

Chinese General Practice ›› 2021, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (36): 4607-4611.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.060
Special Issue: 神经退行性病变最新文章合辑; 帕金森最新文章合辑; 骨健康最新文章合辑; 营养最新文章合辑; 脑健康最新研究合辑
• Monographic Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Published:2021-12-20
Online:2021-12-24
基金资助:XU Xiaohui, TIAN Junmei, CAI Weiwei, ZHAO Yongfei, WANG Yupeng, LIU Chao, DUAN Zhihui. Sex-specific Correlations of Fracture Risk with Nutritional Status,Body Composition and Balance Condition in Parkinson's Disease Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2021, 24(36): 4607-4611.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.060
| 一般资料 | 女(n=31) | 男(n=37) | 检验统计量值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄〔M(P25,P75),岁〕 | 68.0(64.0,72.0) | 71.0(65.0,74.0) | 0.855a | 0.395 | |
| 独居〔n(%)〕 | 0.442b | 0.506 | |||
| 是 | 7(22.6) | 6(16.2) | |||
| 否 | 24(77.4) | 31(83.8) | |||
| 骨折史〔n(%)〕 | 0.112b | 0.738 | |||
| 有 | 2(6.5) | 2(5.4) | |||
| 无 | 29(93.5) | 35(94.6) | |||
| 剂末现象〔n(%)〕 | 0.061b | 0.805 | |||
| 有 | 4(12.9) | 3(8.1) | |||
| 无 | 27(87.1) | 34(91.9) | |||
| 步态冻结现象〔n(%)〕 | 0.352b | 0.553 | |||
| 有 | 1(3.2) | 1(2.7) | |||
| 无 | 30(96.8) | 36(97.3) | |||
| 开关现象〔n(%)〕 | 0.352b | 0.553 | |||
| 有 | 1(3.2) | 1(2.7) | |||
| 无 | 30(96.8) | 36(97.3) | |||
| 未来10年MOF风险〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | 0.89(0.48,2.20) | 0.34(0.12,1.54) | 0.747 | 0.457 | |
未来10年HF风险(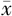 ±s,%) ±s,%) | 1.76±0.53 | 1.65±0.81 | 0.657 | 0.514 | |
股骨颈骨密度T值(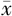 ±s,g/cm2) ±s,g/cm2) | -1.24±1.38 | -0.47±1.51 | 2.192 | 0.032 | |
UPDRS Ⅲ评分(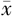 ±s,分) ±s,分) | 35.6±9.6 | 29.1±14.9 | 2.086 | 0.041 | |
MNA评分(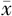 ±s,分) ±s,分) | 23.2±3.2 | 24.6±3.8 | 1.604 | 0.114 | |
BFR(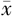 ±s,%) ±s,%) | 31.7±8.6 | 24.9±6.2 | 3.771 | <0.001 | |
BMI(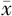 ±s,kg/m2) ±s,kg/m2) | 24.2±3.0 | 23.5±2.5 | 0.996 | 0.323 | |
三头肌皮褶厚度(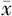 ±s,mm) ±s,mm) | 16.4±5.0 | 12.2±5.2 | 3.385 | 0.001 | |
AC(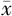 ±s,cm) ±s,cm) | 30.0±13.0 | 28.1±2.7 | 0.875 | 0.385 | |
WHR(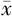 ±s,%) ±s,%) | 0.89±0.06 | 0.88±0.07 | 0.862 | 0.392 | |
躯干肌肉量(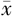 ±s,kg) ±s,kg) | 18.28±2.16 | 22.35±3.21 | 5.991 | <0.001 | |
双上肢肌肉量(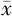 ±s,kg) ±s,kg) | 4.35±1.27 | 5.48±1.01 | 4.087 | <0.001 | |
双下肢肌肉量(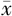 ±s,kg) ±s,kg) | 10.84±1.85 | 14.07±2.76 | 5.543 | <0.001 | |
BBS评分(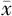 ±s,分) ±s,分) | 2.5±1.0 | 3.0±1.0 | 2.055 | 0.044 | |
ABC评分(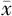 ±s,分) ±s,分) | 59.7±17.2 | 66.3±20.6 | 1.416 | 0.161 | |
Table 1 Comparison of general characteristics of PD patients by sex
| 一般资料 | 女(n=31) | 男(n=37) | 检验统计量值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄〔M(P25,P75),岁〕 | 68.0(64.0,72.0) | 71.0(65.0,74.0) | 0.855a | 0.395 | |
