中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (07): 803-814.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.00.004
所属专题: 高血压最新文章合辑
姚溪1, 裴晓婷1,*, 曲哲2
收稿日期:2021-09-14
修回日期:2022-01-01
出版日期:2022-03-05
发布日期:2022-03-02
通讯作者:
裴晓婷
基金资助:Prevalence,Awareness,Treatment and Control Rates of Hypertension in Chinese Adults: Trend and Associated Factors from 1991 to 2015
YAO Xi1,PEI Xiaoting1*,QU Zhe2
1.Henan Provincial People's Hospital/Henan Eye Hospital/Henan Eye Institute/Henan Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology and Visual Science,Zhengzhou 450003,China
2.Cardiovascular Department,Henan Provincial People's Hospital,Zhengzhou 450003,China
*Corresponding author:PEI Xiaoting,Assistant professor;E-mail:pxt15239273363@163.com
Received:2021-09-14
Revised:2022-01-01
Published:2022-03-05
Online:2022-03-02
摘要: 背景高血压是我国常见的慢性非传染性疾病之一,也是冠状动脉粥样硬化、脑卒中等多种心脑血管疾病的危险因素。近年来,高血压患病率不断增高,而治疗率和控制率却处于较低水平,已成为我国主要的公共卫生问题之一。目的了解1991—2015年中国成人高血压的患病率、知晓率、治疗率、控制率的变化特征。方法利用1991—2015年中国健康与营养调查(CHNS)9轮的调查数据,选择≥18岁且年龄、性别和血压值数据完整的研究对象。收集研究对象的人口学特征、吸烟情况、饮酒情况、身高、体质量、腰围、血压值和疾病史等资料。分析25年间我国成人高血压患病率、知晓率、治疗率和控制率的变化趋势及其影响因素。结果1991年,我国成人高血压的患病率、知晓率、治疗率和控制率分别为14.77%(1 291/8 743)、27.58%(356/1 291)、15.80%(204/1 291)、5.89%(76/1 291),2015年分别为32.67%(4 520/13 834)、48.08%(2 173/4 520)、40.51%(1 831/4 520)、14.65%(662/4 520)。1991—2015年,我国成人高血压患病率基本呈上升趋势,知晓率、治疗率和控制率2000年之后开始呈现上升趋势。25年间,我国成人高血压的患病率、知晓率、治疗率和控制率在不同年龄、性别、行为习惯、知识水平等因素上存在差异。结论我国高血压患病率在不断增加,虽然治疗率和控制率也在增加,但仍处于较低水平,因此需要有关部门采取措施提高居民高血压的治疗和控制水平,以延缓其发展。
中图分类号:
YAO Xi, PEI Xiaoting, QU Zhe.
Prevalence,Awareness,Treatment and Control Rates of Hypertension in Chinese Adults: Trend and Associated Factors from 1991 to 2015 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(07): 803-814.
| 基本特征 | 1991年(n=8 743) | 1993年(n=8 330) | 1997年(n=10 549) | 2000年(n=9 727) | 2004年(n=9 854) | 2006年(n=9 791) | 2009年(n=10 080) | 2011年(n=12 955) | 2015年(n=13 834) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | ||||||||||
| 男 | 16.26 (674/4 146) | 17.60 (697/3 967) | 18.51 (971/5 247) | 23.03 (1 071/4 650) | 25.69 (1 216/4 733) | 24.82 (1 156/44 658) | 31.55 (1 521/4 821) | 30.14 (1 835/6 089) | 34.75 (2 301/6 621) | |
| 女 | 13.42 (617/4 597) | 14.81 (646/4 363) | 15.96 (846/5 302) | 19.91 (1 011/5 077) | 21.93 (1 123/5 121) | 21.31 (1 094/5 133) | 27.63 (1 453/5 259) | 26.27 (1 804/6 866) | 30.76 (2 219/7 213) | |
| χ2值 | 13.919 | 11.735 | 12.023 | 14.034 | 19.237 | 16.944 | 18.589 | 23.828 | 24.973 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||||||
| 18~44① | 5.86 (328/5 597) | 7.06 (364/5 155) | 7.01 (443/6 321) | 9.04 (457/5 056) | 9.50 (413/4 349) | 9.19 (380/4 136) | 11.95 (460/3 850) | 8.83 (408/4 618) | 10.60 (489/4 615) | |
| 45~59② | 21.84 (404/1 850)a | 21.61 (401/1 856)a | 23.54 (585/2 485)a | 25.89 (732/2 827)a | 26.23 (869/3 313)a | 24.51 (796/3 248)a | 31.66 (1 111/3 509)a | 30.07 (1 387/4 612)a | 33.75 (1 542/4 569)a | |
| ≥60③ | 43.13 (559/1 296)ab | 43.82 (578/1 319)ab | 45.27 (789/1 743)ab | 48.43 (893/1 844)ab | 48.22 (1 057/2 192)ab | 44.62 (1 074/2 407)ab | 51.56 (1 403/2 721)ab | 49.50 (1 844/3 725)ab | 53.53 (2 489/4 650)ab | |
| χ2值 | 1 254.820 | 1 102.573 | 1 493.600 | 1 293.850 | 1 224.456 | 1 085.648 | 1 214.885 | 1 702.200 | 1 944.218 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 居住地 | ||||||||||
| 城镇 | 18.99 (540/2 843) | 20.47 (530/2 589) | 21.19 (731/3 450) | 24.40 (815/3 340) | 27.17 (929/3 419) | 25.01 (841/3 362) | 30.06 (1 034/3 440) | 28.30 (1 513/5 347) | 32.02 (1 692/5 284) | |
| 农村 | 12.73 (751/5 900) | 14.16 (813/5 741) | 15.30 (1 086/7 099) | 19.84 (1 267/6 387) | 21.91 (1 410/6 435) | 21.92 (1 409/6 429) | 29.22 (1 940/6 640) | 27.94 (2 126/7 608) | 33.08 (2 828/8 550) | |
| χ2值 | 59.836 | 52.535 | 56.501 | 27.156 | 34.128 | 11.975 | 0.771 | 0.193 | 1.652 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.380 | 0.661 | 0.199 | |
| 文化程度 | ||||||||||
| 文盲/小学① | 19.10 (952/4 985) | 20.37 (906/4 447) | 22.64 (1 142/5 044) | 27.63 (1 181/4 274) | 30.80 (1 335/4 335) | 29.99 (1 245/4 152) | 37.88 (1 595/4 211) | 37.90 (1 760/4 644) | 41.55 (880/2 118) | |
| 初中② | 8.14 (193/2 372)c | 10.57 (252/2 385)c | 11.00 (342/3 109)c | 14.09 (420/2 980)c | 16.93 (527/3 113)c | 17.69 (531/3 002)c | 24.18 (808/3 342)c | 24.71 (990/4 007)c | 30.48 (1 352/4 436)c | |
| 高中/中专③ | 9.12 (106/1 162)c | 10.01 (120/1 199)c | 11.39 (206/1 808)c | 16.71 (291/1 741)c | 19.03 (379/1 992)c | 18.14 (374/2 062)c | 24.03 (470/1 956)c | 23.05 (618/2 681)c | 28.97 (904/3 120)c | |
| 大专及以上④ | 17.22 (31/180)de | 19.85 (27/136)de | 16.46 (40/243) | 21.12 (83/393)cd | 23.41 (92/393)cd | 17.06 (93/545)c | 16.94 (94/555)cde | 16.65 (266/1 598)cde | 19.22 (381/1 982)cde | |
| χ2值 | 187.703 | 149.367 | 233.866 | 217.972 | 223.538 | 200.725 | 257.981 | 381.826 | 245.204 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 婚姻状态 | ||||||||||
| 未婚① | 3.54 (47/1 327) | 5.13 (64/1 248) | 5.30 (99/1 868) | 10.11 (117/1 157) | 9.84 (88/894) | 5.24 (38/725) | 7.14 (49/686) | 6.49 (50/770) | 5.51 (58/1 052) | |
| 已婚② | 15.29 (1 041/6 809)a | 16.45 (1 063/6 461)a | 18.17 (1 425/7 843)a | 21.49 (1 612/7 500)a | 23.33 (1 878/8 051)a | 23.11 (1 882/8 145)a | 29.47 (2 463/8 358)a | 27.84 (3 015/10 830)a | 33.45 (3 880/11 601)a | |
| 离异/丧偶/分居③ | 34.88 (203/582)ab | 36.77 (207/563)ab | 37.72 (278/737)ab | 37.12 (255/687)ab | 42.51 (363/854)ab | 36.33 (323/889)ab | 45.56 (451/990)ab | 44.24 (568/1 284)ab | 50.76 (570/1 123)ab | |
| χ2值 | 320.618 | 289.451 | 407.930 | 189.508 | 262.027 | 218.496 | 287.412 | 342.984 | 522.431 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 体型 | ||||||||||
| 消瘦① | 13.07 (72/5 900) | 14.59 (61/5 741) | 16.90 (71/7 099) | 14.57 (58/6 387) | 21.10 (77/6 435) | 17.37 (62/6 429) | 16.17 (65/6 640) | 13.03 (55/7 608) | 15.84 (61/8 550) | |
| 正常② | 11.27 (723/6 418) | 12.67 (765/6 039) | 15.45 (917/5 937) | 15.58 (938/6 019) | 17.81 (980/5 504) | 17.68 (944/5 338) | 23.59 (1 255/5 320)c | 20.53 (1 338/6 517)c | 25.80 (1 495/5 794)c | |
| 超重③ | 26.69 (356/1 334)cd | 25.39 (361/1 422)cd | 30.23 (545/1 803)cd | 30.35 (732/2 412)cd | 32.74 (831/2 538)cd | 29.90 (777/2 599)cd | 37.73 (1 075/2 849)cd | 36.02 (1 466/4 070)cd | 42.67 (1 812/4 247)cd | |
| 肥胖④ | 46.36 (121/261)cde | 48.63 (124/255)cde | 49.55 (218/440)cde | 49.85 (324/650)cde | 50.88 (376/739)cde | 50.53 (382/756)cde | 54.60 (499/914)cde | 48.81 (740/1 516)cde | 52.92 (941/1 778)cde | |
| χ2值 | 419.295 | 343.593 | 430.925 | 554.589 | 503.053 | 467.579 | 479.315 | 668.910 | 635.271 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 中心性肥胖 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 14.77 (1 291/8 743) | 13.18 (967/7 336) | 13.40 (1 220/9 107) | 16.13 (1 220/7 563) | 18.25 (1 356/7 430) | 17.20 (1 253/7 287) | 21.91 (1 522/6 946) | 20.32 (1 684/8 288) | 23.71 (2 088/8 807) | |
| 是 | - | 37.83 (376/994) | 41.40 (597/1 442) | 39.83 (862/2 164) | 40.55 (983/2 424) | 39.82 (997/2 504) | 46.33 (1 452/3 134) | 41.89 (1 955/4 667) | 48.38 (2 432/5 027) | |
| χ2值 | - | 393.184 | 684.763 | 561.901 | 502.205 | 538.807 | 619.116 | 687.808 | 885.442 | |
| P值 | - | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 吸烟情况 | ||||||||||
| 否① | 14.11 (797/5 649) | 15.31 (832/5 436) | 16.60 (1 178/7 096) | 20.36 (1 343/6 597) | 22.82 (1 512/6 626) | 21.90 (1 466/6 694) | 28.62 (1 980/6 918) | 26.71 (2 398/8 978) | 33.53 (3 164/9 437) | |
| 戒烟② | 25.00 (48/192)a | 22.22 (32/144)a | 25.95 (34/131)a | 36.84 (56/152)a | 40.33 (148/367)a | 38.82 (165/425)a | 47.81 (164/343)a | 41.07 (230/560)a | 55.72 (224/402)a | |
| 现在吸烟③ | 15.38 (440/2 860)a | 17.24 (458/2 657) | 18.51 (593/3 204)a | 23.15 (668/2 885)ab | 23.77 (676/2 844)a | 23.19 (617/2 661)a | 29.44 (829/2 816)a | 29.58 (1 009/3 411)ab | 36.09 (1 084/3 004)ab | |
| χ2值 | 18.784 | 9.089 | 12.548 | 31.012 | 58.865 | 64.738 | 57.884 | 58.943 | 86.444 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.011 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 饮酒情况 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 14.01 (757/5 405) | 15.49 (821/5 300) | 16.91 (1 109/6 557) | 20.38 (1 248/6 125) | 23.12 (1 524/6 593) | 22.21 (1 480/6 664) | 29.66 (1 995/6 727) | 27.95 (2 391/8 556) | 33.71 (3 145/9 330) | |
| 是 | 15.95 (525/3 291) | 17.04 (500/2 934) | 18.26 (675/3 697) | 23.40 (780/3 333) | 25.09 (811/3 233) | 24.66 (770/3 123) | 29.22 (979/3 350) | 28.40 (1 248/4 395) | 37.77 (1 331/3 524) | |
| χ2值 | 6.170 | 3.373 | 2.975 | 11.740 | 4.645 | 7.191 | 0.201 | 0.292 | 18.587 | |
| P值 | 0.013 | 0.066 | 0.085 | 0.001 | 0.031 | 0.007 | 0.654 | 0.589 | <0.001 | |
