

Chinese General Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (32): 4082-4088.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0615
• Original Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-09-13
Revised:2025-04-10
Published:2025-11-15
Online:2025-09-23
Contact:
MA Liangkun, XUAN Lei
通讯作者:
马良坤, 宣磊
作者简介:作者贡献:
李赞梅提出研究思路、设计研究方案、负责论文撰写及修订;李姣负责研究过程实施管理;杨林负责研究方案讨论与论文修改;姚伟伟负责数据收集与整理、统计学分析;马良坤、宣磊负责可行性分析、文章质量控制及审查。
基金资助:CLC Number:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0615
| 特征 | 构成比 | 特征 | 构成比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 家庭月收入 | ||
| 15~24 | 16(6.0) | ≤5 000元/月 | 37(14.0) |
| 25~29 | 83(31.4) | 5 001~10 000元/月 | 97(36.7) |
| 30~34 | 104(39.4) | 10 001~20 000元/月 | 62(23.5) |
| 35~39 | 52(19.7) | 20 001~50 000元/月 | 55(20.8) |
| 40~49 | 9(3.4) | >50 000元/月 | 13(4.9) |
| 孕产阶段 | 自评健康状况 | ||
| 孕早期(0~12周) | 64(24.2) | 一般 | 103(39.1) |
| 孕中期(13~27周) | 63(23.9) | 良好 | 161(60.9) |
| 孕晚期(≥28周) | 72(27.3) | 不良孕产史 | |
| 哺乳期 | 60(22.7) | 有 | 61(23.1) |
| 其他(哺乳期再次妊娠) | 5(1.9) | 无 | 203(76.9) |
| 受教育程度 | 所在省/自治区/直辖市 | ||
| 初中 | 35(13.3) | 福建省 | 83(31.4) |
| 高中 | 26(9.8) | 北京市 | 59(22.3) |
| 大专/本科 | 161(61.0) | 广东省 | 43(16.3) |
| 硕士及以上 | 42(15.9) | 四川省 | 39(14.8) |
| 就业状态 | 其他 | 40(15.1) | |
| 就业 | 182(69.0) | ||
| 非就业 | 82(31.0) | ||
Table 1 General information of the pregnant and postpartum women
| 特征 | 构成比 | 特征 | 构成比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 家庭月收入 | ||
| 15~24 | 16(6.0) | ≤5 000元/月 | 37(14.0) |
| 25~29 | 83(31.4) | 5 001~10 000元/月 | 97(36.7) |
| 30~34 | 104(39.4) | 10 001~20 000元/月 | 62(23.5) |
| 35~39 | 52(19.7) | 20 001~50 000元/月 | 55(20.8) |
| 40~49 | 9(3.4) | >50 000元/月 | 13(4.9) |
| 孕产阶段 | 自评健康状况 | ||
| 孕早期(0~12周) | 64(24.2) | 一般 | 103(39.1) |
| 孕中期(13~27周) | 63(23.9) | 良好 | 161(60.9) |
| 孕晚期(≥28周) | 72(27.3) | 不良孕产史 | |
| 哺乳期 | 60(22.7) | 有 | 61(23.1) |
| 其他(哺乳期再次妊娠) | 5(1.9) | 无 | 203(76.9) |
| 受教育程度 | 所在省/自治区/直辖市 | ||
