脑卒中患者常见的并发症,严重影响患者的生活质量。目前,PSCI在临床治疗中尚未发现有效的针对性治疗措施。大量研究证实核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体蛋白3(NLRP3)炎症小体的活化在PSCI中起关键作用,且对其进行的许多抑制性治疗显示出了改善认知障碍的功效。为此,本文总结了NLRP3炎症小体的活化和影响因素及其与PSCI的关系,发现在PSCI的细胞和动物模型中,针对NLRP3或其炎症小体成分的抑制措施可以减轻炎性反应和相应的病理特征,从而促进其认知功能的恢复,因此,靶向NLRP3炎症小体可能是PSCI治疗的新趋势。然而到目前为止,尽管许多药物和治疗措施已成功鉴定出能够抑制NLRP3炎症小体的活化,但其在临床中的治疗效果和安全性仍有待进一步验证。
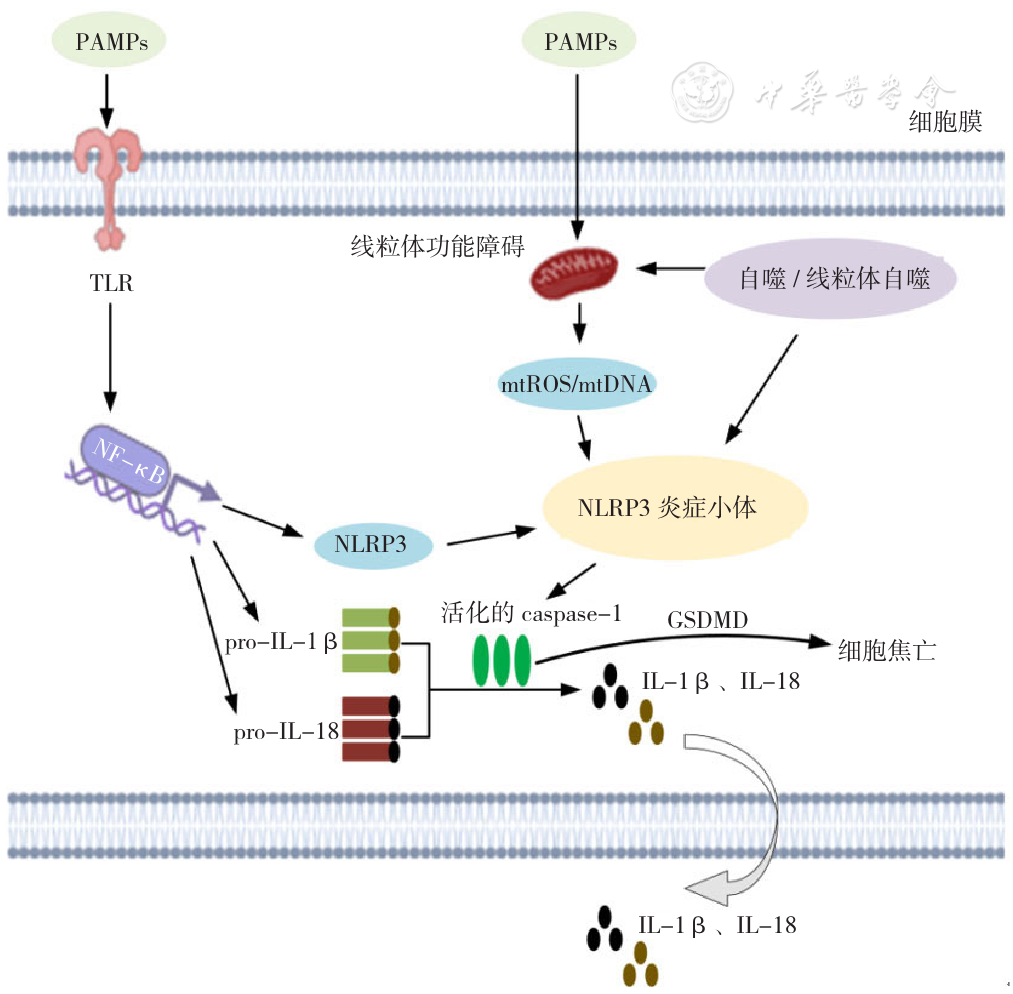
图1 NLRP3炎症小体的活化和调控过程注:PAMPs=病原体相关分子模式,TLR=Toll样受体,NF-κB=核因子κB,mtROS=线粒体活性氧,mtDNA=线粒体DNA,NLRP3=核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体蛋白3,pro-IL-1β=白介素1β前体,pro-IL-18=白介素18前体,caspase-1=半胱氨酸蛋白酶-1,GSDMD=消化道皮肤素D,IL-1β=白介素1β,IL-18=白介素18
Figure 1 Activation and regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 研究类型 | 主要结果 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MATSUYAMA[ | 2020 | 动物实验 | NLRP3炎症小体、IL-18、IL-1β均上调 |
| LI[ | 2022 | 细胞实验 | NLRP3、ASC、caspase-1、IL-1β、IL-18均上调 |
| 吴金波[ | 2021 | 临床研究 | NLRP3 mRNA上调 |
| 李国丽[ | 2022 | 临床研究 | NLRP3、IL-1β、IL-18均上调 |
| 赵凤华[ | 2021 | 临床研究 | NLRP3、ASC、caspase-1、IL-1β均上调 |
表1 NLRP3炎症小体在PSCI中表达量升高的相关研究
Table 1 Studies on the increased expression of NLRP3 inflammasome in PSCI
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 研究类型 | 主要结果 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MATSUYAMA[ | 2020 | 动物实验 | NLRP3炎症小体、IL-18、IL-1β均上调 |
| LI[ | 2022 | 细胞实验 | NLRP3、ASC、caspase-1、IL-1β、IL-18均上调 |
| 吴金波[ | 2021 | 临床研究 | NLRP3 mRNA上调 |
| 李国丽[ | 2022 | 临床研究 | NLRP3、IL-1β、IL-18均上调 |
| 赵凤华[ | 2021 | 临床研究 | NLRP3、ASC、caspase-1、IL-1β均上调 |
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 研究类型 | 干预方式 | 治疗作用机制 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LI[ | 2020 | 动物实验 | MCC950 | 阻断NLRP3寡聚化和形成,减少小胶质细胞数量,增加神经元数量,促进海马神经发生 |
| WANG[ | 2017 | 动物实验 | DY-9836 | 抑制亚硝化应激和NLRP3信号传导 |
| FENG[ | 2021 | 动物实验 | miR-138-5p | 与NLRP3特异性相互作用,改善神经炎症 |
| ZHANG[ | 2021 | 动物+细胞实验 | 牡荆素 | 抑制NLRP3炎症小体介导的炎性反应 |
| ZHANG[ | 2020 | 动物实验 | Kellerin | 抑制NLRP3炎症小体通路的激活,调节小胶质细胞的极化 |
| LI[ | 2017 | 动物实验 | 黄芪甲苷 | 控制ROS的产生来抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化,降低海马中小胶质细胞的过度激活和炎性细胞因子的过度表达 |
