

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (03): 354-362.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.086
Special Issue: 消化系统疾病最新文章合辑
• Evidence-based Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Urease Breath Test and Stool Antigen Test Diagnose Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Patients with Bleeding Peptic Ulcer:a Meta-analysis
1.Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine,Guangzhou 510405,China
2.The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine,Guangzhou 510405,China
*Corresponding author:CHEN Bin,Professor,Chief physician;E-mail:ddwchen@qq.com
LIAO Guibin and GONG Jiaqian are co-first authors
Received:2021-07-02
Revised:2021-09-28
Published:2022-01-20
Online:2021-12-29
通讯作者:
陈斌
基金资助:CLC Number:
LIAO Guibin, GONG Jiaqian, ZHAO Lina, HOU Jiangtao, ZHENG Hongming, LI Yiting, WU Yuan, CHEN Bin.
Urease Breath Test and Stool Antigen Test Diagnose Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Patients with Bleeding Peptic Ulcer:a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(03): 354-362.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.086
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 地区 | 样本量(例) | NSAIDs使用率〔n(%)〕 | H.pylori感染判定标准 | 是否纳入应用PPI或抗生素患者 | 平均取样时间 | H.pylori感染率〔n(%)〕 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TU[ | 1999 | 中国 | 77 | 0 | ①阳性或②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 77(100.0) | 93.5 | - |
| LóPEZ PEÑAS[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 32 | 18(56.3) | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 23(71.9) | 87.0 | 100.0 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 78 | 44(56.4) | ②阳性或④和⑥均阳性 | 是 | <24 h | 68(87.2) | 91.3 | 77.8 |
| CHUNG[ | 2001 | 韩国 | 32 | 0 | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 32(100.0) | 100.0 | - |
| CHUNG[ | 2001 | 韩国 | 32 | 0 | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第7天 | 32(100.0) | 90.6 | - |
| WILDNER-CHRISTENSEN[ | 2002 | 丹麦 | 95 | 70(73.7) | ②阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 44(46.3) | 86.4 | 96.1 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2003 | 西班牙 | 68 | 41(60.3) | ②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 是 | - | 59(86.8) | 93.1 | 87.5 |
| WINIARSKI[ | 2003 | 波兰 | 81 | - | ⑥阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 64(79.0) | 98.4 | 100.0 |
| LIAO[ | 2003 | 中国 | 57 | 0 | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 46(80.7) | 100.0 | 81.8 |
| LO[ | 2005 | 中国 | 55 | 26(47.3) | ①阳性或②③④⑥中至少有3项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 35(63.6) | 94.3 | 85.0 |
| 张厚德[ | 1997 | 中国 | 51 | - | ②和④均阳性 | - | <96 h | 42(82.4) | 73.8 | 100.0 |
| 林勇[ | 2004 | 中国 | 40 | - | ③和⑥均阳性 | 否 | - | 24(60.0) | 37.5 | 87.5 |
| 李舜[ | 2005 | 中国 | 31 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | - | 31(100.0) | 61.3 | - |
| 王醒[ | 2019 | 中国 | 116 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | 第5天 | 56(48.3) | 51.8 | 86.7 |
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the UBT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 地区 | 样本量(例) | NSAIDs使用率〔n(%)〕 | H.pylori感染判定标准 | 是否纳入应用PPI或抗生素患者 | 平均取样时间 | H.pylori感染率〔n(%)〕 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TU[ | 1999 | 中国 | 77 | 0 | ①阳性或②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 77(100.0) | 93.5 | - |