| 独居〔n(%)〕 | 0.442b | 0.506 | |||
| 是 | 7(22.6) | 6(16.2) | |||
| 否 | 24(77.4) | 31(83.8) | |||
| 骨折史〔n(%)〕 | 0.112b | 0.738 | |||
| 有 | 2(6.5) | 2(5.4) | |||
| 无 | 29(93.5) | 35(94.6) | |||
| 剂末现象〔n(%)〕 | 0.061b | 0.805 | |||
| 有 | 4(12.9) | 3(8.1) | |||
| 无 | 27(87.1) | 34(91.9) | |||
| 步态冻结现象〔n(%)〕 | 0.352b | 0.553 | |||
| 有 | 1(3.2) | 1(2.7) | |||
| 无 | 30(96.8) | 36(97.3) | |||
| 开关现象〔n(%)〕 | 0.352b | 0.553 | |||
| 有 | 1(3.2) | 1(2.7) | |||
| 无 | 30(96.8) | 36(97.3) | |||
| 未来10年MOF风险〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | 0.89(0.48,2.20) | 0.34(0.12,1.54) | 0.747 | 0.457 | |
未来10年HF风险(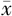 ±s,%) ±s,%) | 1.76±0.53 | 1.65±0.81 | 0.657 | 0.514 | |
股骨颈骨密度T值(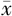 ±s,g/cm2) ±s,g/cm2) | -1.24±1.38 | -0.47±1.51 | 2.192 | 0.032 | |
UPDRS Ⅲ评分(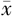 ±s,分) ±s,分) | 35.6±9.6 | 29.1±14.9 | 2.086 | 0.041 | |
MNA评分(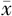 ±s,分) ±s,分) | 23.2±3.2 | 24.6±3.8 | 1.604 | 0.114 | |
BFR(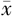 ±s,%) ±s,%) | 31.7±8.6 | 24.9±6.2 | 3.771 | <0.001 | |
BMI(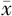 ±s,kg/m2) ±s,kg/m2) | 24.2±3.0 | 23.5±2.5 | 0.996 | 0.323 | |
三头肌皮褶厚度(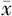 ±s,mm) ±s,mm) | 16.4±5.0 | 12.2±5.2 | 3.385 | 0.001 | |
AC(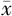 ±s,cm) ±s,cm) | 30.0±13.0 | 28.1±2.7 | 0.875 | 0.385 | |
WHR(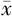 ±s,%) ±s,%) | 0.89±0.06 | 0.88±0.07 | 0.862 | 0.392 | |
躯干肌肉量(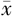 ±s,kg) ±s,kg) | 18.28±2.16 | 22.35±3.21 | 5.991 | <0.001 | |
双上肢肌肉量(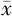 ±s,kg) ±s,kg) | 4.35±1.27 | 5.48±1.01 | 4.087 | <0.001 | |
双下肢肌肉量(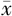 ±s,kg) ±s,kg) | 10.84±1.85 | 14.07±2.76 | 5.543 | <0.001 | |
BBS评分(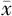 ±s,分) ±s,分) | 2.5±1.0 | 3.0±1.0 | 2.055 | 0.044 | |
ABC评分(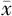 ±s,分) ±s,分) | 59.7±17.2 | 66.3±20.6 | 1.416 | 0.161 | |
| 指标 | 男性 | 女性 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未来10年MOF风险 | 未来10年HF风险 | 股骨颈骨密度T值 | 未来10年MOF风险 | 未来10年HF风险 | 股骨颈骨密度T值 | |||||||
| r(rs)值 | P值 | r(rs)值 | P值 | r(rs)值 | P值 | r(rs)值 | P值 | r(rs)值 | P值 | r(rs)值 | P值 | |
| 年龄 | 0.270a | 0.106 | 0.285a | 0.088 | -0.284a | 0.088 | 0.363a | 0.045 | 0.096a | 0.606 | -0.359a | 0.048 |
| UPDRSⅢ评分 | 0.544 | <0.001 | 0.460 | 0.004 | 0.163 | 0.589 | 0.768 | <0.001 | 0.684 | <0.001 | 0.193 | 0.432 |
| MNA评分 | -0.652 | <0.001 | -0.546 | <0.001 | 0.131 | 0.701 | -0.482 | 0.006 | -0.501 | 0.004 | 0.182 | 0.520 |
| BFR | 0.055 | 0.710 | 0.087 | 0.521 | -0.535 | 0.001 | -0.013 | 0.947 | -0.016 | 0.930 | 0.060 | 0.750 |
| BMI | 0.245 | 0.144 | 0.052 | 0.760 | -0.183 | 0.278 | -0.228 | 0.217 | -0.205 | 0.269 | 0.020 | 0.915 |
| 三头肌皮褶厚度 | 0.128 | 0.452 | -0.043 | 0.802 | -0.134 | 0.430 | -0.058 | 0.758 | 0.022 | 0.905 | -0.048 | 0.798 |
| AC | 0.121 | 0.135 | 0.160 | 0.128 | -0.356 | 0.051 | -0.094 | 0.614 | 0.081 | 0.665 | -0.129 | 0.489 |