| LIU[ | 2020 | 动物实验 | 蛇床子素 | 改善海马神经元损伤,抑制小胶质细胞活化,并通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化减少海马中的Aβ沉积 |
| BANG[ | 2019 | 动物实验 | 梅素 | 抑制神经胶质增生并减弱NLRP3和NF-κB的激活 |
| SHI[ | 2021 | 网络药理学和分子对接 | 益智通脉汤 | 抑制NLRP3炎症小体、TNF信号通路和toll样受体信号通路 |
| XIA[ | 2019 | 动物实验 | 小脑顶核电刺激 | 下调NLRP3、caspase-1、IL-1β、IL-18的表达,抑制自噬过程和炎性反应,从而减轻神经元的凋亡 |
| DU[ | 2018 | 动物实验 | 针刺足三里和百会穴 | 减少海马神经元丢失和氧化应激,降低硫氧还蛋白相互作用蛋白、NLRP3、caspase-1和IL-1β的表达 |
| ZHONG[ | 2022 | 动物实验 | 电针神庭和百会穴 | 上调线粒体自噬相关蛋白和抑制ROS诱导的NLRP3炎症小体活化发挥神经保护作用 |
表2 抑制NLRP3炎症小体改善PSCI的研究
Table 2 Studies on inhibition NLRP3 inflammasome to improve PSCI
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 研究类型 | 干预方式 | 治疗作用机制 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LI[ | 2020 | 动物实验 | MCC950 | 阻断NLRP3寡聚化和形成,减少小胶质细胞数量,增加神经元数量,促进海马神经发生 |
| WANG[ | 2017 | 动物实验 | DY-9836 | 抑制亚硝化应激和NLRP3信号传导 |
| FENG[ | 2021 | 动物实验 | miR-138-5p | 与NLRP3特异性相互作用,改善神经炎症 |
| ZHANG[ | 2021 | 动物+细胞实验 | 牡荆素 | 抑制NLRP3炎症小体介导的炎性反应 |
| ZHANG[ | 2020 | 动物实验 | Kellerin | 抑制NLRP3炎症小体通路的激活,调节小胶质细胞的极化 |
| LI[ | 2017 | 动物实验 | 黄芪甲苷 | 控制ROS的产生来抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化,降低海马中小胶质细胞的过度激活和炎性细胞因子的过度表达 |
| LIU[ | 2020 | 动物实验 | 蛇床子素 | 改善海马神经元损伤,抑制小胶质细胞活化,并通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化减少海马中的Aβ沉积 |
| BANG[ | 2019 | 动物实验 | 梅素 | 抑制神经胶质增生并减弱NLRP3和NF-κB的激活 |
| SHI[ | 2021 | 网络药理学和分子对接 | 益智通脉汤 | 抑制NLRP3炎症小体、TNF信号通路和toll样受体信号通路 |
| XIA[ | 2019 | 动物实验 | 小脑顶核电刺激 | 下调NLRP3、caspase-1、IL-1β、IL-18的表达,抑制自噬过程和炎性反应,从而减轻神经元的凋亡 |
| DU[ | 2018 | 动物实验 | 针刺足三里和百会穴 | 减少海马神经元丢失和氧化应激,降低硫氧还蛋白相互作用蛋白、NLRP3、caspase-1和IL-1β的表达 |
| ZHONG[ | 2022 | 动物实验 | 电针神庭和百会穴 | 上调线粒体自噬相关蛋白和抑制ROS诱导的NLRP3炎症小体活化发挥神经保护作用 |
| [1] |
董强,郭起浩,罗本燕,等. 卒中后认知障碍管理专家共识[J]. 中国卒中杂志,2017,12(6):519-531.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
李程飞,潘益凯,李曦,等. 线粒体相关内质网膜(MAMs)在心血管疾病中的研究进展[J]. 心脏杂志,2022,34(1):79-84.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
吴金波,杨春兰,姚振兴,等. 血清sRAGE、25-羟维生素-D3、NLRP3 mRNA与高血压脑出血患者发生认知功能损害的关系[J]. 中国医师杂志,2021,23(10):1492-1495,1500.