| 每天睡眠时长(h) | ||||||||||
| <7① | - | - | - | - | 29.49 (292/990) | 27.45 (289/1 053) | 39.72 (433/ 1 090) | 36.07 (606/1 680) | 42.76 (658/1 539) | |
| 7~<9② | - | - | - | - | 21.46 (1 273/5 933)a | 20.92 (1 267/6 055)a | 27.56 (1 819/6 599)a | 25.98 (2 255/8 679)a | 32.33 (2 882/8 914)a | |
| ≥9③ | - | - | - | - | 26.48 (769/2 904)b | 25.92 (694/2 677)b | 30.08 (711/2 364)a | 30.00 (778/2 593)ab | 38.69 (884/2 285)ab | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 47.236 | 39.408 | 67.084 | 76.762 | 82.135 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 对膳食指南的了解状况 | ||||||||||
| 不了解 | - | - | - | - | 23.80 (2 129/8 947) | 23.14 (2 000/8 643) | 29.90 (2 585/8 646) | 28.92 (2 733/9 451) | 36.23 (3 399/9 382) | |
| 了解 | - | - | - | - | 23.31 (165/708) | 21.74 (237/1 090) | 26.94 (371/1 377) | 25.82 (896/3 470) | 31.09 (1 081/3 477) | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 0.087 | 1.067 | 4.990 | 12.047 | 29.511 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.768 | 0.302 | 0.025 | 0.001 | <0.001 | |
表1 1991—2015年我国不同特征成人高血压患病率比较〔%(n/N)〕
Table 1 Comparison of hypertension prevalence among Chinese adults with different characteristics from 1991 to 2015
| 基本特征 | 1991年(n=8 743) | 1993年(n=8 330) | 1997年(n=10 549) | 2000年(n=9 727) | 2004年(n=9 854) | 2006年(n=9 791) | 2009年(n=10 080) | 2011年(n=12 955) | 2015年(n=13 834) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | ||||||||||
| 男 | 16.26 (674/4 146) | 17.60 (697/3 967) | 18.51 (971/5 247) | 23.03 (1 071/4 650) | 25.69 (1 216/4 733) | 24.82 (1 156/44 658) | 31.55 (1 521/4 821) | 30.14 (1 835/6 089) | 34.75 (2 301/6 621) | |
| 女 | 13.42 (617/4 597) | 14.81 (646/4 363) | 15.96 (846/5 302) | 19.91 (1 011/5 077) | 21.93 (1 123/5 121) | 21.31 (1 094/5 133) | 27.63 (1 453/5 259) | 26.27 (1 804/6 866) | 30.76 (2 219/7 213) | |
| χ2值 | 13.919 | 11.735 | 12.023 | 14.034 | 19.237 | 16.944 | 18.589 | 23.828 | 24.973 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||||||
| 18~44① | 5.86 (328/5 597) | 7.06 (364/5 155) | 7.01 (443/6 321) | 9.04 (457/5 056) | 9.50 (413/4 349) | 9.19 (380/4 136) | 11.95 (460/3 850) | 8.83 (408/4 618) | 10.60 (489/4 615) | |
| 45~59② | 21.84 (404/1 850)a | 21.61 (401/1 856)a | 23.54 (585/2 485)a | 25.89 (732/2 827)a | 26.23 (869/3 313)a | 24.51 (796/3 248)a | 31.66 (1 111/3 509)a | 30.07 (1 387/4 612)a | 33.75 (1 542/4 569)a | |
| ≥60③ | 43.13 (559/1 296)ab | 43.82 (578/1 319)ab | 45.27 (789/1 743)ab | 48.43 (893/1 844)ab | 48.22 (1 057/2 192)ab | 44.62 (1 074/2 407)ab | 51.56 (1 403/2 721)ab | 49.50 (1 844/3 725)ab | 53.53 (2 489/4 650)ab | |
| χ2值 | 1 254.820 | 1 102.573 | 1 493.600 | 1 293.850 | 1 224.456 | 1 085.648 | 1 214.885 | 1 702.200 | 1 944.218 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 居住地 | ||||||||||
| 城镇 | 18.99 (540/2 843) | 20.47 (530/2 589) | 21.19 (731/3 450) | 24.40 (815/3 340) | 27.17 (929/3 419) | 25.01 (841/3 362) | 30.06 (1 034/3 440) | 28.30 (1 513/5 347) | 32.02 (1 692/5 284) | |
| 农村 | 12.73 (751/5 900) | 14.16 (813/5 741) | 15.30 (1 086/7 099) | 19.84 (1 267/6 387) | 21.91 (1 410/6 435) | 21.92 (1 409/6 429) | 29.22 (1 940/6 640) | 27.94 (2 126/7 608) | 33.08 (2 828/8 550) | |
| χ2值 | 59.836 | 52.535 | 56.501 | 27.156 | 34.128 | 11.975 | 0.771 | 0.193 | 1.652 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.380 | 0.661 | 0.199 | |
| 文化程度 | ||||||||||
| 文盲/小学① | 19.10 (952/4 985) | 20.37 (906/4 447) | 22.64 (1 142/5 044) | 27.63 (1 181/4 274) | 30.80 (1 335/4 335) | 29.99 (1 245/4 152) | 37.88 (1 595/4 211) | 37.90 (1 760/4 644) | 41.55 (880/2 118) | |
| 初中② | 8.14 (193/2 372)c | 10.57 (252/2 385)c | 11.00 (342/3 109)c | 14.09 (420/2 980)c | 16.93 (527/3 113)c | 17.69 (531/3 002)c | 24.18 (808/3 342)c | 24.71 (990/4 007)c | 30.48 (1 352/4 436)c | |
| 高中/中专③ | 9.12 (106/1 162)c | 10.01 (120/1 199)c | 11.39 (206/1 808)c | 16.71 (291/1 741)c | 19.03 (379/1 992)c | 18.14 (374/2 062)c | 24.03 (470/1 956)c | 23.05 (618/2 681)c | 28.97 (904/3 120)c | |
| 大专及以上④ | 17.22 (31/180)de | 19.85 (27/136)de | 16.46 (40/243) | 21.12 (83/393)cd | 23.41 (92/393)cd | 17.06 (93/545)c | 16.94 (94/555)cde | 16.65 (266/1 598)cde | 19.22 (381/1 982)cde | |
| χ2值 | 187.703 | 149.367 | 233.866 | 217.972 | 223.538 | 200.725 | 257.981 | 381.826 | 245.204 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 婚姻状态 | ||||||||||
| 未婚① | 3.54 (47/1 327) | 5.13 (64/1 248) | 5.30 (99/1 868) | 10.11 (117/1 157) | 9.84 (88/894) | 5.24 (38/725) | 7.14 (49/686) | 6.49 (50/770) | 5.51 (58/1 052) | |
| 已婚② | 15.29 (1 041/6 809)a | 16.45 (1 063/6 461)a | 18.17 (1 425/7 843)a | 21.49 (1 612/7 500)a | 23.33 (1 878/8 051)a | 23.11 (1 882/8 145)a | 29.47 (2 463/8 358)a | 27.84 (3 015/10 830)a | 33.45 (3 880/11 601)a | |
| 离异/丧偶/分居③ | 34.88 (203/582)ab | 36.77 (207/563)ab | 37.72 (278/737)ab | 37.12 (255/687)ab | 42.51 (363/854)ab | 36.33 (323/889)ab | 45.56 (451/990)ab | 44.24 (568/1 284)ab | 50.76 (570/1 123)ab | |
| χ2值 | 320.618 | 289.451 | 407.930 | 189.508 | 262.027 | 218.496 | 287.412 | 342.984 | 522.431 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 体型 | ||||||||||
| 消瘦① | 13.07 (72/5 900) | 14.59 (61/5 741) | 16.90 (71/7 099) | 14.57 (58/6 387) | 21.10 (77/6 435) | 17.37 (62/6 429) | 16.17 (65/6 640) | 13.03 (55/7 608) | 15.84 (61/8 550) | |
| 正常② | 11.27 (723/6 418) | 12.67 (765/6 039) | 15.45 (917/5 937) | 15.58 (938/6 019) | 17.81 (980/5 504) | 17.68 (944/5 338) | 23.59 (1 255/5 320)c | 20.53 (1 338/6 517)c | 25.80 (1 495/5 794)c | |
| 超重③ | 26.69 (356/1 334)cd | 25.39 (361/1 422)cd | 30.23 (545/1 803)cd | 30.35 (732/2 412)cd | 32.74 (831/2 538)cd | 29.90 (777/2 599)cd | 37.73 (1 075/2 849)cd | 36.02 (1 466/4 070)cd | 42.67 (1 812/4 247)cd | |
| 肥胖④ | 46.36 (121/261)cde | 48.63 (124/255)cde | 49.55 (218/440)cde | 49.85 (324/650)cde | 50.88 (376/739)cde | 50.53 (382/756)cde | 54.60 (499/914)cde | 48.81 (740/1 516)cde | 52.92 (941/1 778)cde | |
| χ2值 | 419.295 | 343.593 | 430.925 | 554.589 | 503.053 | 467.579 | 479.315 | 668.910 | 635.271 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 中心性肥胖 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 14.77 (1 291/8 743) | 13.18 (967/7 336) | 13.40 (1 220/9 107) | 16.13 (1 220/7 563) | 18.25 (1 356/7 430) | 17.20 (1 253/7 287) | 21.91 (1 522/6 946) | 20.32 (1 684/8 288) | 23.71 (2 088/8 807) | |
| 是 | - | 37.83 (376/994) | 41.40 (597/1 442) | 39.83 (862/2 164) | 40.55 (983/2 424) | 39.82 (997/2 504) | 46.33 (1 452/3 134) | 41.89 (1 955/4 667) | 48.38 (2 432/5 027) | |
| χ2值 | - | 393.184 | 684.763 | 561.901 | 502.205 | 538.807 | 619.116 | 687.808 | 885.442 | |
| P值 | - | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 吸烟情况 | ||||||||||
| 否① | 14.11 (797/5 649) | 15.31 (832/5 436) | 16.60 (1 178/7 096) | 20.36 (1 343/6 597) | 22.82 (1 512/6 626) | 21.90 (1 466/6 694) | 28.62 (1 980/6 918) | 26.71 (2 398/8 978) | 33.53 (3 164/9 437) | |
| 戒烟② | 25.00 (48/192)a | 22.22 (32/144)a | 25.95 (34/131)a | 36.84 (56/152)a | 40.33 (148/367)a | 38.82 (165/425)a | 47.81 (164/343)a | 41.07 (230/560)a | 55.72 (224/402)a | |
| 现在吸烟③ | 15.38 (440/2 860)a | 17.24 (458/2 657) | 18.51 (593/3 204)a | 23.15 (668/2 885)ab | 23.77 (676/2 844)a | 23.19 (617/2 661)a | 29.44 (829/2 816)a | 29.58 (1 009/3 411)ab | 36.09 (1 084/3 004)ab | |
| χ2值 | 18.784 | 9.089 | 12.548 | 31.012 | 58.865 | 64.738 | 57.884 | 58.943 | 86.444 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.011 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 饮酒情况 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 14.01 (757/5 405) | 15.49 (821/5 300) | 16.91 (1 109/6 557) | 20.38 (1 248/6 125) | 23.12 (1 524/6 593) | 22.21 (1 480/6 664) | 29.66 (1 995/6 727) | 27.95 (2 391/8 556) | 33.71 (3 145/9 330) | |
| 是 | 15.95 (525/3 291) | 17.04 (500/2 934) | 18.26 (675/3 697) | 23.40 (780/3 333) | 25.09 (811/3 233) | 24.66 (770/3 123) | 29.22 (979/3 350) | 28.40 (1 248/4 395) | 37.77 (1 331/3 524) | |
| χ2值 | 6.170 | 3.373 | 2.975 | 11.740 | 4.645 | 7.191 | 0.201 | 0.292 | 18.587 | |
| P值 | 0.013 | 0.066 | 0.085 | 0.001 | 0.031 | 0.007 | 0.654 | 0.589 | <0.001 | |
| 每天睡眠时长(h) | ||||||||||
| <7① | - | - | - | - | 29.49 (292/990) | 27.45 (289/1 053) | 39.72 (433/ 1 090) | 36.07 (606/1 680) | 42.76 (658/1 539) | |
| 7~<9② | - | - | - | - | 21.46 (1 273/5 933)a | 20.92 (1 267/6 055)a | 27.56 (1 819/6 599)a | 25.98 (2 255/8 679)a | 32.33 (2 882/8 914)a | |
| ≥9③ | - | - | - | - | 26.48 (769/2 904)b | 25.92 (694/2 677)b | 30.08 (711/2 364)a | 30.00 (778/2 593)ab | 38.69 (884/2 285)ab | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 47.236 | 39.408 | 67.084 | 76.762 | 82.135 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 对膳食指南的了解状况 | ||||||||||