| LóPEZ PEÑAS[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 32 | 18(56.3) | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 23(71.9) | 87.0 | 100.0 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 78 | 44(56.4) | ②阳性或④和⑥均阳性 | 是 | <24 h | 68(87.2) | 91.3 | 77.8 |
| CHUNG[ | 2001 | 韩国 | 32 | 0 | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 32(100.0) | 100.0 | - |
| CHUNG[ | 2001 | 韩国 | 32 | 0 | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第7天 | 32(100.0) | 90.6 | - |
| WILDNER-CHRISTENSEN[ | 2002 | 丹麦 | 95 | 70(73.7) | ②阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 44(46.3) | 86.4 | 96.1 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2003 | 西班牙 | 68 | 41(60.3) | ②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 是 | - | 59(86.8) | 93.1 | 87.5 |
| WINIARSKI[ | 2003 | 波兰 | 81 | - | ⑥阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 64(79.0) | 98.4 | 100.0 |
| LIAO[ | 2003 | 中国 | 57 | 0 | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 46(80.7) | 100.0 | 81.8 |
| LO[ | 2005 | 中国 | 55 | 26(47.3) | ①阳性或②③④⑥中至少有3项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 35(63.6) | 94.3 | 85.0 |
| 张厚德[ | 1997 | 中国 | 51 | - | ②和④均阳性 | - | <96 h | 42(82.4) | 73.8 | 100.0 |
| 林勇[ | 2004 | 中国 | 40 | - | ③和⑥均阳性 | 否 | - | 24(60.0) | 37.5 | 87.5 |
| 李舜[ | 2005 | 中国 | 31 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | - | 31(100.0) | 61.3 | - |
| 王醒[ | 2019 | 中国 | 116 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | 第5天 | 56(48.3) | 51.8 | 86.7 |
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 地区 | 样本量(例) | NSAIDs使用率〔n(%)〕 | H.pylori感染判定标准 | 是否纳入应用PPI或抗生素患者 | 平均取样时间 | 试剂盒 | H.pylori感染率〔n(%)〕 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LóPEZ PEÑAS[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 32 | 18(56.3) | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 23(71.9) | 95.7 | 33.3 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2003 | 西班牙 | 68 | 41(60.3) | ②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 是 | <48 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 59(86.8) | 96.6 | 33.3 |
| PEITZ[ | 2003 | 德国 | 114 | 55(48.2) | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 是 | <24h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 56(49.1) | 83.9 | 89.7 |
| PEITZ[ | 2003 | 德国 | 109 | - | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 是 | 第2天 | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 53(48.6) | 79.2 | 87.5 |
| VAN LEERDAM[ | 2003 | 荷兰 | 36 | 20(55.6) | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 否 | - | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 15(41.7) | 100.0 | 52.4 |
| LIN[ | 2004 | 中国 | 93 | - | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 否 | <72 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 47(50.5) | 81.6 | 68.2 |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | 单克隆酶免疫试验 | 34(100.0) | 94.1 | - |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 34(100.0) | 73.5 | - |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | HpSA免疫快检卡 | 34(100.0) | 58.8 | - |
| 于涛[ | 2006 | 中国 | 15 | - | ②③⑤中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | HpSA免疫快检卡 | 10(66.7) | 100.0 | 80.0 |