| 初中 | 35(13.3) | 福建省 | 83(31.4) |
| 高中 | 26(9.8) | 北京市 | 59(22.3) |
| 大专/本科 | 161(61.0) | 广东省 | 43(16.3) |
| 硕士及以上 | 42(15.9) | 四川省 | 39(14.8) |
| 就业状态 | 其他 | 40(15.1) | |
| 就业 | 182(69.0) | ||
| 非就业 | 82(31.0) | ||
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 孕产阶段 | -0.656 | 0.151 | 18.891 | <0.001 | 0.519(0.386~0.697) |
| 既往中医药使用史 | 2.241 | 0.376 | 35.542 | <0.001 | 9.399(4.500~19.633) |
| 年龄 | 0.019 | 0.175 | 0.011 | 0.915 | 1.019(0.722~1.437) |
| 受教育程度 | -0.052 | 0.208 | 0.063 | 0.802 | 0.949(0.631~1.428) |
| 就业状态 | -0.443 | 0.395 | 1.261 | 0.262 | 0.642(0.296~1.392) |
| 家庭月收入 | -0.232 | 0.165 | 1.990 | 0.158 | 0.793(0.574~1.095) |
| 自评健康状况 | 0.226 | 0.243 | 0.861 | 0.354 | 1.253(0.778~2.019) |
| 不良孕产史 | -0.636 | 0.373 | 2.914 | 0.088 | 0.529(0.255~1.099) |
Table 2 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of influencing factors for TCM use among pregnant and postpartum women
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 孕产阶段 | -0.656 | 0.151 | 18.891 | <0.001 | 0.519(0.386~0.697) |
| 既往中医药使用史 | 2.241 | 0.376 | 35.542 | <0.001 | 9.399(4.500~19.633) |
| 年龄 | 0.019 | 0.175 | 0.011 | 0.915 | 1.019(0.722~1.437) |
| 受教育程度 | -0.052 | 0.208 | 0.063 | 0.802 | 0.949(0.631~1.428) |
| 就业状态 | -0.443 | 0.395 | 1.261 | 0.262 | 0.642(0.296~1.392) |
| 家庭月收入 | -0.232 | 0.165 | 1.990 | 0.158 | 0.793(0.574~1.095) |
| 自评健康状况 | 0.226 | 0.243 | 0.861 | 0.354 | 1.253(0.778~2.019) |
| 不良孕产史 | -0.636 | 0.373 | 2.914 | 0.088 | 0.529(0.255~1.099) |
| 路径关系 | β | SE | CR | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主观规范→行为意向 | 0.435 | 0.049 | 5.259 | <0.001 |
| 感知行为控制→行为意向 | 0.294 | 0.055 | 3.299 | <0.001 |
| 既往中医药使用经历→行为意向 | 0.240 | 0.080 | 3.431 | <0.001 |
| 态度→行为意向 | 0.304 | 0.042 | 3.466 | <0.001 |
| 主观规范→态度 | 0.459 | 0.050 | 6.012 | <0.001 |
| 感知行为控制→态度 | 0.591 | 0.056 | 7.233 | <0.001 |
| 既往中医药使用经历→态度 | 0.306 | 0.046 | 4.411 | <0.001 |