| 不了解 | - | - | - | - | 23.80 (2 129/8 947) | 23.14 (2 000/8 643) | 29.90 (2 585/8 646) | 28.92 (2 733/9 451) | 36.23 (3 399/9 382) | |
| 了解 | - | - | - | - | 23.31 (165/708) | 21.74 (237/1 090) | 26.94 (371/1 377) | 25.82 (896/3 470) | 31.09 (1 081/3 477) | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 0.087 | 1.067 | 4.990 | 12.047 | 29.511 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.768 | 0.302 | 0.025 | 0.001 | <0.001 | |
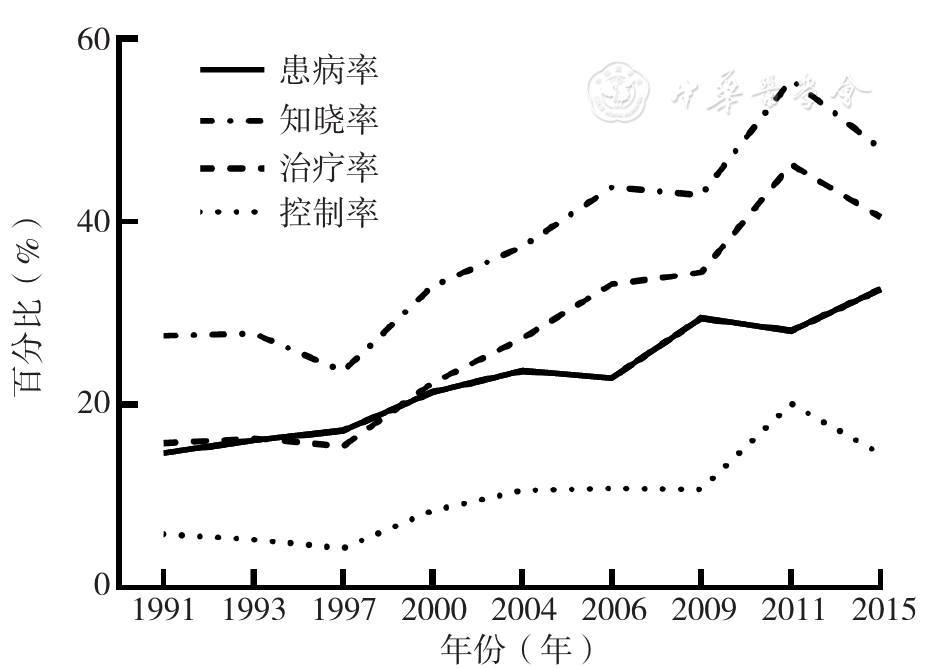
图1 我国成年人1991—2015年高血压患病率、知晓率、治疗率和控制率的变化趋势
Figure 1 Trends in prevalence,awareness,treatment and control rates of hypertension among Chinese adults from 1991 to 2015
| 基本特征 | 1991年(n=1 291) | 1993年(n=1 343) | 1997年(n=1 817) | 2000年(n=2 082) | 2004年(n=2 339) | 2006年(n=2 250) | 2009年(n=2 974) | 2011年(n=3 639) | 2015年(n=4 520) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | ||||||||||
| 男 | 22.26 (150/674) | 25.39 (177/697) | 20.70 (201/971) | 26.98 (289/1 071) | 31.66 (385/1 216) | 39.36 (455/1 156) | 37.74 (574/1 521) | 50.68 (930/1 835) | 45.11 (1 038/2 301) | |
| 女 | 33.39 (206/617) | 30.50 (197/646) | 27.07 (229/846) | 39.37 (398/1 011) | 43.46 (488/1 123) | 48.45 (530/1 094) | 48.45 (704/1 453) | 60.48 (1 091/1 804) | 51.15 (1 135/2 219) | |
| χ2值 | 19.988 | 4.341 | 10.149 | 36.069 | 34.714 | 18.854 | 34.803 | 35.348 | 16.500 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.037 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||||||
| 18~44① | 21.04 (69/328) | 12.36 (45/364) | 9.71 (43/443) | 15.54 (71/457) | 16.95 (70/413) | 19.47 (74/380) | 19.13 (88/460) | 29.17 (119/408) | 21.88 (107/489) | |
| 45~59② | 30.20 (122/404)a | 32.92 (132/401)a | 24.62 (144/585)a | 34.56 (253/732)a | 37.86 (329/869)a | 43.47 (346/796)a | 40.05 (445/1 111)a | 53.06 (736/1 387)a | 40.73 (628/1 542)a | |
| ≥60③ | 29.52 (165/559)a | 34.08 (197/578)a | 30.80 (243/789)ab | 40.65 (363/893)ab | 44.84 (474/1 057)ab | 52.61 (565/1 074)ab | 53.10 (745/1 403)ab | 63.23 (1 166/1 844)ab | 57.77 (1 438/2 489)ab | |
| χ2值 | 9.469 | 59.754 | 70.297 | 87.485 | 98.949 | 125.245 | 169.289 | 162.551 | 261.559 | |
| P值 | 0.009 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 居住地 | ||||||||||
| 城镇 | 32.59 (176/540) | 34.91 (185/530) | 30.10 (220/731) | 38.77 (316/815) | 44.46 (413/929) | 55.77 (469/841) | 54.06 (559/1 034) | 66.09 (1 000/1 513) | 57.15 (967/1 692) | |
| 农村 | 23.97 (180/751) | 23.25 (189/813) | 19.34 (210/1 086) | 29.28 (371/1 267) | 32.62 (460/1 410) | 36.62 (516/1 409) | 37.06 (719/1 940) | 48.02 (1 021/2 126) | 42.64 (1 206/2 828) | |
| χ2值 | 11.700 | 21.703 | 27.995 | 20.208 | 33.516 | 78.430 | 79.544 | 116.876 | 89.240 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | |
| 文化程度 | ||||||||||
| 文盲/小学① | 28.26 (269/952) | 29.03 (263/906) | 24.26 (277/1 142) | 32.85 (388/1 181) | 40.00 (534/1 335) | 45.06 (561/1 245) | 45.20 (721/1 595) | 54.09 (952/1 760) | 50.91 (448/880) | |
| 初中② | 22.28 (43/193) | 20.24 (51/252)c | 18.42 (63/342) | 32.62 (137/420) | 30.74 (162/527)c | 34.84 (185/531)c | 37.13 (300/808)c | 52.53 (520/990) | 44.45 (601/1 352)c | |
| 高中/中专③ | 31.13 (33/106) | 30.00 (36/120) | 24.76 (51/206) | 32.30 (94/291) | 38.79 (147/379) | 48.40 (181/374)d | 44.47 (209/470) | 60.03 (371/618)d | 47.90 (433/904) | |
| 大专及以上④ | 22.58 (7/31) | 40.74 (11/27) | 35.00 (14/40) | 32.53 (27/83) | 31.52 (29/92) | 58.06 (54/93)d | 48.94 (46/94) | 65.79 (175/266)cd | 49.08 (187/381) | |
| χ2值 | 3.991 | 10.422 | 8.408 | 0.036 | 15.511 | 29.024 | 16.289 | 21.507 | 9.573 | |
| P值 | 0.262 | 0.015 | 0.038 | 0.998 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.023 | |
| 婚姻状态 | ||||||||||
| 未婚① | 8.51 (4/47) | 7.81 (5/64) | 12.12 (12/99) | 25.64 (30/117) | 18.18 (16/88) | 18.42 (7/38) | 8.16 (4/49) | 18.00 (9/50) | 18.97 (11/58) | |
| 已婚② | 28.05 (292/1 041)a | 29.63 (315/1 063)a | 23.65 (337/1 425)a | 32.94 (531/1 612) | 36.95 (694/1 878)a | 42.83 (806/1 882)a | 42.02 (1 035/2 463)a | 54.96 (1 657/3 015)a | 46.93 (1 821/3 880)a | |
| 离异/丧偶/分居③ | 29.56 (60/203)a | 25.12 (52/207)a | 28.06 (78/278)a | 36.86 (94/255) | 44.35 (161/363)ab | 52.63 (170/323)ab | 51.88 (234/451)ab | 61.80 (351/568)ab | 58.77 (335/570)ab | |
| χ2值 | 9.070 | 15.224 | 10.262 | 4.588 | 21.537 | 20.899 | 39.755 | 37.946 | 47.843 | |
| P值 | 0.011 | <0.001 | 0.006 | 0.101 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 体型 | ||||||||||
| 消瘦① | 18.06 (13/72) | 22.95 (14/61) | 11.27 (8/71) | 27.59 (16/58) | 22.08 (17/77) | 40.32 (25/62) | 32.31 (21/65) | 54.55 (30/55) | 34.43 (21/61) | |
| 正常② | 22.13 (160/723) | 21.05 (161/765) | 16.90 (155/917) | 26.23 (246/938) | 31.12 (305/980) | 35.91 (339/944) | 38.25 (480/1 255) | 49.93 (668/1 338) | 41.47 (620/1 495) | |
| 超重③ | 32.87 (117/356)d | 34.07 (123/361)d | 24.59 (134/545)d | 36.34 (266/732)d | 38.03 (316/831)cd | 45.17 (351/777)d | 44.65 (480/1 075)d | 57.91 (849/1 466)d | 46.91 (850/1 812)d | |
| 肥胖④ | 47.93 (58/121)cde | 54.03 (67/124)cde | 35.32 (77/218)cde | 44.44 (144/324)d | 48.40 (182/376)cde | 54.45 (208/382)de | 47.70 (238/499)d | 59.05 (437/740)d | 51.97 (489/941)cd | |
| χ2值 | 44.288 | 67.626 | 43.826 | 43.230 | 43.027 | 41.438 | 19.476 | 23.855 | 29.719 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 中心性肥胖 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 27.58 (356/1 291) | 23.06 (223/967) | 20.82 (254/1 220) | 28.03 (342/1 220) | 33.11 (449/1 356) | 38.31 (480/1 253) | 39.95 (608/1 522) | 51.43 (866/1 684) | 45.16 (943/2 088) | |
| 是 | - | 40.16 (151/376) | 29.48 (176/597) | 40.02 (345/862) | 43.13 (424/983) | 50.65 (505/997) | 46.14 (670/1 452) | 59.08 (1 155/1 955) | 50.58 (1 230/2 432) | |
| χ2值 | - | 39.393 | 16.645 | 32.846 | 24.464 | 34.372 | 11.640 | 21.464 | 13.186 | |
| P值 | - | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 吸烟情况 | ||||||||||
| 否① | 31.74 (253/797) | 30.29 (252/832) | 27.50 (324/1 178) | 37.53 (504/1 343) | 40.08 (606/1 512) | 45.63 (669/1 466) | 45.25 (896/1 980) | 58.30 (1 398/2 398) | 48.80 (1 544/3 164) | |
| 戒烟② | 16.67 (8/48)a | 31.25 (10/32) | 32.35 (11/34)a | 39.29 (22/56)a | 43.92 (65/148)a | 57.58 (95/165)a | 50.61 (83/164)a | 68.70 (158/230)a | 58.93 (132/224)a | |
| 现在吸烟③ | 21.14 (93/440)b | 23.36 (107/458)b | 16.02 (95/593)b | 23.35 (156/668)b | 29.88 (202/676)b | 35.66 (220/617)ab | 35.95 (298/829)b | 45.99 (464/1 009)ab | 41.79 (453/1 084)ab | |
| χ2值 | 18.940 | 7.224 | 30.054 | 41.573 | 23.650 | 31.351 | 24.803 | 60.808 | 28.021 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.027 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 饮酒情况 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 30.12 (228/757) | 30.82 (253/821) | 26.87 (298/1 109) | 36.22 (452/1 248) | 41.73 (636/1 524) | 48.65 (720/1 480) | 47.12 (940/1 995) | 58.51 (1 399/2 391) | 49.83 (1 567/3 145) | |
| 是 | 24.00 (126/525) | 23.20 (116/500) | 18.22 (123/675) | 28.08 (219/780) | 29.22 (237/811) | 34.42 (265/770) | 34.53 (338/979) | 49.84 (622/1 248) | 42.45 (565/1 331) | |
| χ2值 | 5.807 | 8.954 | 17.409 | 14.369 | 35.382 | 41.687 | 42.496 | 24.969 | 20.397 | |
| P值 | 0.016 | 0.003 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 每天睡眠时长(h) | ||||||||||
| <7① | - | - | - | - | 40.07 (117/292) | 46.71 (135/289) | 47.11 (204/433) | 63.04 (382/606) | 55.93 (368/658) | |
| 7~9② | - | - | - | - | 35.51 (452/1 273) | 41.52 (526/1 267) | 39.80 (724/1 819)a | 53.30 (1 202/2 255)a | 45.18 (1 302/2 882)a | |
| ≥9③ | - | - | - | - | 39.14 (301/769) | 46.69 (324/694) | 48.95 (348/711)b | 56.17 (437/778)a | 47.74 (422/884)a | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 3.823 | 6.031 | 20.819 | 18.482 | 24.926 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.148 | 0.049 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 对膳食指南的了解状况 | ||||||||||
| 不了解 | - | - | - | - | 37.39 (796/2 129) | 43.00 (860/2 000) | 42.32 (1 094/2 585) | 52.25 (1 428/2 733) | 46.31 (1 574/3 399) | |
| 了解 | - | - | - | - | 40.00 (66/165) | 50.21 (119/237) | 47.71 (177/371) | 65.63 (588/896) | 51.80 (560/1 081) | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 0.445 | 4.477 | 3.843 | 48.885 | 9.932 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.559 | 0.034 | 0.049 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
表2 1991—2015年我国不同特征成人高血压知晓率比较〔%(n/N)〕
Table 2 Comparison of hypertension awareness rate among Chinese adults with different characteristics from 1991 to 2015
| 基本特征 | 1991年(n=1 291) | 1993年(n=1 343) | 1997年(n=1 817) | 2000年(n=2 082) | 2004年(n=2 339) | 2006年(n=2 250) | 2009年(n=2 974) | 2011年(n=3 639) | 2015年(n=4 520) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | ||||||||||