|
| [47] |
李国丽,许海霞,岑岚,等. NLRP3炎症小体的活化水平与急性缺血性脑卒中患者认知功能改变的关系[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志,2022,30(2):67-71.
|
| [48] |
赵凤华,李万春,阮世旺,等. NLRP3炎症小体的活化水平与急性缺血性脑卒中患者认知功能改变的关系[J]. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2021,30(6):515-521. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn371468-20210105-00009.
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [1] | 南子晴, 蔺莉. 妊娠期尿潴留的诊治进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(36): 4608-4612. |
| [2] | 白海威, 米小昆, 刘青蕊, 祝琳, 王英南, 刘俊艳, 韩颖. 血清尿酸对非小细胞肺癌患者围术期急性缺血性卒中的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(36): 4545-4551. |
| [3] | 王小雪, 毛乐乐, 王子君, 杨慕坤, 白文佩, 刁翯. 自体富血小板浓缩物在妇科领域中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4472-4476. |
| [4] | 刘欣怡, 刘占东. 慢性疲劳综合征相关焦虑及抑郁的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4477-4482. |
| [5] | 罗伟刚, 尹园园, 刘万虎, 徐玉珠, 曹晓芸, 步玮, 张玲雁, 任慧玲. 三酰甘油葡萄糖指数与单发皮质下梗死患者发生早期神经功能恶化的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4419-4424. |
| [6] | 刘颖宏, 杨晓娟. Takayasu动脉炎妊娠期间临床管理的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4483-4486. |
| [7] | 秦凤银, 张绮珊, 赖锦佳, 黄奕敏, 韩郭茵, 孙兴兰, 王芬, 谭益冰. 广东省社区居民脑卒中高危筛查意向的现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4283-4289. |
| [8] | 张思宇, 周郁秋, 杜晓慧, 王正君. 精神病未治期及其早期干预的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4110-4117. |
| [9] | 王旭, 魏戌, 朱立国, 冯天笑, 王志鹏, 师彬. 医工结合的中医手法治疗脊柱退行性疾病疗效机制研究:思路与前景[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4118-4124. |
| [10] | 辛功恺, 丛欣, 袁磊, 程悦彤, 倪翠萍, 张巍巍, 張平平, 刘宇. 失智症老年人综合评估工具的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4103-4109. |
| [11] | 苏凯奇, 吕转, 吴明莉, 罗萌, 高静, 聂晨晨, 刘昊, 冯晓东. 电针对缺血再灌注后学习记忆障碍大鼠BDNF/TrkB/PI3K/Akt通路的影响及对海马神经元保护作用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4187-4193. |
| [12] | 尹苗苗, 崔立玲, 李雅晴, 王利群, 张玥, 巫嘉陵. 双任务对后循环缺血性脑卒中伴前庭症状患者步行能力的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4207-4212. |
| [13] | 杨宇轩, 张晗, 杜娟, 王玲玲, 谢玉磊, 尹开明, 张波. 眼动追踪的动态任务评估脑卒中后单侧空间忽略的价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4020-4025. |
| [14] | 孟江涛, 杨思宇, 孙蕾, 雷瑞宁, 赵晓霞. 弥散张量成像联合运动诱发电位评估脑梗死偏瘫患者运动功能预后价值的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4098-4102. |
| [15] | 蹇秋枫, 徐荣华, 姚倩, 周媛媛. 中国老年脑卒中患者认知障碍患病率和影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4070-4079. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