Table 3 Structural equation model analysis results on influencing factors of pregnant and breastfeeding women's intention to use TCM
| 路径关系 | β | SE | CR | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主观规范→行为意向 | 0.435 | 0.049 | 5.259 | <0.001 |
| 感知行为控制→行为意向 | 0.294 | 0.055 | 3.299 | <0.001 |
| 既往中医药使用经历→行为意向 | 0.240 | 0.080 | 3.431 | <0.001 |
| 态度→行为意向 | 0.304 | 0.042 | 3.466 | <0.001 |
| 主观规范→态度 | 0.459 | 0.050 | 6.012 | <0.001 |
| 感知行为控制→态度 | 0.591 | 0.056 | 7.233 | <0.001 |
| 既往中医药使用经历→态度 | 0.306 | 0.046 | 4.411 | <0.001 |
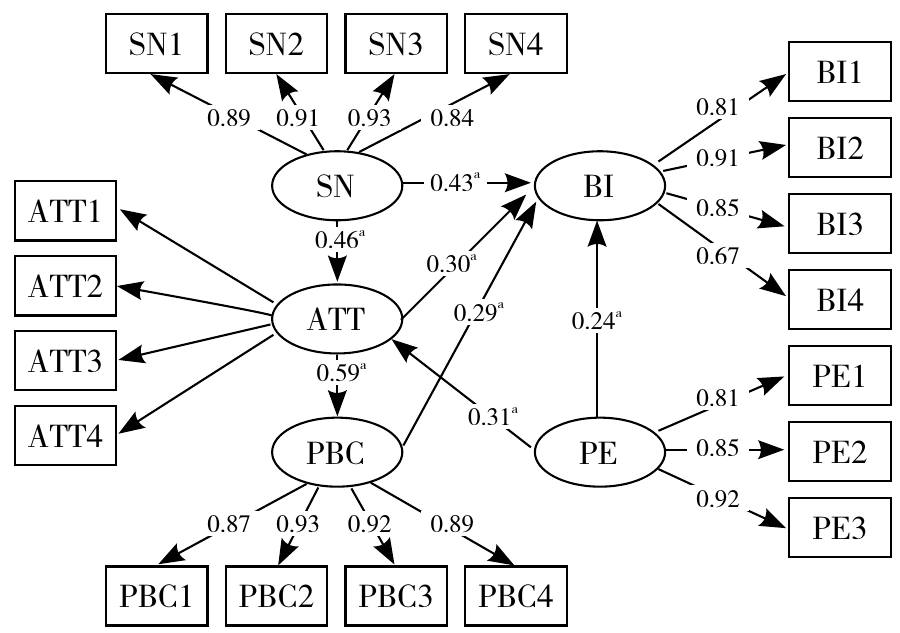
Figure 2 The results of structural equation model on influencing factors of pregnant and breastfeeding women's intention to use traditional Chinese medicine
| [1] |
中共中央 国务院关于促进中医药传承创新发展的意见[EB/OL].(2019-10-20)[2024-07-11].
|
| [2] |
王景尚,刘晓巍,王昕,等. 中医药治疗产科领域临床优势病种的探讨[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(20):206-218. DOI:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20212091.
|
| [3] |
国家中医药管理局.关于印发推进妇幼健康领域中医药工作实施方案(2021-2025年)的通知[EB/OL]. [2024-07-15].
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
沈晓妍,谢小芳,沈浩,等. 妊娠期中药应用安全性评价的思路与策略[J]. 医药导报,2023,42(6):858-862. DOI:10.3870/j.issn.1004-0781.2023.06.013.
|
| [8] |
潘艳婷. 三甲医院产妇对产后中医护理服务认知度和需求的调查[J]. 中医药管理杂志,2022,30(17):62-64. DOI:10.16690/j.cnki.1007-9203.2022.17.015.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
香港妇女孕产期401例中医养生方法调查研究[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2022.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
朱婷婷,何源. 近十年国内外计划行为理论应用现状及热点分析[J]. 南京医科大学学报(社会科学版),2020,20(1):77-83.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
北京市卫生健康委员会 北京市中医管理局 关于印发北京市妇幼健康领域中医药"升降浮沉"工程实施方案的通知[EB/OL]. [2024-11-25].
|
| [26] |
福建省卫生健康委员会. 福建省卫生健康委员会关于开展健康福建行动中医药健康促进专项活动的通知[EB/OL]. [2024-11-27].
|
| [27] |
国家卫生健康委办公厅,国家中医药局综合司. 关于妇幼健康领域中医药工作推进情况的通报[EB/OL]. [2024-11-25].
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
新华社. 国务院办公厅印发《"十四五"中医药发展规划》:强化中医药特色人才队伍建设[J]. 中国人才,2022(4):6.