| 男 | 22.26 (150/674) | 25.39 (177/697) | 20.70 (201/971) | 26.98 (289/1 071) | 31.66 (385/1 216) | 39.36 (455/1 156) | 37.74 (574/1 521) | 50.68 (930/1 835) | 45.11 (1 038/2 301) | |
| 女 | 33.39 (206/617) | 30.50 (197/646) | 27.07 (229/846) | 39.37 (398/1 011) | 43.46 (488/1 123) | 48.45 (530/1 094) | 48.45 (704/1 453) | 60.48 (1 091/1 804) | 51.15 (1 135/2 219) | |
| χ2值 | 19.988 | 4.341 | 10.149 | 36.069 | 34.714 | 18.854 | 34.803 | 35.348 | 16.500 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.037 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||||||
| 18~44① | 21.04 (69/328) | 12.36 (45/364) | 9.71 (43/443) | 15.54 (71/457) | 16.95 (70/413) | 19.47 (74/380) | 19.13 (88/460) | 29.17 (119/408) | 21.88 (107/489) | |
| 45~59② | 30.20 (122/404)a | 32.92 (132/401)a | 24.62 (144/585)a | 34.56 (253/732)a | 37.86 (329/869)a | 43.47 (346/796)a | 40.05 (445/1 111)a | 53.06 (736/1 387)a | 40.73 (628/1 542)a | |
| ≥60③ | 29.52 (165/559)a | 34.08 (197/578)a | 30.80 (243/789)ab | 40.65 (363/893)ab | 44.84 (474/1 057)ab | 52.61 (565/1 074)ab | 53.10 (745/1 403)ab | 63.23 (1 166/1 844)ab | 57.77 (1 438/2 489)ab | |
| χ2值 | 9.469 | 59.754 | 70.297 | 87.485 | 98.949 | 125.245 | 169.289 | 162.551 | 261.559 | |
| P值 | 0.009 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 居住地 | ||||||||||
| 城镇 | 32.59 (176/540) | 34.91 (185/530) | 30.10 (220/731) | 38.77 (316/815) | 44.46 (413/929) | 55.77 (469/841) | 54.06 (559/1 034) | 66.09 (1 000/1 513) | 57.15 (967/1 692) | |
| 农村 | 23.97 (180/751) | 23.25 (189/813) | 19.34 (210/1 086) | 29.28 (371/1 267) | 32.62 (460/1 410) | 36.62 (516/1 409) | 37.06 (719/1 940) | 48.02 (1 021/2 126) | 42.64 (1 206/2 828) | |
| χ2值 | 11.700 | 21.703 | 27.995 | 20.208 | 33.516 | 78.430 | 79.544 | 116.876 | 89.240 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | |
| 文化程度 | ||||||||||
| 文盲/小学① | 28.26 (269/952) | 29.03 (263/906) | 24.26 (277/1 142) | 32.85 (388/1 181) | 40.00 (534/1 335) | 45.06 (561/1 245) | 45.20 (721/1 595) | 54.09 (952/1 760) | 50.91 (448/880) | |
| 初中② | 22.28 (43/193) | 20.24 (51/252)c | 18.42 (63/342) | 32.62 (137/420) | 30.74 (162/527)c | 34.84 (185/531)c | 37.13 (300/808)c | 52.53 (520/990) | 44.45 (601/1 352)c | |
| 高中/中专③ | 31.13 (33/106) | 30.00 (36/120) | 24.76 (51/206) | 32.30 (94/291) | 38.79 (147/379) | 48.40 (181/374)d | 44.47 (209/470) | 60.03 (371/618)d | 47.90 (433/904) | |
| 大专及以上④ | 22.58 (7/31) | 40.74 (11/27) | 35.00 (14/40) | 32.53 (27/83) | 31.52 (29/92) | 58.06 (54/93)d | 48.94 (46/94) | 65.79 (175/266)cd | 49.08 (187/381) | |
| χ2值 | 3.991 | 10.422 | 8.408 | 0.036 | 15.511 | 29.024 | 16.289 | 21.507 | 9.573 | |
| P值 | 0.262 | 0.015 | 0.038 | 0.998 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.023 | |
| 婚姻状态 | ||||||||||
| 未婚① | 8.51 (4/47) | 7.81 (5/64) | 12.12 (12/99) | 25.64 (30/117) | 18.18 (16/88) | 18.42 (7/38) | 8.16 (4/49) | 18.00 (9/50) | 18.97 (11/58) | |
| 已婚② | 28.05 (292/1 041)a | 29.63 (315/1 063)a | 23.65 (337/1 425)a | 32.94 (531/1 612) | 36.95 (694/1 878)a | 42.83 (806/1 882)a | 42.02 (1 035/2 463)a | 54.96 (1 657/3 015)a | 46.93 (1 821/3 880)a | |
| 离异/丧偶/分居③ | 29.56 (60/203)a | 25.12 (52/207)a | 28.06 (78/278)a | 36.86 (94/255) | 44.35 (161/363)ab | 52.63 (170/323)ab | 51.88 (234/451)ab | 61.80 (351/568)ab | 58.77 (335/570)ab | |
| χ2值 | 9.070 | 15.224 | 10.262 | 4.588 | 21.537 | 20.899 | 39.755 | 37.946 | 47.843 | |
| P值 | 0.011 | <0.001 | 0.006 | 0.101 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 体型 | ||||||||||
| 消瘦① | 18.06 (13/72) | 22.95 (14/61) | 11.27 (8/71) | 27.59 (16/58) | 22.08 (17/77) | 40.32 (25/62) | 32.31 (21/65) | 54.55 (30/55) | 34.43 (21/61) | |
| 正常② | 22.13 (160/723) | 21.05 (161/765) | 16.90 (155/917) | 26.23 (246/938) | 31.12 (305/980) | 35.91 (339/944) | 38.25 (480/1 255) | 49.93 (668/1 338) | 41.47 (620/1 495) | |
| 超重③ | 32.87 (117/356)d | 34.07 (123/361)d | 24.59 (134/545)d | 36.34 (266/732)d | 38.03 (316/831)cd | 45.17 (351/777)d | 44.65 (480/1 075)d | 57.91 (849/1 466)d | 46.91 (850/1 812)d | |
| 肥胖④ | 47.93 (58/121)cde | 54.03 (67/124)cde | 35.32 (77/218)cde | 44.44 (144/324)d | 48.40 (182/376)cde | 54.45 (208/382)de | 47.70 (238/499)d | 59.05 (437/740)d | 51.97 (489/941)cd | |
| χ2值 | 44.288 | 67.626 | 43.826 | 43.230 | 43.027 | 41.438 | 19.476 | 23.855 | 29.719 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 中心性肥胖 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 27.58 (356/1 291) | 23.06 (223/967) | 20.82 (254/1 220) | 28.03 (342/1 220) | 33.11 (449/1 356) | 38.31 (480/1 253) | 39.95 (608/1 522) | 51.43 (866/1 684) | 45.16 (943/2 088) | |
| 是 | - | 40.16 (151/376) | 29.48 (176/597) | 40.02 (345/862) | 43.13 (424/983) | 50.65 (505/997) | 46.14 (670/1 452) | 59.08 (1 155/1 955) | 50.58 (1 230/2 432) | |
| χ2值 | - | 39.393 | 16.645 | 32.846 | 24.464 | 34.372 | 11.640 | 21.464 | 13.186 | |
| P值 | - | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 吸烟情况 | ||||||||||
| 否① | 31.74 (253/797) | 30.29 (252/832) | 27.50 (324/1 178) | 37.53 (504/1 343) | 40.08 (606/1 512) | 45.63 (669/1 466) | 45.25 (896/1 980) | 58.30 (1 398/2 398) | 48.80 (1 544/3 164) | |
| 戒烟② | 16.67 (8/48)a | 31.25 (10/32) | 32.35 (11/34)a | 39.29 (22/56)a | 43.92 (65/148)a | 57.58 (95/165)a | 50.61 (83/164)a | 68.70 (158/230)a | 58.93 (132/224)a | |
| 现在吸烟③ | 21.14 (93/440)b | 23.36 (107/458)b | 16.02 (95/593)b | 23.35 (156/668)b | 29.88 (202/676)b | 35.66 (220/617)ab | 35.95 (298/829)b | 45.99 (464/1 009)ab | 41.79 (453/1 084)ab | |
| χ2值 | 18.940 | 7.224 | 30.054 | 41.573 | 23.650 | 31.351 | 24.803 | 60.808 | 28.021 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.027 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 饮酒情况 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 30.12 (228/757) | 30.82 (253/821) | 26.87 (298/1 109) | 36.22 (452/1 248) | 41.73 (636/1 524) | 48.65 (720/1 480) | 47.12 (940/1 995) | 58.51 (1 399/2 391) | 49.83 (1 567/3 145) | |
| 是 | 24.00 (126/525) | 23.20 (116/500) | 18.22 (123/675) | 28.08 (219/780) | 29.22 (237/811) | 34.42 (265/770) | 34.53 (338/979) | 49.84 (622/1 248) | 42.45 (565/1 331) | |
| χ2值 | 5.807 | 8.954 | 17.409 | 14.369 | 35.382 | 41.687 | 42.496 | 24.969 | 20.397 | |
| P值 | 0.016 | 0.003 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 每天睡眠时长(h) | ||||||||||
| <7① | - | - | - | - | 40.07 (117/292) | 46.71 (135/289) | 47.11 (204/433) | 63.04 (382/606) | 55.93 (368/658) | |
| 7~9② | - | - | - | - | 35.51 (452/1 273) | 41.52 (526/1 267) | 39.80 (724/1 819)a | 53.30 (1 202/2 255)a | 45.18 (1 302/2 882)a | |
| ≥9③ | - | - | - | - | 39.14 (301/769) | 46.69 (324/694) | 48.95 (348/711)b | 56.17 (437/778)a | 47.74 (422/884)a | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 3.823 | 6.031 | 20.819 | 18.482 | 24.926 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.148 | 0.049 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 对膳食指南的了解状况 | ||||||||||
| 不了解 | - | - | - | - | 37.39 (796/2 129) | 43.00 (860/2 000) | 42.32 (1 094/2 585) | 52.25 (1 428/2 733) | 46.31 (1 574/3 399) | |
| 了解 | - | - | - | - | 40.00 (66/165) | 50.21 (119/237) | 47.71 (177/371) | 65.63 (588/896) | 51.80 (560/1 081) | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 0.445 | 4.477 | 3.843 | 48.885 | 9.932 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.559 | 0.034 | 0.049 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 基本特征 | 1991年(n=1 291) | 1993年(n=1 343) | 1997年(n=1 817) | 2000年(n=2 082) | 2004年(n=2 339) | 2006年(n=2 250) | 2009年(n=2 974) | 2011年(n=3 639) | 2015年(n=4 520) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | ||||||||||
| 男 | 12.02 (81/674) | 15.93 (111/697) | 13.80 (134/971) | 17.65 (189/1 071) | 22.04 (268/1 216) | 28.37 (328/1 156) | 29.19 (444/1 521) | 40.82 (749/1 835) | 37.07 (853/2 301) | |
| 女 | 19.94 (123/617) | 16.87 (109/646) | 17.38 (147/846) | 27.40 (277/1 011) | 32.95 (370/1 123) | 38.30 (419/1 094) | 40.06 (582/1 453) | 51.88 (936/1 804) | 44.07 (978/2 219) | |
| χ2值 | 15.177 | 0.220 | 4.421 | 28.467 | 35.584 | 24.971 | 38.811 | 44.814 | 22.988 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.639 | 0.035 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||||||
| 18~44① | 7.32 (24/328) | 4.40 (16/364) | 4.74 (21/443) | 7.88 (36/457) | 10.17 (42/413) | 12.63 (48/380) | 12.39 (57/460) | 18.14 (74/408) | 15.54 (76/489) | |
| 45~59② | 18.32 (74/404)a | 17.46 (70/401)a | 14.87 (87/585)a | 22.13 (162/732)a | 26.81 (233/869)a | 31.03 (247/796)a | 29.79 (331/1 111)a | 43.40 (602/1 387)a | 32.75 (505/1 542)a | |