| 王醒[ | 2019 | 中国 | 116 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | 第5天 | 单克隆免疫层析试验 | 56(48.3) | 91.1 | 83.3 |
Table 2 Basic characteristics of the SAT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 地区 | 样本量(例) | NSAIDs使用率〔n(%)〕 | H.pylori感染判定标准 | 是否纳入应用PPI或抗生素患者 | 平均取样时间 | 试剂盒 | H.pylori感染率〔n(%)〕 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LóPEZ PEÑAS[ | 2001 | 西班牙 | 32 | 18(56.3) | ②③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 23(71.9) | 95.7 | 33.3 |
| GRIÑó[ | 2003 | 西班牙 | 68 | 41(60.3) | ②阳性或③④⑥中至少有2项阳性 | 是 | <48 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 59(86.8) | 96.6 | 33.3 |
| PEITZ[ | 2003 | 德国 | 114 | 55(48.2) | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 是 | <24h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 56(49.1) | 83.9 | 89.7 |
| PEITZ[ | 2003 | 德国 | 109 | - | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 是 | 第2天 | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 53(48.6) | 79.2 | 87.5 |
| VAN LEERDAM[ | 2003 | 荷兰 | 36 | 20(55.6) | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 否 | - | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 15(41.7) | 100.0 | 52.4 |
| LIN[ | 2004 | 中国 | 93 | - | ①阳性或②和③均阳性 | 否 | <72 h | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 47(50.5) | 81.6 | 68.2 |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | 单克隆酶免疫试验 | 34(100.0) | 94.1 | - |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | 多克隆酶免疫试验 | 34(100.0) | 73.5 | - |
| GISBERT[ | 2004 | 西班牙 | 34 | 22(64.7) | ②③④中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | 第2.8天 | HpSA免疫快检卡 | 34(100.0) | 58.8 | - |
| 于涛[ | 2006 | 中国 | 15 | - | ②③⑤中至少有2项阳性 | 否 | <24 h | HpSA免疫快检卡 | 10(66.7) | 100.0 | 80.0 |
| 王醒[ | 2019 | 中国 | 116 | - | ②阳性 | 否 | 第5天 | 单克隆免疫层析试验 | 56(48.3) | 91.1 | 83.3 |
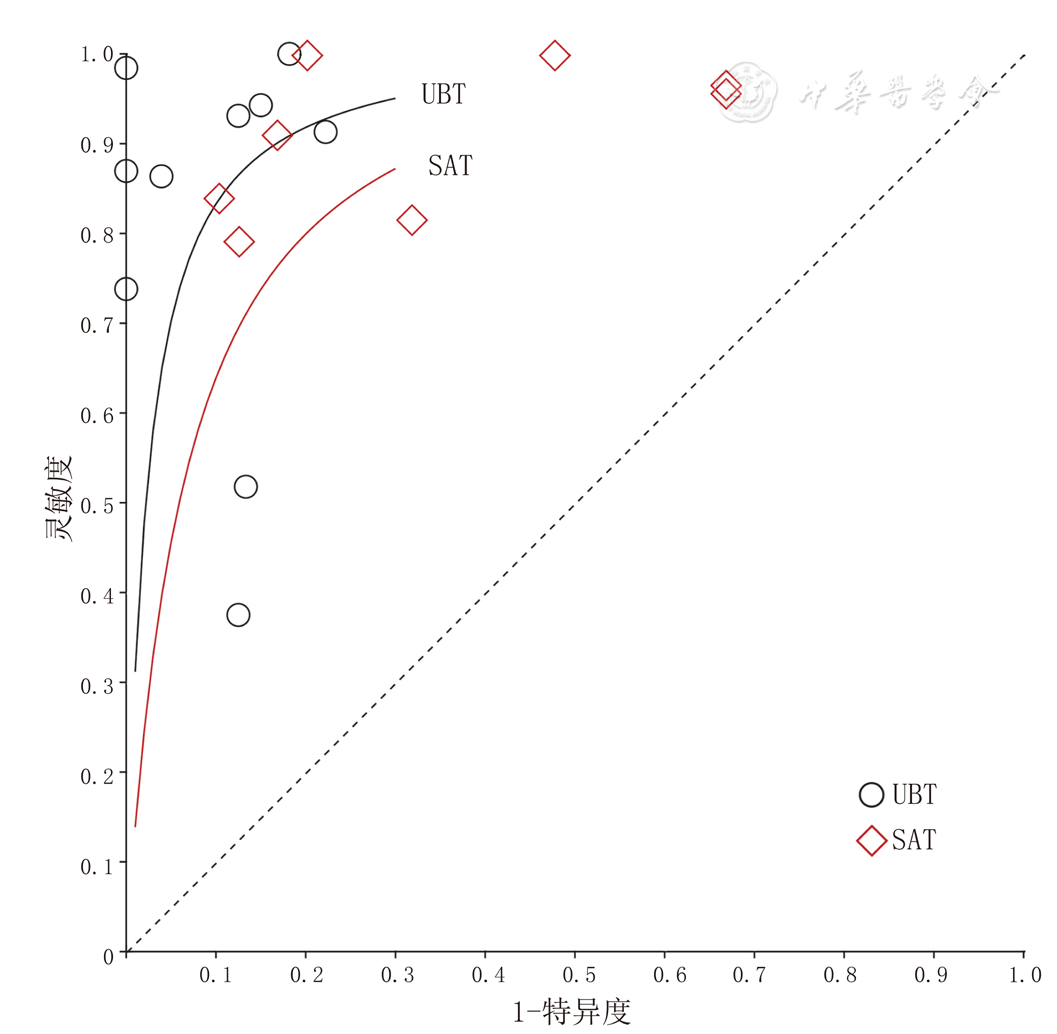
Figure 9 Comprehensive receiver operating characteristic curve of the UBT and SAT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
| 检查方式 | 亚组 | 研究数量(项) | 合并灵敏度 | 合并特异度 | 合并诊断比值比 | 合并阳性似然比 | 合并阴性似然比 | SROC曲线下面积 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBT | 取样时间<24 h | 8[ | 0.94(0.91,0.96) | 0.92(0.85,0.96) | 119.27(49.06,289.94) | 7.78(4.04,14.97) | 0.09(0.05,0.17) | 0.97(0.96,0.98) |
| 取样时间>3 d | 3[ | 0.69(0.60,0.76) | 0.88(0.78,0.94) | 11.84(2.01,69.85) | 4.37(1.93,9.89) | 0.41(0.21,0.80) | 0.81(0.78,0.83) | |
| 复合标准 | 10[ | 0.89(0.86,0.92) | 0.87(0.77,0.93) | 46.65(14.98,145.29) | 5.30(3.10,9.06) | 0.15(0.06,0.37) | 0.92(0.89,0.94) | |
| 单一标准 | 4[ | 0.76(0.70,0.82) | 0.92(0.86,0.96) | 87.63(4.42,173.31) | 11.53(2.09,63.66) | 0.14(0.02,0.81) | 0.94(0.92,0.96) | |
| SAT | 取样时间<24 h | 3[ | 0.89(0.80,0.95) | 0.82(0.71,0.90) | 37.24(14.19,97.76) | 3.47(0.74,16.14) | 0.17(0.09,0.30) | 0.93(0.90,0.95) |
| 取样时间2~3 d | 6[ | 0.82(0.77,0.87) | 0.75(0.66,0.82) | 15.26(7.76,30.01) | 2.77(1.23,6.24) | 0.24(0.16,0.35) | 0.87(0.80,0.95) |
Table 3 Subgroup analysis results of the UBT and SAT aimed to detect H.pylori infection in patients with peptic ulcer bleeding
| 检查方式 | 亚组 | 研究数量(项) | 合并灵敏度 | 合并特异度 | 合并诊断比值比 | 合并阳性似然比 | 合并阴性似然比 | SROC曲线下面积 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBT | 取样时间<24 h | 8[ | 0.94(0.91,0.96) | 0.92(0.85,0.96) | 119.27(49.06,289.94) | 7.78(4.04,14.97) | 0.09(0.05,0.17) | 0.97(0.96,0.98) |