| WHR | 0.194 | 0.249 | 0.086 | 0.611 | -0.120 | 0.478 | 0.312 | 0.087 | 0.004 | 0.985 | -0.394 | 0.028 |
| 躯干肌肉量 | -0.147 | 0.384 | -0.107 | 0.528 | 0.251 | 0.134 | -0.173 | 0.351 | -0.189 | 0.310 | -0.099 | 0.597 |
| 双上肢肌肉量 | -0.190 | 0.259 | -0.139 | 0.411 | 0.239 | 0.155 | -0.073 | 0.698 | -0.385 | 0.032 | 0.119 | 0.523 |
| 双下肢肌肉量 | -0.648 | <0.001 | -0.553 | <0.001 | 0.621 | <0.001 | -0.572 | 0.001 | -0.638 | <0.001 | 0.436 | 0.014 |
| BBS评分 | -0.610 | <0.001 | -0.553 | <0.001 | 0.142 | 0.676 | -0.403 | 0.024 | -0.485 | 0.006 | 0.337 | 0.063 |
| ABC评分 | -0.708 | <0.001 | -0.642 | <0.001 | 0.144 | 0.672 | -0.800 | <0.001 | -0.718 | <0.001 | 0.146 | 0.653 |
Table 2 Correlation analysis of fracture risk and T-score of femoral neck bone mineral density with other indicators in PD patients by sex
| 指标 | 男性 | 女性 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未来10年MOF风险 | 未来10年HF风险 | 股骨颈骨密度T值 | 未来10年MOF风险 | 未来10年HF风险 | 股骨颈骨密度T值 | |||||||
| r(rs)值 | P值 | r(rs)值 | P值 | r(rs)值 | P值 | r(rs)值 | P值 | r(rs)值 | P值 | r(rs)值 | P值 | |
| 年龄 | 0.270a | 0.106 | 0.285a | 0.088 | -0.284a | 0.088 | 0.363a | 0.045 | 0.096a | 0.606 | -0.359a | 0.048 |
| UPDRSⅢ评分 | 0.544 | <0.001 | 0.460 | 0.004 | 0.163 | 0.589 | 0.768 | <0.001 | 0.684 | <0.001 | 0.193 | 0.432 |
| MNA评分 | -0.652 | <0.001 | -0.546 | <0.001 | 0.131 | 0.701 | -0.482 | 0.006 | -0.501 | 0.004 | 0.182 | 0.520 |
| BFR | 0.055 | 0.710 | 0.087 | 0.521 | -0.535 | 0.001 | -0.013 | 0.947 | -0.016 | 0.930 | 0.060 | 0.750 |
| BMI | 0.245 | 0.144 | 0.052 | 0.760 | -0.183 | 0.278 | -0.228 | 0.217 | -0.205 | 0.269 | 0.020 | 0.915 |
| 三头肌皮褶厚度 | 0.128 | 0.452 | -0.043 | 0.802 | -0.134 | 0.430 | -0.058 | 0.758 | 0.022 | 0.905 | -0.048 | 0.798 |
| AC | 0.121 | 0.135 | 0.160 | 0.128 | -0.356 | 0.051 | -0.094 | 0.614 | 0.081 | 0.665 | -0.129 | 0.489 |
| WHR | 0.194 | 0.249 | 0.086 | 0.611 | -0.120 | 0.478 | 0.312 | 0.087 | 0.004 | 0.985 | -0.394 | 0.028 |
| 躯干肌肉量 | -0.147 | 0.384 | -0.107 | 0.528 | 0.251 | 0.134 | -0.173 | 0.351 | -0.189 | 0.310 | -0.099 | 0.597 |
| 双上肢肌肉量 | -0.190 | 0.259 | -0.139 | 0.411 | 0.239 | 0.155 | -0.073 | 0.698 | -0.385 | 0.032 | 0.119 | 0.523 |
| 双下肢肌肉量 | -0.648 | <0.001 | -0.553 | <0.001 | 0.621 | <0.001 | -0.572 | 0.001 | -0.638 | <0.001 | 0.436 | 0.014 |
| BBS评分 | -0.610 | <0.001 | -0.553 | <0.001 | 0.142 | 0.676 | -0.403 | 0.024 | -0.485 | 0.006 | 0.337 | 0.063 |
| ABC评分 | -0.708 | <0.001 | -0.642 | <0.001 | 0.144 | 0.672 | -0.800 | <0.001 | -0.718 | <0.001 | 0.146 | 0.653 |
| 指标 | 未来10年MOF风险 | 未来10年HF风险 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | |
| UPDRS Ⅲ评分 | 0.252 | 0.043 | 0.186 | 0.139 |
| MNA评分 | -0.245 | 0.049 | -0.222 | 0.045 |
| BFR | 0.038 | 0.547 | 0.041 | 0.435 |
| BMI | -0.040 | 0.749 | -0.136 | 0.280 |
| 三头肌皮褶厚度 | -0.020 | 0.875 | -0.110 | 0.382 |
| AC | 0.027 | 0.830 | -0.215 | 0.085 |
| WHR | 0.046 | 0.713 | 0.223 | 0.075 |
| 躯干肌肉量 | -0.073 | 0.561 | -0.060 | 0.638 |
| 双上肢肌肉量 | -0.009 | 0.944 | -0.150 | 0.234 |
| 双下肢肌肉量 | -0.376 | 0.002 | -0.344 | 0.005 |
| BBS评分 | -0.245 | 0.049 | -0.288 | 0.020 |