| ≥60③ | 18.96 (106/559)a | 23.18 (134/578)a | 21.93 (173/789)ab | 30.01 (268/893)ab | 34.34 (363/1 057)ab | 42.09 (452/1 074)ab | 45.47 (638/1 403)ab | 54.72 (1 009/1 844)ab | 50.22 (1 250/2 489)ab | |
| χ2值 | 23.866 | 58.037 | 64.329 | 85.288 | 87.005 | 112.414 | 185.165 | 187.389 | 262.427 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 居住地 | ||||||||||
| 城镇 | 20.37 (110/540) | 22.83 (121/530) | 20.38 (149/731) | 28.71 (234/815) | 34.45 (320/929) | 42.09 (354/841) | 46.62 (482/1 034) | 57.17 (865/1 513) | 50.71 (858/1 692) | |
| 农村 | 12.52 (94/751) | 12.18 (99/813) | 12.15 (132/1 086) | 18.31 (232/1 267) | 22.55 (318/1 410) | 27.89 (393/1 409) | 28.04 (544/1 940) | 38.57 (820/2 126) | 34.41 (973/2 828) | |
| χ2值 | 14.563 | 26.582 | 22.627 | 30.882 | 39.247 | 47.888 | 102.975 | 123.009 | 116.759 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 文化程度 | ||||||||||
| 文盲/小学① | 15.97 (152/952) | 16.45 (149/906) | 15.41 (176/1 142) | 22.52 (266/1 181) | 28.84 (385/1 335) | 34.70 (432/1 245) | 36.99 (590/1 595) | 44.94 (791/1 760) | 42.05 (370/880) | |
| 初中② | 8.81 (17/193) | 13.10 (33/252) | 12.28 (42/342) | 21.67 (91/420) | 22.20 (117/527)c | 25.05 (133/531)c | 27.60 (223/808)c | 43.23 (428/990) | 37.43 (506/1 352) | |
| 高中/中专③ | 24.53 (26/106)d | 18.33 (22/120) | 17.96 (37/206) | 20.62 (60/291) | 29.55 (112/379) | 36.10 (135/374)d | 36.81 (173/470)d | 51.62 (319/618)cd | 40.71 (368/904) | |
| 大专及以上④ | 19.35 (6/31) | 25.93 (7/27) | 22.50 (9/40) | 25.30 (21/83) | 25.00 (23/92) | 46.24 (43/93)d | 40.43 (38/94) | 54.51 (145/266)cd | 43.57 (166/381) | |
| χ2值 | 13.547 | 4.119 | 5.152 | 1.024 | 10.240 | 25.741 | 23.971 | 19.293 | 7.460 | |
| P值 | 0.004 | 0.249 | 0.161 | 0.795 | 0.017 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.059 | |
| 婚姻状态 | ||||||||||
| 未婚① | 4.26 (2/47) | 4.69 (3/64) | 11.11 (11/99) | 20.51 (24/117) | 13.64 (12/88) | 5.26 (2/38) | 4.08 (2/49) | 12.00 (6/50) | 13.79 (8/58) | |
| 已婚② | 16.14 (168/1 041) | 17.22 (183/1 063)a | 15.93 (227/1 425) | 21.65 (349/1 612) | 26.36 (495/1 878)a | 32.25 (607/1 882)a | 33.50 (825/2 463)a | 45.70 (1 378/3 015)a | 39.51 (1 533/3 880)a | |
| 离异/丧偶/分居③ | 16.75 (34/203) | 16.43 (34/207)a | 14.75 (41/278) | 27.84 (71/255) | 35.54 (129/363)ab | 42.11 (136/323)ab | 43.46 (196/451)ab | 52.29 (297/568)ab | 50.00 (285/570)ab | |
| χ2值 | 4.935 | 6.880 | 1.778 | 5.110 | 20.727 | 25.678 | 37.168 | 32.284 | 40.090 | |
| P值 | 0.085 | 0.032 | 0.411 | 0.078 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 体型 | ||||||||||
| 消瘦① | 11.11 (8/72) | 8.20 (5/61) | 8.45 (6/71) | 12.07 (7/58) | 16.88 (13/77) | 35.48 (22/62) | 24.62 (16/65) | 29.09 (16/55) | 27.87 (17/61) | |
| 正常② | 11.89 (86/723) | 12.16 (93/765) | 9.49 (87/917) | 17.38 (163/938) | 21.73 (213/980) | 26.38 (249/944) | 29.64 (372/1 255) | 40.51 (542/1 338) | 34.25 (512/1 495) | |
| 超重③ | 18.54 (66/356)d | 18.84 (68/361)d | 17.25 (94/545)d | 24.73 (181/732)d | 28.40 (236/831)d | 34.23 (266/777)d | 35.35 (380/1 075)d | 49.11 (720/1 466)cd | 40.01 (725/1 812)d | |
| 肥胖④ | 31.40 (38/121)cde | 37.90 (47/124)cde | 27.06 (59/218)cde | 32.10 (104/324)cd | 38.03 (143/376)cde | 42.15 (161/382)d | 41.88 (209/499)cd | 51.22 (379/740)cd | 44.42 (418/941)d | |
| χ2值 | 33.992 | 56.827 | 52.844 | 37.196 | 41.887 | 33.727 | 27.890 | 36.395 | 29.757 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 中心性肥胖 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 15.80 (204/1 291) | 12.31 (119/967) | 12.46 (152/1 220) | 17.79 (217/1 220) | 22.79 (309/1 356) | 28.89 (362/1 253) | 30.88 (470/1 522) | 41.21 (694/1 684) | 36.69 (766/2 088) | |
| 是 | - | 26.86 (101/376) | 21.61 (129/597) | 28.89 (249/862) | 33.47 (329/983) | 38.62 (385/997) | 38.29 (556/1 452) | 50.69 (991/1 955) | 43.79 (1 065/2 432) | |
| χ2值 | - | 41.874 | 25.665 | 35.820 | 32.187 | 23.678 | 18.064 | 32.695 | 23.535 | |
| P值 | - | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 吸烟情况 | ||||||||||
| 否① | 19.07 (152/797) | 17.67 (147/832) | 18.34 (216/1 178) | 26.14 (351/1 343) | 30.16 (456/1 512) | 35.88 (526/1 466) | 37.53 (743/1 980) | 50.00 (1 199/2 398) | 41.59 (1 316/3 164) | |
| 戒烟② | 8.33 (4/48)a | 15.63 (5/32) | 26.47 (9/34)a | 25.00 (14/56)a | 35.14 (52/148)a | 41.82 (69/165)a | 39.63 (65/164)a | 54.35 (125/230)a | 51.34 (115/224)a | |
| 现在吸烟③ | 10.91 (48/440)b | 14.19 (65/458) | 9.44 (56/593)b | 14.82 (99/668)b | 19.23 (130/676)b | 24.64 (152/617)b | 26.18 (217/829)b | 35.68 (360/1 009)b | 33.67 (365/1 084)ab | |
| χ2值 | 16.266 | 2.616 | 26.864 | 33.024 | 32.719 | 30.666 | 35.361 | 64.975 | 33.342 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.270 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 饮酒情况 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 18.23 (138/757) | 18.03 (148/821) | 17.85 (198/1 109) | 25.80 (322/1 248) | 32.28 (492/1 524) | 37.84 (560/1 480) | 39.25 (783/1 995) | 50.77 (1 214/2 391) | 42.70 (1 343/3 145) | |
| 是 | 12.57 (66/525) | 14.00 (70/500) | 11.70 (79/675) | 16.92 (132/780) | 18.00 (146/811) | 24.29 (187/770) | 24.82 (243/979) | 37.74 (471/1 248) | 34.18 (455/1 331) | |
| χ2值 | 7.418 | 3.657 | 12.101 | 21.775 | 53.918 | 41.944 | 60.489 | 56.023 | 28.233 | |
| P值 | 0.006 | 0.056 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 每天睡眠时长(h) | ||||||||||
| <7① | - | - | - | - | 27.05 (79/292) | 36.33 (105/289) | 38.34 (166/433) | 50.99 (309/606) | 48.18 (317/658) | |
| 7~<9② | - | - | - | - | 25.84 (329/1 273) | 31.10 (394/1 267) | 31.83 (579/1 819)a | 44.35 (1 000/2 255)a | 37.44 (1 079/2 882)a | |
| ≥9③ | - | - | - | - | 29.52 (227/769) | 35.73 (248/694) | 39.52 (281/711)b | 48.33 (376/778) | 41.18 (364/884)a | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 3.306 | 5.816 | 16.442 | 10.113 | 26.675 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.191 | 0.055 | <0.001 | 0.006 | <0.001 | |
| 对膳食指南的了解状况 | ||||||||||
| 不了解 | - | - | - | - | 27.05 (576/2 129) | 32.15 (643/2 000) | 33.81 (874/2 585) | 43.32 (1 184/2 733) | 38.60 (1 312/3 399) | |
| 了解 | - | - | - | - | 32.12 (53/165) | 41.77 (99/237) | 39.62 (147/371) | 55.58 (498/896) | 45.14 (488/1 081) | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 2.014 | 8.850 | 4.847 | 40.774 | 14.612 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.156 | 0.003 | 0.028 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
表3 1991—2015年我国不同特征成人高血压治疗率比较〔%(n/N)〕
Table 3 Comparison of hypertension treatment rate among Chinese adults with different characteristics from 1991 to 2015
| 基本特征 | 1991年(n=1 291) | 1993年(n=1 343) | 1997年(n=1 817) | 2000年(n=2 082) | 2004年(n=2 339) | 2006年(n=2 250) | 2009年(n=2 974) | 2011年(n=3 639) | 2015年(n=4 520) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | ||||||||||
| 男 | 12.02 (81/674) | 15.93 (111/697) | 13.80 (134/971) | 17.65 (189/1 071) | 22.04 (268/1 216) | 28.37 (328/1 156) | 29.19 (444/1 521) | 40.82 (749/1 835) | 37.07 (853/2 301) | |
| 女 | 19.94 (123/617) | 16.87 (109/646) | 17.38 (147/846) | 27.40 (277/1 011) | 32.95 (370/1 123) | 38.30 (419/1 094) | 40.06 (582/1 453) | 51.88 (936/1 804) | 44.07 (978/2 219) | |
| χ2值 | 15.177 | 0.220 | 4.421 | 28.467 | 35.584 | 24.971 | 38.811 | 44.814 | 22.988 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.639 | 0.035 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||||||
| 18~44① | 7.32 (24/328) | 4.40 (16/364) | 4.74 (21/443) | 7.88 (36/457) | 10.17 (42/413) | 12.63 (48/380) | 12.39 (57/460) | 18.14 (74/408) | 15.54 (76/489) | |
| 45~59② | 18.32 (74/404)a | 17.46 (70/401)a | 14.87 (87/585)a | 22.13 (162/732)a | 26.81 (233/869)a | 31.03 (247/796)a | 29.79 (331/1 111)a | 43.40 (602/1 387)a | 32.75 (505/1 542)a | |
| ≥60③ | 18.96 (106/559)a | 23.18 (134/578)a | 21.93 (173/789)ab | 30.01 (268/893)ab | 34.34 (363/1 057)ab | 42.09 (452/1 074)ab | 45.47 (638/1 403)ab | 54.72 (1 009/1 844)ab | 50.22 (1 250/2 489)ab | |
| χ2值 | 23.866 | 58.037 | 64.329 | 85.288 | 87.005 | 112.414 | 185.165 | 187.389 | 262.427 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 居住地 | ||||||||||
| 城镇 | 20.37 (110/540) | 22.83 (121/530) | 20.38 (149/731) | 28.71 (234/815) | 34.45 (320/929) | 42.09 (354/841) | 46.62 (482/1 034) | 57.17 (865/1 513) | 50.71 (858/1 692) | |
| 农村 | 12.52 (94/751) | 12.18 (99/813) | 12.15 (132/1 086) | 18.31 (232/1 267) | 22.55 (318/1 410) | 27.89 (393/1 409) | 28.04 (544/1 940) | 38.57 (820/2 126) | 34.41 (973/2 828) | |
| χ2值 | 14.563 | 26.582 | 22.627 | 30.882 | 39.247 | 47.888 | 102.975 | 123.009 | 116.759 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 文化程度 | ||||||||||
| 文盲/小学① | 15.97 (152/952) | 16.45 (149/906) | 15.41 (176/1 142) | 22.52 (266/1 181) | 28.84 (385/1 335) | 34.70 (432/1 245) | 36.99 (590/1 595) | 44.94 (791/1 760) | 42.05 (370/880) | |