| 取样时间>3 d | 3[ | 0.69(0.60,0.76) | 0.88(0.78,0.94) | 11.84(2.01,69.85) | 4.37(1.93,9.89) | 0.41(0.21,0.80) | 0.81(0.78,0.83) | |
| 复合标准 | 10[ | 0.89(0.86,0.92) | 0.87(0.77,0.93) | 46.65(14.98,145.29) | 5.30(3.10,9.06) | 0.15(0.06,0.37) | 0.92(0.89,0.94) | |
| 单一标准 | 4[ | 0.76(0.70,0.82) | 0.92(0.86,0.96) | 87.63(4.42,173.31) | 11.53(2.09,63.66) | 0.14(0.02,0.81) | 0.94(0.92,0.96) | |
| SAT | 取样时间<24 h | 3[ | 0.89(0.80,0.95) | 0.82(0.71,0.90) | 37.24(14.19,97.76) | 3.47(0.74,16.14) | 0.17(0.09,0.30) | 0.93(0.90,0.95) |
| 取样时间2~3 d | 6[ | 0.82(0.77,0.87) | 0.75(0.66,0.82) | 15.26(7.76,30.01) | 2.77(1.23,6.24) | 0.24(0.16,0.35) | 0.87(0.80,0.95) |
| [1] | LAINE L, BARKUN A N, SALTZMAN J R,et al. ACG clinical guideline:upper gastrointestinal and ulcer bleeding[J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2021,116(5):899-917. DOI:10.14309/ajg.0000000000001245. |
| [2] | 王锦萍,崔毅,王锦辉,等. 上消化道出血15年临床流行病学变化趋势[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志,2017,20(4):425-431. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0274.2017.04.012. |
| [3] | 中华消化杂志编辑委员会,中华消化外科杂志编辑委员会. 急性非静脉曲张性上消化道出血多学科防治共识[J]. 中华消化杂志,2019,39(12):793-799. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2019.12.001. |
| [4] | 邬兰,张永,曾宪涛. QUADAS-2在诊断准确性研究的质量评价工具中的应用[J]. 湖北医药学院学报,2013,32(3):201-208. |
| [5] | 曾宪涛,何明武. 诊断准确性试验Meta分析软件一本通[M]. 北京:军事医学科学出版社,2014. |
| [6] | 周支瑞,胡志德. 疯狂统计学[M]. 长沙:中南大学出版社,2018. |
| [7] | 吴景玲,葛龙,张俊华,等. 多个诊断性试验准确性的比较:网状Meta分析方法介绍[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2017,17(8):987-992. DOI:10.7507/1672-2531.201706041. |
| [8] | 高亚,孙凤,武珊珊,等. 网络Meta分析研究进展系列(五):诊断试验准确性网络Meta分析[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2020,12(10):1161-1165. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4055.2020.10.03. |
| [9] | TU T C, LEE C L, WU C H,et al. Comparison of invasive and noninvasive tests for detecting Helicobacter pylori infection in bleeding peptic ulcers[J]. Gastrointest Endosc,1999,49(3 Pt 1):302-306. DOI:10.1016/s0016-5107(99)70005-2. |
| [10] | LóPEZ PEÑAS D, NARANJO RODRíGUEZ A, MUÑOZ MOLINERO J,et al. Efficacy of fecal detection of Helicobacter pylori with the HpSA technique in patients with upper digestive hemorrhage[J]. Gastroenterol Hepatol,2001,24(1):5-8. |
| [11] | GRIÑó P, PASCUAL S, SUCH J,et al. Comparison of diagnostic methods for Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol,2001,36(12):1254-1258. DOI:10.1080/003655201317097083. |
| [12] | CHUNG I K, HONG S J, KIM E J,et al. What is the best method to diagnose Helicobacter infection in bleeding peptic ulcers?:a prospective trial[J]. Korean J Intern Med,2001,16(3):147-152. DOI:10.3904/kjim.2001.16.3.147. |
| [13] | WILDNER-CHRISTENSEN M, TOUBORG LASSEN A, LINDEBJERG J,et al. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in bleeding peptic ulcer patients,evaluation of urea-based tests[J]. Digestion,2002,66(1):9-13. DOI:10.1159/000064421. |
| [14] | GRIÑó P, PASCUAL S, SUCH J,et al. Comparison of stool immunoassay with standard methods for detection of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with upper-gastrointestinal bleeding of peptic origin[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2003,15(5):525-529. DOI:10.1097/01.meg.0000059114.41030.a9. |