| ABC评分 | -0.402 | 0.001 | -0.358 | 0.003 |
Table 3 Partial correlation analysis of fracture risk with other indicators after controlling for gender,age and T-score of femoral neck bone mineral density in PD patients
| 指标 | 未来10年MOF风险 | 未来10年HF风险 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | |
| UPDRS Ⅲ评分 | 0.252 | 0.043 | 0.186 | 0.139 |
| MNA评分 | -0.245 | 0.049 | -0.222 | 0.045 |
| BFR | 0.038 | 0.547 | 0.041 | 0.435 |
| BMI | -0.040 | 0.749 | -0.136 | 0.280 |
| 三头肌皮褶厚度 | -0.020 | 0.875 | -0.110 | 0.382 |
| AC | 0.027 | 0.830 | -0.215 | 0.085 |
| WHR | 0.046 | 0.713 | 0.223 | 0.075 |
| 躯干肌肉量 | -0.073 | 0.561 | -0.060 | 0.638 |
| 双上肢肌肉量 | -0.009 | 0.944 | -0.150 | 0.234 |
| 双下肢肌肉量 | -0.376 | 0.002 | -0.344 | 0.005 |
| BBS评分 | -0.245 | 0.049 | -0.288 | 0.020 |
| ABC评分 | -0.402 | 0.001 | -0.358 | 0.003 |
| [1] | SHEARD J M, ASH S, SILBURN P A,et al.Prevalence of malnutrition in Parkinson's disease:a systematic review[J].Nutr Rev,2011,69(9):520-532.DOI:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2011.00413.x. |
| [2] | 洪维,朱晓颖,程群,等.老年髋部骨折患者肌肉减少症与骨密度的关系[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2014,7(2):106-112. |
| [3] | WANG J, WANG X J, FANG Z,et al.The effect of FRAX on the prediction of osteoporotic fractures in urban middle-aged and elderly healthy Chinese adults[J].Clinics (Sao Paulo),2017,72(5):289-293.DOI:10.6061/clinics/2017(05)06. |
| [4] | SCOTT D, CHANDRASEKARA S D, LASLETT L L,et al.Associations of sarcopenic obesity and dynapenic obesity with bone mineral density and incident fractures over 5-10 years in community-dwelling older adults[J].Calcif Tissue Int,2016,99(1):30-42.DOI:10.1007/s00223-016-0123-9. |
| [5] | POSTUMA R B, BERG D, STERN M,et al.MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease[J].Mov Disord,2015,30(12):1591-1601.DOI:10.1002/mds.26424. |
| [6] | CHEN K K, JIN Z H, GAO L,et al.Efficacy of short-term multidisciplinary intensive rehabilitation in patients with different Parkinson's disease motor subtypes:a prospective pilot study with 3-month follow-up[J].Neural Regen Res,2021,16(7):1336-1343.DOI:10.4103/1673-5374.301029. |
| [7] | FERESHTEHNEJAD S M, GHAZI L, SADEGHI M,et al.Prevalence of malnutrition in patients with Parkinson's disease:a comparative study with healthy controls using Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA) questionnaire[J].J Parkinsons Dis,2014,4(3):473-481.DOI:10.3233/JPD-130323. |
| [8] | FERRAZZOLI D, FASANO A, MAESTRI R,et al.Balance dysfunction in Parkinson's disease:the role of posturography in developing a rehabilitation program[J].Parkinsons Dis,2015,2015:520128.DOI:10.1155/2015/520128. |
| [9] | SCHEPENS S, GOLDBERG A, WALLACE M.The short version of the Activities-specific Balance Confidence (ABC) scale:its validity,reliability,and relationship to balance impairment and Falls in older adults[J].Arch Gerontol Geriatr,2010,51(1):9-12.DOI:10.1016/j.archger.2009.06.003. |
| [10] | MÜLLER A, MÜNGERSDORF M, REICHMANN H,et al.Olfactory function in Parkinsonian syndromes[J].J Clin Neurosci,2002,9(5):521-524.DOI:10.1054/jocn.2001.1071. |