| 初中② | 8.81 (17/193) | 13.10 (33/252) | 12.28 (42/342) | 21.67 (91/420) | 22.20 (117/527)c | 25.05 (133/531)c | 27.60 (223/808)c | 43.23 (428/990) | 37.43 (506/1 352) | |
| 高中/中专③ | 24.53 (26/106)d | 18.33 (22/120) | 17.96 (37/206) | 20.62 (60/291) | 29.55 (112/379) | 36.10 (135/374)d | 36.81 (173/470)d | 51.62 (319/618)cd | 40.71 (368/904) | |
| 大专及以上④ | 19.35 (6/31) | 25.93 (7/27) | 22.50 (9/40) | 25.30 (21/83) | 25.00 (23/92) | 46.24 (43/93)d | 40.43 (38/94) | 54.51 (145/266)cd | 43.57 (166/381) | |
| χ2值 | 13.547 | 4.119 | 5.152 | 1.024 | 10.240 | 25.741 | 23.971 | 19.293 | 7.460 | |
| P值 | 0.004 | 0.249 | 0.161 | 0.795 | 0.017 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.059 | |
| 婚姻状态 | ||||||||||
| 未婚① | 4.26 (2/47) | 4.69 (3/64) | 11.11 (11/99) | 20.51 (24/117) | 13.64 (12/88) | 5.26 (2/38) | 4.08 (2/49) | 12.00 (6/50) | 13.79 (8/58) | |
| 已婚② | 16.14 (168/1 041) | 17.22 (183/1 063)a | 15.93 (227/1 425) | 21.65 (349/1 612) | 26.36 (495/1 878)a | 32.25 (607/1 882)a | 33.50 (825/2 463)a | 45.70 (1 378/3 015)a | 39.51 (1 533/3 880)a | |
| 离异/丧偶/分居③ | 16.75 (34/203) | 16.43 (34/207)a | 14.75 (41/278) | 27.84 (71/255) | 35.54 (129/363)ab | 42.11 (136/323)ab | 43.46 (196/451)ab | 52.29 (297/568)ab | 50.00 (285/570)ab | |
| χ2值 | 4.935 | 6.880 | 1.778 | 5.110 | 20.727 | 25.678 | 37.168 | 32.284 | 40.090 | |
| P值 | 0.085 | 0.032 | 0.411 | 0.078 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 体型 | ||||||||||
| 消瘦① | 11.11 (8/72) | 8.20 (5/61) | 8.45 (6/71) | 12.07 (7/58) | 16.88 (13/77) | 35.48 (22/62) | 24.62 (16/65) | 29.09 (16/55) | 27.87 (17/61) | |
| 正常② | 11.89 (86/723) | 12.16 (93/765) | 9.49 (87/917) | 17.38 (163/938) | 21.73 (213/980) | 26.38 (249/944) | 29.64 (372/1 255) | 40.51 (542/1 338) | 34.25 (512/1 495) | |
| 超重③ | 18.54 (66/356)d | 18.84 (68/361)d | 17.25 (94/545)d | 24.73 (181/732)d | 28.40 (236/831)d | 34.23 (266/777)d | 35.35 (380/1 075)d | 49.11 (720/1 466)cd | 40.01 (725/1 812)d | |
| 肥胖④ | 31.40 (38/121)cde | 37.90 (47/124)cde | 27.06 (59/218)cde | 32.10 (104/324)cd | 38.03 (143/376)cde | 42.15 (161/382)d | 41.88 (209/499)cd | 51.22 (379/740)cd | 44.42 (418/941)d | |
| χ2值 | 33.992 | 56.827 | 52.844 | 37.196 | 41.887 | 33.727 | 27.890 | 36.395 | 29.757 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 中心性肥胖 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 15.80 (204/1 291) | 12.31 (119/967) | 12.46 (152/1 220) | 17.79 (217/1 220) | 22.79 (309/1 356) | 28.89 (362/1 253) | 30.88 (470/1 522) | 41.21 (694/1 684) | 36.69 (766/2 088) | |
| 是 | - | 26.86 (101/376) | 21.61 (129/597) | 28.89 (249/862) | 33.47 (329/983) | 38.62 (385/997) | 38.29 (556/1 452) | 50.69 (991/1 955) | 43.79 (1 065/2 432) | |
| χ2值 | - | 41.874 | 25.665 | 35.820 | 32.187 | 23.678 | 18.064 | 32.695 | 23.535 | |
| P值 | - | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 吸烟情况 | ||||||||||
| 否① | 19.07 (152/797) | 17.67 (147/832) | 18.34 (216/1 178) | 26.14 (351/1 343) | 30.16 (456/1 512) | 35.88 (526/1 466) | 37.53 (743/1 980) | 50.00 (1 199/2 398) | 41.59 (1 316/3 164) | |
| 戒烟② | 8.33 (4/48)a | 15.63 (5/32) | 26.47 (9/34)a | 25.00 (14/56)a | 35.14 (52/148)a | 41.82 (69/165)a | 39.63 (65/164)a | 54.35 (125/230)a | 51.34 (115/224)a | |
| 现在吸烟③ | 10.91 (48/440)b | 14.19 (65/458) | 9.44 (56/593)b | 14.82 (99/668)b | 19.23 (130/676)b | 24.64 (152/617)b | 26.18 (217/829)b | 35.68 (360/1 009)b | 33.67 (365/1 084)ab | |
| χ2值 | 16.266 | 2.616 | 26.864 | 33.024 | 32.719 | 30.666 | 35.361 | 64.975 | 33.342 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.270 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 饮酒情况 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 18.23 (138/757) | 18.03 (148/821) | 17.85 (198/1 109) | 25.80 (322/1 248) | 32.28 (492/1 524) | 37.84 (560/1 480) | 39.25 (783/1 995) | 50.77 (1 214/2 391) | 42.70 (1 343/3 145) | |
| 是 | 12.57 (66/525) | 14.00 (70/500) | 11.70 (79/675) | 16.92 (132/780) | 18.00 (146/811) | 24.29 (187/770) | 24.82 (243/979) | 37.74 (471/1 248) | 34.18 (455/1 331) | |
| χ2值 | 7.418 | 3.657 | 12.101 | 21.775 | 53.918 | 41.944 | 60.489 | 56.023 | 28.233 | |
| P值 | 0.006 | 0.056 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 每天睡眠时长(h) | ||||||||||
| <7① | - | - | - | - | 27.05 (79/292) | 36.33 (105/289) | 38.34 (166/433) | 50.99 (309/606) | 48.18 (317/658) | |
| 7~<9② | - | - | - | - | 25.84 (329/1 273) | 31.10 (394/1 267) | 31.83 (579/1 819)a | 44.35 (1 000/2 255)a | 37.44 (1 079/2 882)a | |
| ≥9③ | - | - | - | - | 29.52 (227/769) | 35.73 (248/694) | 39.52 (281/711)b | 48.33 (376/778) | 41.18 (364/884)a | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 3.306 | 5.816 | 16.442 | 10.113 | 26.675 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.191 | 0.055 | <0.001 | 0.006 | <0.001 | |
| 对膳食指南的了解状况 | ||||||||||
| 不了解 | - | - | - | - | 27.05 (576/2 129) | 32.15 (643/2 000) | 33.81 (874/2 585) | 43.32 (1 184/2 733) | 38.60 (1 312/3 399) | |
| 了解 | - | - | - | - | 32.12 (53/165) | 41.77 (99/237) | 39.62 (147/371) | 55.58 (498/896) | 45.14 (488/1 081) | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 2.014 | 8.850 | 4.847 | 40.774 | 14.612 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.156 | 0.003 | 0.028 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 基本特征 | 1991年(n=1 291) | 1993年(n=1 343) | 1997年(n=1 817) | 2000年(n=2 082) | 2004年(n=2 339) | 2006年(n=2 250) | 2009年(n=2 974) | 2011年(n=3 639) | 2015年(n=4 520) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | ||||||||||
| 男 | 5.34 (36/674) | 4.73 (33/697) | 4.33 (42/971) | 6.54 (70/1 071) | 9.70 (118/1 216) | 9.34 (108/1 156) | 9.27 (141/1 521) | 18.20 (334/1 835) | 13.95 (321/2 301) | |
| 女 | 6.48 (40/617) | 5.88 (38/646) | 4.37 (37/846) | 10.48 (106/1 011) | 11.75 (132/1 123) | 12.52 (137/1 094) | 12.32 (179/1 453) | 22.12 (399/1 804) | 15.37 (341/2 219) | |
| χ2值 | 0.758 | 0.882 | 0.003 | 10.478 | 2.571 | 5.859 | 7.195 | 8.672 | 1.814 | |
| P值 | 0.384 | 0.348 | 0.960 | 0.001 | 0.109 | 0.015 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.178 | |
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||||||
| 18~44① | 7.01 (23/328) | 4.67 (17/364) | 3.84 (17/443) | 5.69 (26/457) | 5.81 (24/413) | 4.21 (16/380) | 5.65 (26/460) | 10.54 (43/408) | 5.73 (28/489) | |
| 45~59② | 7.43 (30/404) | 5.99 (24/401) | 4.44 (26/585) | 8.88 (65/732) | 11.16 (97/869)a | 11.68 (93/796)a | 10.44 (116/1 111)a | 19.75 (274/1 387)a | 12.32 (190/1 542)a | |
| ≥60③ | 4.11 (23/559) | 5.19 (30/578) | 4.56 (36/789) | 9.52 (85/893)a | 12.20 (129/1 057)a | 12.66 (136/1 074)a | 12.69 (178/1 403)a | 22.56 (416/1 844)a | 17.84 (444/2 489)ab | |
| χ2值 | 5.646 | 0.677 | 0.378 | 5.993 | 13.041 | 21.468 | 18.043 | 30.219 | 58.081 | |
| P值 | 0.059 | 0.713 | 0.828 | 0.049 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 居住地 | ||||||||||
| 城镇 | 6.30 (34/540) | 5.47 (29/530) | 5.20 (38/731) | 11.53 (94/815) | 13.89 (129/929) | 16.17 (136/841) | 15.18 (157/1 034) | 29.61 (448/1 513) | 22.64 (383/1 692) | |
| 农村 | 5.59 (42/751) | 5.17 (42/813) | 3.78 (41/1 086) | 6.47 (82/1 267) | 8.58 (121/1 410) | 7.74 (109/1 409) | 8.40 (163/1 940) | 13.41 (285/2 126) | 9.87 (279/2 828) | |
| χ2值 | 0.281 | 0.060 | 2.127 | 16.420 | 16.506 | 38.619 | 32.306 | 144.298 | 138.102 | |
| P值 | 0.596 | 0.807 | 0.145 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 文化程度 | ||||||||||
| 文盲/小学① | 4.62 (44/952) | 5.41 (49/906) | 4.64 (53/1 142) | 7.45 (88/1 181) | 11.09 (148/1 335) | 10.76 (134/1 245) | 10.72 (171/1 595) | 15.97 (281/1 760) | 13.41 (118/880) | |
| 初中② | 7.77 (15/193) | 4.76 (12/252) | 3.80 (13/342) | 9.52 (40/420) | 8.54 (45/527) | 7.34 (39/531) | 10.02 (81/808) | 20.91 (207/990)c | 13.61 (184/1 352) | |
| 高中/中专③ | 11.32 (12/106)c | 5.00 (6/120) | 3.40 (7/206) | 9.62 (28/291) | 12.66 (48/379) | 13.10 (49/374)d | 11.70 (55/470) | 26.86 (166/618)cd | 15.93 (144/904) | |
| 大专及以上④ | 16.13 (5/31)c | 3.70 (1/27) | 10.00 (4/40) | 10.84 (9/83) | 9.78 (9/92) | 24.73 (23/93)cde | 13.83 (13/94) | 29.70 (79/266)cd | 22.05 (84/381)cd | |
| χ2值 | 15.401 | 0.309 | 3.870 | 3.290 | 4.390 | 27.070 | 1.809 | 51.837 | 19.163 | |
| P值 | 0.002 | 0.958 | 0.276 | 0.349 | 0.222 | <0.001 | 0.613 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 婚姻状态 | ||||||||||
| 未婚① | 2.13 (1/47) | 3.13 (2/64) | 3.03 (3/99) | 5.98 (7/117) | 5.68 (5/88) | 2.63 (1/38) | 2.04 (1/49) | 12.00 (6/50) | 5.17 (3/58) | |
| 已婚② | 6.15 (64/1 041) | 5.93 (63/1 063) | 4.63 (66/1 425) | 8.75 (141/1 612) | 10.97 (206/1 878) | 11.05 (208/1 882) | 10.64 (262/2 463) | 20.23 (610/3 015) | 14.51 (563/3 880) | |