|
| [1] | ZHAO Ziqi, LIU Mingyue, WANG Nan, LUO Zhenghao, CHEN Xinyang, LI Zheng, ZHANG Shangmingzhu, ZHANG Haoruo, CHEN Jiaqi, ZHENG Yizhan, ZHANG Xiujun, WU Jianhui. The Relationship between Lifestyle Factors and Depression: a Cross-sectional Study of Community Populations [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(33): 4148-4158. |
| [2] | ZHAO Ziqi, CHEN Jiaqi, ZHU Hongmin, ZHENG Yizhan, WANG Huan, HU Jiaqi, LIU Mingyue, WANG Nan, LUO Zhenghao, CHEN Xinyang, LI Zheng, ZHANG Shangmingzhu, ZHANG Haoruo, XUAN Xiaoqing, WU Jianhui, ZHANG Xiujun. A Cross-sectional Study on the Relationship between Social Support and Depression in Community Population [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(29): 3660-3667. |
| [3] | ZHAN Yang, ZHAO Ruyi, SUN Hongling, JIANG Nan, NI Zijun, ZHU Lingli. Investigation on the Status Quo of "Internet +" Home Care Quality in 60 Medical Institutions [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(28): 3548-3553. |
| [4] | ZHANG Ruimin, DONG Zheyi, LI Shuang, WANG Qian, CHEN Xiangmei. Traditional Chinese Medicine Factors Associated with Diabetic Nephropathy Diagnosed by Renal Biopsy [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3307-3313. |
| [5] | FAN Boyang, ZHANG Yu, SUN Wenning, ZHANG Huifang, WANG Yingjie, ZHANG Ao, ZHAO Yang, WANG Haipeng. Study of Behavioral Intention and Influencing Factors of Integrated Medical and Preventive Care Provided by Grassroots Doctors for Patients with Chronic Diseases [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3144-3150. |
| [6] | ZHANG Luyi, YU Ruihong, WANG Qi, ZHANG Xiaoyu, LI Xiang, WANG Zhongxuan, ZHU Dongshan. The Impact of Circadian Syndrome and Metabolic Syndrome on Subjective and Objective Cognitive Functions: a Cross-sectional Analysis from the Pingyin Cohort [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(20): 2481-2490. |
| [7] | HAN Zheng, SUN Meng, FU Fanglin, PAN Yaojia, WANG Weiqiang. A Study on the Relationship between the Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity in Individuals Aged 50 and Above [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(18): 2278-2284. |
| [8] | FU Chunying, YU Ruihong, WANG Qi, LI Meiling, WANG Xiaoyi, ZHU Dongshan. The Association between Female Reproductive Factors and Subjective and Objective Cognitive Function: a Cross-sectional Analysis from the Pingyin Cohort [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(08): 980-988. |
| [9] | SUN Zhenzhen, CUI Qian, LOU Qingqing, CHEN Xiaodong, FANG Dan, YAO Ping, YUAN Xiaodan. Effect of Physical Activities on the Carotid Intima-media Thickening in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(06): 697-704. |
| [10] | LI Chengcheng, ZHOU Shangcheng, HE Kaiyue, LIU Ailing, LIANG Shanshan, GAO Jing, ZHONG Ailin. A Study of Space Allocation and Optimization of Traditional Chinese Medical Institutions Based on Medical Service Radius: a Case Study of Zengcheng District, Guangzhou City [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(02): 234-241. |
| [11] | SI Jianping, WANG Xianju, GUO Qing. Performance Evaluation and Obstacle Factor Diagnosis of Community Embedded Integrated Medical and Nursing Care with Characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(34): 4327-4335. |
| [12] | ZHANG Qiang, TANG Min, GUANG Yajie, LIU Dan, ZHAO Xueyan, ZHAO Yuanyuan, ZHANG Lin, NUERBAHETI. Analysis of the Current Status of Atrial Fibrillation Epidemiological Survey in Shihezi Area of Xinjiang Corps [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(33): 4162-4167. |
| [13] | WU Qingyue, CHEN Xiaoling, ZHOU Xunqiong, YANG Jingyuan, ZHOU Quanxiang, YANG Xing. Study on the Relationship between Inter-arm Blood Pressure Difference and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Rural Elderly People [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(29): 3616-3622. |
| [14] | LIU Xin, WEI Yanan, LIU Jie, WANG Jingtong. Research of Influencing Factors for Physical Impairment Combined with Cognitive Impairment in the Elderly [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(26): 3281-3288. |
| [15] | CAO Deli, ZHOU Wei, ZHANG Xiufang, JIANG Lin, BAO Xing, SHEN Qinghua. The Willingness of General Practitioners to Participate in Graded Diagnosis and Treatment Based on the Fusion Model of TPB and TAM [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(25): 3108-3114. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||