| [15] | WINIARSKI M, BIELANSKI W, PLONKA M,et al. The usefulness of capsulated 13C-urea breath test in diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol,2003,37(1):34-38. DOI:10.1097/00004836-200307000-00010. |
| [16] | LIAO C C, LEE C L, LAI Y C,et al. Accuracy of three diagnostic tests used alone and in combination for detecting Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with bleeding gastric ulcers[J]. Chin Med J (Engl),2003,116(12):1821-1826. |
| [17] | LO C C, LAI K H, PENG N J,et al. Polymerase chain reaction:a sensitive method for detecting Helicobacter pylori infection in bleeding peptic ulcers[J]. World J Gastroenterol,2005,11(25):3909-3914. DOI:10.3748/wjg.v11.i25.3909. |
| [18] | 张厚德,杜冀晖,苏卓娃,等. 上消化道出血对14C-尿素呼气试验准确性影响[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,1997,6(2):66-67. |
| [19] | 林勇,李荣洲,郑超秀,等. 14C-尿素呼气试验在消化性溃疡并出血病人假阴性原因分析[J]. 浙江临床医学,2004,6(7):577. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-7664.2004.07.023. |
| [20] | 李舜,张家云,邓咏梅. 14C-尿素呼气试验在不同胃黏膜病变中的诊断价值及影响因素分析[J]. 实用医学杂志,2005,21(5):477-478. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2005.05.015. |
| [21] | 王醒,高广周,石峥,等. 粪便幽门螺杆菌检测在上消化道溃疡出血患者中的价值[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(25):165-166. DOI:10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2019.25.123. |
| [22] | PEITZ U, LEODOLTER A, KAHL S,et al. Antigen stool test for assessment of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther,2003,17(8):1075-1084. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2036.2003.01548.x. |
| [23] | VAN LEERDAM M E, VAN DER ENDE A, TEN KATE F J,et al. Lack of accuracy of the noninvasive Helicobacter pylori stool antigen test in patients with gastroduodenal ulcer bleeding[J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2003,98(4):798-801. DOI:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07387.x. |
| [24] | LIN H J, LO W C, PERNG C L,et al. Helicobacter pylori stool antigen test in patients with bleeding peptic ulcers[J]. Helicobacter,2004,9(6):663-668. DOI:10.1111/j.1083-4389.2004.00276.x. |
| [25] | GISBERT J P, TRAPERO M, CALVET X,et al. Evaluation of three different tests for the detection of stool antigens to diagnose Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther,2004,19(8):923-929. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01932.x. |
| [26] | 于涛. 幽门螺杆菌粪便抗原检测卡的应用及质子泵抑制剂对其结果的影响[D]. 广州:中山大学,2006. |
| [27] | 田金徽,陈杰峰. 诊断试验系统评价/Meta分析指导手册[M]. 北京:中国医药科技出版社,2015. |
| [28] | MALFERTHEINER P, MEGRAUD F, O'MORAIN C A,et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the maastricht V/Florence consensus report[J]. Gut,2017,66(1):6-30. DOI:10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312288. |
| [29] | 中华医学会,中华医学会杂志社,中华医学会全科医学分会,等. 幽门螺杆菌感染基层诊疗指南(2019年)[J]. 中华全科医师杂志,2020,19(5):397-402. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn114798-20200223-00158. |
| [30] | 《中华内科杂志》编辑委员会,《中华医学杂志》编辑委员会,《中华消化杂志》编辑委员会,等. 急性非静脉曲张性上消化道出血诊治指南(2018年,杭州)[J]. 中华内科杂志,2019,58(3):173-180. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2019.03.005. |
| [1] | XU Jialan, YAN Hong, WEN Jun, ZHOU Zitong, WANG Siyu. Prevalence of Potentially Inappropriate Medication in Older Adults with Cancer: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [2] | ZHANG Tianyu, YU Haibo, CHEN Fei, LI Xin, ZHANG Jiajia, ZHAN Xiaokai, SHEN Man, TANG Ran, FAN Sibin, ZHAO Fengyi, HUANG Zhongxia. Meta-analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Systemic Treatment for POEMS Syndrome [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3447-3455. |