| 离异/丧偶/分居③ | 5.42 (11/203) | 2.90 (6/207) | 3.60 (10/278) | 9.02 (23/255) | 10.47 (38/363) | 10.84 (35/323) | 12.20 (55/451) | 20.07 (114/568) | 16.49 (94/570) | |
| χ2值 | 1.407 | 3.797 | 1.052 | 1.118 | 2.484 | 2.725 | 4.894 | 2.076 | 5.775 | |
| P值 | 0.495 | 0.150 | 0.591 | 0.572 | 0.289 | 0.256 | 0.087 | 0.354 | 0.056 | |
| 体型 | ||||||||||
| 消瘦① | 2.78 (2/72) | 6.56 (4/61) | 4.23 (3/71) | 12.07 (7/58) | 10.39 (8/77) | 12.90 (8/62) | 6.15 (4/65) | 21.82 (12/55) | 14.75 (9/61) | |
| 正常② | 6.64 (48/723) | 4.58 (35/765) | 3.60 (33/917) | 6.61 (62/938) | 10.00 (98/980) | 10.17 (96/944) | 10.36 (130/1 255) | 19.88 (266/1 338) | 15.45 (231/1 495) | |
| 超重③ | 3.65 (13/356) | 5.82 (21/361) | 5.69 (31/545) | 10.11 (74/732) | 12.03 (100/831) | 11.45 (89/777) | 12.19 (131/1 075) | 21.69 (318/1 466) | 16.56 (300/1 812) | |
| 肥胖④ | 9.92 (12/121)e | 7.26 (9/124) | 5.05 (11/218) | 9.88 (32/324) | 10.37 (39/376) | 12.04 (46/382) | 9.82 (49/499) | 17.70 (131/740) | 12.22 (115/941)e | |
| χ2值 | 8.739 | 2.143 | 3.714 | 8.458 | 2.044 | 1.474 | 4.327 | 5.061 | 9.147 | |
| P值 | 0.033 | 0.543 | 0.294 | 0.037 | 0.563 | 0.688 | 0.228 | 0.167 | 0.027 | |
| 中心性肥胖 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 5.89 (76/1 291) | 4.96 (48/967) | 3.52 (43/1 220) | 6.97 (85/1 220) | 10.03 (136/1 356) | 10.38 (130/1 253) | 10.38 (158/1 522) | 20.67 (348/1 684) | 14.32 (299/2 088) | |
| 是 | - | 6.12 (23/376) | 6.03 (36/597) | 10.56 (91/862) | 11.60 (114/983) | 11.53 (115/997) | 11.16 (162/1 452) | 19.69 (385/1 955) | 14.93 (363/2 432) | |
| χ2值 | - | 0.719 | 6.051 | 8.410 | 1.467 | 0.769 | 0.466 | 0.531 | 0.330 | |
| P值 | - | 0.396 | 0.014 | 0.004 | 0.226 | 0.380 | 0.495 | 0.466 | 0.566 | |
| 吸烟情况 | ||||||||||
| 否① | 6.40 (51/797) | 5.29 (44/832) | 4.84 (57/1 178) | 9.46 (127/1 343) | 11.64 (176/1 512) | 11.46 (168/1 466) | 11.62 (230/1 980) | 21.43 (514/2 398) | 14.60 (462/3 164) | |
| 戒烟② | 2.08 (1/48) | 9.38 (3/32) | 8.82 (3/34) | 8.93 (5/56) | 15.54 (23/148)a | 16.97 (28/165)a | 12.20 (20/164) | 28.70 (66/230)a | 19.20 (43/224) | |
| 现在吸烟③ | 5.45 (24/440) | 5.02 (23/458) | 3.20 (19/593) | 6.44 (43/668) | 7.54 (51/676)b | 7.94 (49/617)b | 8.44 (70/829)b | 15.16 (153/1 009)ab | 14.21 (154/1 084) | |
| χ2值 | 1.770 | 1.130 | 4.156 | 5.264 | 12.071 | 12.294 | 6.493 | 28.487 | 3.834 | |
| P值 | 0.413 | 0.568 | 0.125 | 0.072 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.039 | <0.001 | 0.147 | |
| 饮酒情况 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 6.34 (48/757) | 5.48 (45/821) | 5.14 (57/1 109) | 9.21 (115/1 248) | 12.07 (184/1 524) | 11.89 (176/1 480) | 11.98 (239/1 995) | 21.20 (507/2 391) | 15.17 (477/3 145) | |
| 是 | 5.33 (28/525) | 5.00 (25/500) | 3.11 (21/675) | 7.56 (59/780) | 8.14 (66/811) | 8.96 (69/770) | 8.27 (81/979) | 18.11 (226/1 248) | 13.90 (185/1 331) | |
| χ2值 | 0.564 | 0.143 | 4.130 | 1.667 | 8.575 | 4.484 | 9.394 | 4.885 | 1.192 | |
| P值 | 0.453 | 0.705 | 0.042 | 0.197 | 0.003 | 0.034 | 0.002 | 0.027 | 0.275 | |
| 每天睡眠时长(h) | ||||||||||
| <7① | - | - | - | - | 11.64 (34/292) | 9.69 (28/289) | 9.70 (42/433) | 22.61 (137/606) | 17.02 (112/658) | |
| 7~<9② | - | - | - | - | 10.45 (133/1 273) | 10.73 (136/1 267) | 10.67 (194/1 819) | 20.35 (459/2 255) | 14.95 (431/2 882) | |
| ≥9③ | - | - | - | - | 10.53 (81/769) | 11.67 (81/694) | 11.67 (83/711) | 17.61 (137/778) | 11.31 (100/884)ab | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 0.368 | 0.898 | 1.141 | 5.456 | 11.075 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.832 | 0.638 | 0.565 | 0.065 | 0.004 | |
| 对膳食指南的了解状况 | ||||||||||
| 不了解 | - | - | - | - | 10.71 (228/2 129) | 10.45 (209/2 000) | 10.37 (268/2 585) | 18.00 (492/2 733) | 13.86 (471/3 399) | |
| 了解 | - | - | - | - | 9.70 (16/165) | 14.77 (35/237) | 13.48 (50/371) | 26.90 (241/896) | 17.67 (191/1 081) | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 0.165 | 4.065 | 3.268 | 33.124 | 9.463 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.685 | 0.044 | 0.071 | <0.001 | 0.002 | |
表4 1991—2015年我国不同特征成人高血压控制率比较〔%(n/N)〕
Table 4 Comparison of hypertension control rate among Chinese adults with different characteristics from 1991 to 2015
| 基本特征 | 1991年(n=1 291) | 1993年(n=1 343) | 1997年(n=1 817) | 2000年(n=2 082) | 2004年(n=2 339) | 2006年(n=2 250) | 2009年(n=2 974) | 2011年(n=3 639) | 2015年(n=4 520) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | ||||||||||
| 男 | 5.34 (36/674) | 4.73 (33/697) | 4.33 (42/971) | 6.54 (70/1 071) | 9.70 (118/1 216) | 9.34 (108/1 156) | 9.27 (141/1 521) | 18.20 (334/1 835) | 13.95 (321/2 301) | |
| 女 | 6.48 (40/617) | 5.88 (38/646) | 4.37 (37/846) | 10.48 (106/1 011) | 11.75 (132/1 123) | 12.52 (137/1 094) | 12.32 (179/1 453) | 22.12 (399/1 804) | 15.37 (341/2 219) | |
| χ2值 | 0.758 | 0.882 | 0.003 | 10.478 | 2.571 | 5.859 | 7.195 | 8.672 | 1.814 | |
| P值 | 0.384 | 0.348 | 0.960 | 0.001 | 0.109 | 0.015 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.178 | |
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||||||
| 18~44① | 7.01 (23/328) | 4.67 (17/364) | 3.84 (17/443) | 5.69 (26/457) | 5.81 (24/413) | 4.21 (16/380) | 5.65 (26/460) | 10.54 (43/408) | 5.73 (28/489) | |
| 45~59② | 7.43 (30/404) | 5.99 (24/401) | 4.44 (26/585) | 8.88 (65/732) | 11.16 (97/869)a | 11.68 (93/796)a | 10.44 (116/1 111)a | 19.75 (274/1 387)a | 12.32 (190/1 542)a | |
| ≥60③ | 4.11 (23/559) | 5.19 (30/578) | 4.56 (36/789) | 9.52 (85/893)a | 12.20 (129/1 057)a | 12.66 (136/1 074)a | 12.69 (178/1 403)a | 22.56 (416/1 844)a | 17.84 (444/2 489)ab | |
| χ2值 | 5.646 | 0.677 | 0.378 | 5.993 | 13.041 | 21.468 | 18.043 | 30.219 | 58.081 | |
| P值 | 0.059 | 0.713 | 0.828 | 0.049 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 居住地 | ||||||||||
| 城镇 | 6.30 (34/540) | 5.47 (29/530) | 5.20 (38/731) | 11.53 (94/815) | 13.89 (129/929) | 16.17 (136/841) | 15.18 (157/1 034) | 29.61 (448/1 513) | 22.64 (383/1 692) | |
| 农村 | 5.59 (42/751) | 5.17 (42/813) | 3.78 (41/1 086) | 6.47 (82/1 267) | 8.58 (121/1 410) | 7.74 (109/1 409) | 8.40 (163/1 940) | 13.41 (285/2 126) | 9.87 (279/2 828) | |
| χ2值 | 0.281 | 0.060 | 2.127 | 16.420 | 16.506 | 38.619 | 32.306 | 144.298 | 138.102 | |
| P值 | 0.596 | 0.807 | 0.145 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 文化程度 | ||||||||||
| 文盲/小学① | 4.62 (44/952) | 5.41 (49/906) | 4.64 (53/1 142) | 7.45 (88/1 181) | 11.09 (148/1 335) | 10.76 (134/1 245) | 10.72 (171/1 595) | 15.97 (281/1 760) | 13.41 (118/880) | |
| 初中② | 7.77 (15/193) | 4.76 (12/252) | 3.80 (13/342) | 9.52 (40/420) | 8.54 (45/527) | 7.34 (39/531) | 10.02 (81/808) | 20.91 (207/990)c | 13.61 (184/1 352) | |
| 高中/中专③ | 11.32 (12/106)c | 5.00 (6/120) | 3.40 (7/206) | 9.62 (28/291) | 12.66 (48/379) | 13.10 (49/374)d | 11.70 (55/470) | 26.86 (166/618)cd | 15.93 (144/904) | |
| 大专及以上④ | 16.13 (5/31)c | 3.70 (1/27) | 10.00 (4/40) | 10.84 (9/83) | 9.78 (9/92) | 24.73 (23/93)cde | 13.83 (13/94) | 29.70 (79/266)cd | 22.05 (84/381)cd | |
| χ2值 | 15.401 | 0.309 | 3.870 | 3.290 | 4.390 | 27.070 | 1.809 | 51.837 | 19.163 | |
| P值 | 0.002 | 0.958 | 0.276 | 0.349 | 0.222 | <0.001 | 0.613 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 婚姻状态 | ||||||||||
| 未婚① | 2.13 (1/47) | 3.13 (2/64) | 3.03 (3/99) | 5.98 (7/117) | 5.68 (5/88) | 2.63 (1/38) | 2.04 (1/49) | 12.00 (6/50) | 5.17 (3/58) | |
| 已婚② | 6.15 (64/1 041) | 5.93 (63/1 063) | 4.63 (66/1 425) | 8.75 (141/1 612) | 10.97 (206/1 878) | 11.05 (208/1 882) | 10.64 (262/2 463) | 20.23 (610/3 015) | 14.51 (563/3 880) | |
| 离异/丧偶/分居③ | 5.42 (11/203) | 2.90 (6/207) | 3.60 (10/278) | 9.02 (23/255) | 10.47 (38/363) | 10.84 (35/323) | 12.20 (55/451) | 20.07 (114/568) | 16.49 (94/570) | |
| χ2值 | 1.407 | 3.797 | 1.052 | 1.118 | 2.484 | 2.725 | 4.894 | 2.076 | 5.775 | |
| P值 | 0.495 | 0.150 | 0.591 | 0.572 | 0.289 | 0.256 | 0.087 | 0.354 | 0.056 | |
| 体型 | ||||||||||
| 消瘦① | 2.78 (2/72) | 6.56 (4/61) | 4.23 (3/71) | 12.07 (7/58) | 10.39 (8/77) | 12.90 (8/62) | 6.15 (4/65) | 21.82 (12/55) | 14.75 (9/61) | |
| 正常② | 6.64 (48/723) | 4.58 (35/765) | 3.60 (33/917) | 6.61 (62/938) | 10.00 (98/980) | 10.17 (96/944) | 10.36 (130/1 255) | 19.88 (266/1 338) | 15.45 (231/1 495) | |
| 超重③ | 3.65 (13/356) | 5.82 (21/361) | 5.69 (31/545) | 10.11 (74/732) | 12.03 (100/831) | 11.45 (89/777) | 12.19 (131/1 075) | 21.69 (318/1 466) | 16.56 (300/1 812) | |
| 肥胖④ | 9.92 (12/121)e | 7.26 (9/124) | 5.05 (11/218) | 9.88 (32/324) | 10.37 (39/376) | 12.04 (46/382) | 9.82 (49/499) | 17.70 (131/740) | 12.22 (115/941)e | |
| χ2值 | 8.739 | 2.143 | 3.714 | 8.458 | 2.044 | 1.474 | 4.327 | 5.061 | 9.147 | |
| P值 | 0.033 | 0.543 | 0.294 | 0.037 | 0.563 | 0.688 | 0.228 | 0.167 | 0.027 | |