| [11] | MACIA F, PERLEMOINE C, COMAN I,et al.Parkinson's disease patients with bilateral subthalamic deep brain stimulation gain weight[J].Mov Disord,2004,19(2):206-212.DOI:10.1002/mds.10630. |
| [12] | ZORRILLA E P, TACHÉ Y, KOOB G F.Nibbling at CRF receptor control of feeding and gastrocolonic motility[J].Trends Pharmacol Sci,2003,24(8):421-427.DOI:10.1016/S0165-6147(03)00177-9. |
| [13] | FADEL J, DEUTCH A Y.Anatomical substrates of orexin-dopamine interactions:lateral hypothalamic projections to the ventral tegmental area[J].Neuroscience,2002,111(2):379-387.DOI:10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00017-9. |
| [14] | WILLS A M, LI R S, PÉREZ A,et al.Predictors of weight loss in early treated Parkinson's disease from the NET-PD LS-1 cohort[J].J Neurol,2017,264(8):1746-1753.DOI:10.1007/s00415-017-8562-4. |
| [15] | SCHEPENS S, GOLDBERG A, WALLACE M.The short version of the Activities-specific Balance Confidence (ABC) scale:its validity,reliability,and relationship to balance impairment and Falls in older adults[J].Arch Gerontol Geriatr,2010,51(1):9-12.DOI:10.1016/j.archger.2009.06.003. |
| [16] | US Preventive Services Task Force, CURRY S J, KRIST A H,et al.Screening for osteoporosis to prevent fractures:US preventive services task force recommendation statement[J].JAMA,2018,319(24):2521-2531.DOI:10.1001/jama.2018.7498. |
| [17] | ZHANG Y, HAO Q, GE M,et al.Association of sarcopenia and fractures in community-dwelling older adults:a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies[J].Osteoporos Int,2018,29(6):1253-1262.DOI:10.1007/s00198-018-4429-5. |
| [18] | YU R, LEUNG J, WOO J.Sarcopenia combined with FRAX probabilities improves fracture risk prediction in older Chinese men[J].J Am Med Dir Assoc,2014,15(12):918-923.DOI:10.1016/j.jamda.2014.07.011. |
| [19] | COMPSTON J, COOPER A, COOPER C,et al.UK clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis[J].Arch Osteoporos,2017,12(1):43.DOI:10.1007/s11657-017-0324-5. |
| [20] | SZULC P, FEYT C, CHAPURLAT R.High risk of fall,poor physical function,and low grip strength in men with fracture-the STRAMBO study[J].J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle,2016,7(3):299-311.DOI:10.1002/jcsm.12066. |
| [21] | VAN DER MARCK M A, DICKE H C, UC E Y,et al.Body mass index in Parkinson's disease:a meta-analysis[J].Parkinsonism Relat Disord,2012,18(3):263-267.DOI:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.10.016. |
| [22] | DI MONACO M, CASTIGLIONI C, VALLERO F,et al.Sarcopenia is more prevalent in men than in women after hip fracture:a cross-sectional study of 591 inpatients[J].Arch Gerontol Geriatr,2012,55(2):e48-52.DOI:10.1016/j.archger.2012.05.002. |
| [23] | VERSCHUEREN S, GIELEN E, O'NEILL T W,et al.Sarcopenia and its relationship with bone mineral density in middle-aged and elderly European men[J].Osteoporos Int,2013,24(1):87-98.DOI:10.1007/s00198-012-2057-z. |
| [24] | PAHOR M, MANINI T, CESARI M.Sarcopenia:clinical evaluation,biological markers and other evaluation tools[J].J Nutr Health Aging,2009,13(8):724-728.DOI:10.1007/s12603-009-0204-9. |