| [3] | QUAN Jialin, ZHU Lin, SU Yu, CHEN Zekai, CHEN Ziqi, ZHANG Zhuofan. Research on the Improvement Effect of Exercise Modes on the Executive Function of Overweight or Obese Children or Adolescents: a Network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [4] | JIANG Shihua, ZHU Zheng, REN Yingying, ZHU Yaolei, WANG Yue, GAO Xibin. Meta Analysis of the Prevalence and Risk Factors of Myopia in Chinese Children and Adolescents [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 3043-3052. |
| [5] | LI Hao, LI Jiangtao, LIU Dan, WANG Jianjun. Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab, Anifrolumab, and Telitacicept on the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a Network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2924-2933. |
| [6] | WANG Xiaolin, LI Qiuyue, ZHOU Yanjun, ZHANG Jinhui, LIANG Tao. Incidence and Risk of Cardiovascular Toxicity with Fruquintinib in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2934-2940. |
| [7] | MA Panpan, WANG Sijing, YOU Na, DING Dafa, LU Yibing. Efficacy and Safety of Danuglipron and Orforglipron in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(21): 2679-2685. |
| [8] | HU Wanqin, YU Shenyan, CAO Xuehua, XIANG Feng, JIA Yu. Factors Associated with Precocious Puberty in Chinese Children: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(21): 2661-2671. |
| [9] | ADILI Tuersun, CHENG Gang. Meta-analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(21): 2686-2691. |
| [10] | GUO Shengteng, ZHANG Fenfen, WAN Di, YU Dongmei, WANG Qinghua. Risk Factors for Severe Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Acute Lung Injury: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(20): 2546-2554. |
| [11] | WANG Biqing, ZHANG Ping, YANG Hongxia, WANG Qian, JU Chunxiao, ZHAO Junnan, MEI Jun, ZHANG Ying, XU Fengqin. Meta-analysis of Prevalence and Development Trend of Mild Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Hypertensive Patients in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2186-2192. |
| [12] | FAN Yu, LI Rong, GONG Shuangying, YANG Xiaojuan, LI Rui. Meta-analysis of the Incidence of Postpartum Depression among Maternal Spouses in China [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2179-2185. |
| [13] | HE Yun, FAN Huanfang, MA Pan, XU Shaoqing, YANG Liu, JIN Mingzhe, ZHANG Mingrui, CHEN Jiaqi. Effect of Postoperative Upper Extremity Lymphedema after Breast Cancer Treated with Different Acupuncture and Moxibustion Therapies: a Network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1788-1794. |
| [14] | ZHU Shengjie, DIAO Huaqiong, HANG Xiaoyi, SUN Wenjun. Network Meta-analysis of Different Traditional Chinese Medicine Injections for the Treatment of Posterior Circulatory Ischemic Vertigo [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1795-1808. |
| [15] | WANG Xiaoyu, FENG Zhenzhen, WANG Jun, GUO Xiaochuan, LI Jiansheng. Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: a Systematic Review [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(12): 1527-1537. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||