| 中心性肥胖 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 5.89 (76/1 291) | 4.96 (48/967) | 3.52 (43/1 220) | 6.97 (85/1 220) | 10.03 (136/1 356) | 10.38 (130/1 253) | 10.38 (158/1 522) | 20.67 (348/1 684) | 14.32 (299/2 088) | |
| 是 | - | 6.12 (23/376) | 6.03 (36/597) | 10.56 (91/862) | 11.60 (114/983) | 11.53 (115/997) | 11.16 (162/1 452) | 19.69 (385/1 955) | 14.93 (363/2 432) | |
| χ2值 | - | 0.719 | 6.051 | 8.410 | 1.467 | 0.769 | 0.466 | 0.531 | 0.330 | |
| P值 | - | 0.396 | 0.014 | 0.004 | 0.226 | 0.380 | 0.495 | 0.466 | 0.566 | |
| 吸烟情况 | ||||||||||
| 否① | 6.40 (51/797) | 5.29 (44/832) | 4.84 (57/1 178) | 9.46 (127/1 343) | 11.64 (176/1 512) | 11.46 (168/1 466) | 11.62 (230/1 980) | 21.43 (514/2 398) | 14.60 (462/3 164) | |
| 戒烟② | 2.08 (1/48) | 9.38 (3/32) | 8.82 (3/34) | 8.93 (5/56) | 15.54 (23/148)a | 16.97 (28/165)a | 12.20 (20/164) | 28.70 (66/230)a | 19.20 (43/224) | |
| 现在吸烟③ | 5.45 (24/440) | 5.02 (23/458) | 3.20 (19/593) | 6.44 (43/668) | 7.54 (51/676)b | 7.94 (49/617)b | 8.44 (70/829)b | 15.16 (153/1 009)ab | 14.21 (154/1 084) | |
| χ2值 | 1.770 | 1.130 | 4.156 | 5.264 | 12.071 | 12.294 | 6.493 | 28.487 | 3.834 | |
| P值 | 0.413 | 0.568 | 0.125 | 0.072 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.039 | <0.001 | 0.147 | |
| 饮酒情况 | ||||||||||
| 否 | 6.34 (48/757) | 5.48 (45/821) | 5.14 (57/1 109) | 9.21 (115/1 248) | 12.07 (184/1 524) | 11.89 (176/1 480) | 11.98 (239/1 995) | 21.20 (507/2 391) | 15.17 (477/3 145) | |
| 是 | 5.33 (28/525) | 5.00 (25/500) | 3.11 (21/675) | 7.56 (59/780) | 8.14 (66/811) | 8.96 (69/770) | 8.27 (81/979) | 18.11 (226/1 248) | 13.90 (185/1 331) | |
| χ2值 | 0.564 | 0.143 | 4.130 | 1.667 | 8.575 | 4.484 | 9.394 | 4.885 | 1.192 | |
| P值 | 0.453 | 0.705 | 0.042 | 0.197 | 0.003 | 0.034 | 0.002 | 0.027 | 0.275 | |
| 每天睡眠时长(h) | ||||||||||
| <7① | - | - | - | - | 11.64 (34/292) | 9.69 (28/289) | 9.70 (42/433) | 22.61 (137/606) | 17.02 (112/658) | |
| 7~<9② | - | - | - | - | 10.45 (133/1 273) | 10.73 (136/1 267) | 10.67 (194/1 819) | 20.35 (459/2 255) | 14.95 (431/2 882) | |
| ≥9③ | - | - | - | - | 10.53 (81/769) | 11.67 (81/694) | 11.67 (83/711) | 17.61 (137/778) | 11.31 (100/884)ab | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 0.368 | 0.898 | 1.141 | 5.456 | 11.075 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.832 | 0.638 | 0.565 | 0.065 | 0.004 | |
| 对膳食指南的了解状况 | ||||||||||
| 不了解 | - | - | - | - | 10.71 (228/2 129) | 10.45 (209/2 000) | 10.37 (268/2 585) | 18.00 (492/2 733) | 13.86 (471/3 399) | |
| 了解 | - | - | - | - | 9.70 (16/165) | 14.77 (35/237) | 13.48 (50/371) | 26.90 (241/896) | 17.67 (191/1 081) | |
| χ2值 | - | - | - | - | 0.165 | 4.065 | 3.268 | 33.124 | 9.463 | |
| P值 | - | - | - | - | 0.685 | 0.044 | 0.071 | <0.001 | 0.002 | |
| [1] | BANERJEE S, MUKHERJEE T K, BASU S. Prevalence,awareness,and control of hypertension in the slums of Kolkata[J]. Indian Heart J,2016,68(3):286-294. |
| [2] | FENG Y J, WANG H C, LI Y C,et al. Hypertension screening and follow-up management by primary health care system among Chinese population aged 35 years and above[J]. Biomed Environ Sci,2015,28(5):330-340. DOI:10.3967/bes2015.047. |
| [3] | RUBINSTEIN A L, IRAZOLA V E, CALANDRELLI M,et al. Prevalence,awareness,treatment,and control of hypertension in the Southern Cone of Latin America[J]. Am J Hypertens,2016,29(12):1343-1352. DOI:10.1093/ajh/hpw092. |
| [4] | MENENDEZ E, DELGADO E, FERNANDEZ-VEGA F,et al. Prevalence,diagnosis,treatment,and control of hypertension in Spain. Results of the diabetes study[J]. Rev Esp Cardiol,2016,69(6):572-578. DOI:10.1016/j.rec.2015.11.034. |
| [5] | ABDUL-RAZAK S, DAHER A M, RAMLI A S,et al. Prevalence,awareness,treatment,control and socio demographic determinants of hypertension in Malaysian adults[J]. BMC Public Health,2016,16:351. DOI:10.1186/s12889-016-3008-y. |
| [6] | KHOSRAVI A, EMAMIAN M H, SHARIATI M,et al. The prevalence of pre-hypertension and hypertension in an Iranian urban population[J]. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev,2014,21(2):127-135. DOI:10.1007/s40292-013-0035-y. |
| [7] | KJELDSEN S E. Hypertension and cardiovascular risk:general aspects[J]. Pharmacol Res,2018,129:95-99. DOI:10.1016/j.phrs.2017.11.003. |
| [8] | 吕燕宇,张兵,王惠君,等. 1991—2015年我国9省成年农民高血压患病率,知晓率和治疗率的变化趋势及人口经济学差异[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2020,41(4):498-503. |
| [9] | LU J, LU Y, WANG X,et al. Prevalence,awareness,treatment,and control of hypertension in China:data from 1.7 million adults in a population-based screening study(China PEACE Million Persons Project)[J]. Lancet,2017,390(10112):2549-2558. DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32478-9. |
| [10] | 洪怡,张卫珍,张华,等. 上海市杨浦区高血压的患病率、知晓率及治疗和控制状况[J]. 中国临床医学,2015,22(1):99-101. |
| [11] | MILLS K T, BUNDY J D, KELLY T N,et al. Global disparities of hypertension prevalence and control:a systematic analysis of population-based studies from 90 countries[J]. Circulation,2016,134(6):441-450. |
| [12] | GUPTA R. Convergence in urban-rural prevalence of hypertension in India[J]. J Hum Hypertens,2016,30(2):79-82. DOI:10.1038/jhh.2015.48. |
| [13] | 孙爱丽,李国菊,魏涛. 戒烟与高血压发病风险的荟萃分析[J]. 中华医学杂志,2019,99(26):2068-2072. |
| [14] | HAN B, CHEN W Z, LI Y C,et al. Sleep and hypertension[J]. Sleep Breath,2020,24(1):351-356. DOI:10.1007/s11325-019-01907-2. |
| [15] | 赵健,张伋,苏畅,等. 2015年中国15个省份城乡成年男性吸烟与睡眠时间关联性分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2021,42(2):284-290. |
| [16] | 刘彩,何强,王薇. 天津市居民服药依从性现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中国卫生事业管理,2016,33(1):42-45. |
| [17] | 范国辉,王增武,张林峰,等. 2013年北方四区县农村高血压患病率、知晓率、治疗率和控制率调查[J]. 中华医学杂志,2015,95(8):616-620. |
| [18] | DING L, XU Y, WANG L M,et al. Smoking and its relation to metabolic status among Chinese adults:analysis of a nationwide survey[J]. Biomed Environ Sci,2016,29(9):619-627. |
| [19] | SACKS F M, SVETKEY L P, VOLLMER W M,et al. Effects on blood pressure of reduced dietary sodium and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension(DASH) diet. DASH-sodium collaborative research group[J]. N Engl J Med,2001,344(1):3-10. |
| [20] | XU L, MENG Q, HE S,et al. The effects of health education on patients with hypertension in China:a meta-analysis[J]. Health Educ J,2014,73(2):137-149. |
| [21] | NOHR E A, LIEW Z. How to investigate and adjust for selection bias in cohort studies[J]. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand,2018,97(4):407-416. DOI:10.1111/aogs.13319. |
| [1] | 刘芹, 程敏, 江凤琼, 李小玉. 中国儿童青少年遗尿症患病率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(06): 763-770. |
| [2] | 方湘, 宋海齐, 廖晓阳, 刘力滴, 张鹏, 贾禹, 杨梓钰, 杨荣, 刘如辉. 中国妊娠期高血压疾病的管理建议:基于《2023年澳大利亚和新西兰产科医学协会妊娠期高血压疾病指南摘要》[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(06): 649-654. |
| [3] | 张萍淑, 薛晶, 邢爱君, 王连辉, 马倩, 符永山, 元小冬. 急性后循环缺血性脑卒中患者睡眠状态变化与预后影响因素的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(05): 548-553. |
| [4] | 朱露, 艾军, 廖生武, 黄淑婷, 龚妮容, 孔耀中, 刘德慧, 窦献蕊, 张广清. 预后营养指数对腹膜透析患者心血管疾病死亡的影响:一项多中心回顾性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(05): 568-574. |
| [5] | 张家鸣, 王欣宇, 王道荣, 孙晓芳. 17~45岁肥胖门诊患者的6分钟步行试验距离参考方程研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(03): 330-334. |
| [6] | 马晓燕, 崔恩慈, 薛群, 刘荣, 张学武, 王浅, 王德斌, 沈兴蓉. 农村地区高血压患者服药情况及影响因素研究:基于家庭医生签约服务[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(03): 365-371. |
| [7] | 姜申, 吴静, 周佳丽, 蒋德楠, 孙炜迪, 程思清, 朱思雨, 侯乐莹, 宋培歌. 童年逆境与成年期高血压患病的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(03): 358-364. |
| [8] | 吕垚, 周伊恒, 刘力滴, 杨荣, 张鹏, 朱雅文, 代华, 廖晓阳, 雷弋, 杨梓钰. 美国肥胖医学协会《肥胖和高血压临床实践声明》解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(03): 272-279. |
| [9] | 高焱, 杨淑显, 范雷, 常亮, 高莉, 张寒雪, 李卉, 康锴. 老年人群骨关节疾病流行特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(03): 280-284. |
| [10] | 齐鸣瑞, 王文娟, 田利民. 中国西北地区老年高血压人群的健康相关生命质量研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 199-207. |
| [11] | 卢静, 孙国珍, 王洁, 高敏, 于甜栖, 孙姝怡, 王琴, 温高芹. 慢性心力衰竭患者社会衰弱现状及其影响因素可解释性分析研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 220-227. |
| [12] | 刘庆平, 柯居中, 宋家慧, 高娇娇, 李智韬, 王小楠, 邱桦, 周弋, 阮晓楠, 吴抗. 糖尿病发病时间趋势及其与中国内脏脂肪指数的关系:一项前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 183-192. |
| [13] | 舒婷, 兰志鹏, 巫霞, 罗映娟, 杨柳. 宫颈癌筛查妇女高危型人乳头瘤病毒感染现状及影响因素研究:基于成都市45万人群[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 213-219. |
| [14] | 张高钰, 王子涵, 高雪菲, 张瑾, 代天顾, 何清, 樊佳溶, 黄力, 李琳. 基于三酰甘油葡萄糖指数联合血管弹性指标的绝经后女性高血压患者冠心病发生风险模型开发研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(01): 39-46. |
| [15] | 安然, 唐昕, 齐士格, 王志会, 崔露, 张晗, 郭浩岩. 社区老年人照护需求现状及影响因素研究:基于三省的基线调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(01): 59-64. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