| [25] | WANG C, SWERDLOFF R S, IRANMANESH A,et al.Transdermal testosterone gel improves sexual function,mood,muscle strength,and body composition parameters in hypogonadal men[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2000,85(8):2839-2853.DOI:10.1210/jcem.85.8.6747. |
| [26] | BORST S E.Interventions for sarcopenia and muscle weakness in older people[J].Age Ageing,2004,33(6):548-555.DOI:10.1093/ageing/afh201. |
| [27] | KALILANI L, ASGHARNEJAD M, PALOKANGAS T,et al.Comparing the incidence of Falls/fractures in Parkinson's disease patients in the US population[J].PLoS One,2016,11(9):e0161689.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0161689. |
| [1] | LU Donglei, YANG Fengying, FENG Zhanpeng, CAO Liquan, TAN Sijie. Conccurent Training Can Improve the Physical Health in Diabesity Individuals: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3410-3421. |
| [2] | ZHU Chen, YU Jiawen, JIANG Hao, GAN Panpan, XIA Tian, XU Haitao, DU Yingying. Research on the Predictive Value of Lipid Characteristics about Digestive System Tumors for Normal Phase Angles [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3385-3390. |
| [3] | LU Donglei, TAN Sijie, YANG Fengying. The Improvement of Maximal Fat Oxidation Intensity on Body Composition, Cardiopulmonary Function, and Lipid Metabolism in Overweight or Obese Individuals: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(03): 335-345. |
| [4] | XU Lili, ZHENG Wei, YUAN Xianxian, MA Kaiwen, ZHANG Puyang, LI Guanghui. The Relationship between Body Composition in Early Pregnancy and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Population of Normal BMI Pregnant Women [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(29): 3602-3607. |
| [5] | YU Chunyan, DONG Fen, LEI Jieping, YANG Ting, XIA Jingen, QUMU Shiwei, YANG Tianyi, LI Xiaopan. Correlation between Body Composition and Cardiopulmonary Exercise Capacity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(29): 3629-3634. |
| [6] | YU Haidong, PAN Miaomiao, GU Hongqin, LIU Tao, DAI Jie, LIU Linghua, HOU Junping, YANG Li, SHI Meifang, ZHAO Chao. Correlation Analysis between Depressive, Cognitive Symptoms and Nutritional Metabolism in the Elderly in Community [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(28): 3540-3545. |
| [7] | ZHANG Dongliang, MA Yingchun, REN Jianwei, WANG Lei, ZHAO Jingxin, LIN Xuya. Body Composition Analysis of the Effect of Water Load Parameters on Prognosis of Patients with Different Modes of Dialysis: a Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(21): 2586-2591. |
| [8] | WU Fangfang, DU Shanshan, DU Xin, XU Rufu, SUN Aihua, KONG Peiyan, GAO Lei, ZHANG Xi. Effect of Pre-transplant Skeletal Muscle Mass on Early Outcome of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(14): 1723-1728. |
| [9] | ZENG Li, WANG Huihui, WANG Xiaoyu, GONG Weiyi, HU Chunqiu. Comparison of the Predictive Value of Four Nutritional Evaluation Methods for Postoperative Complications of Lumbar Degenerative Diseases [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(11): 1349-1355. |
| [10] | LIANG Keke, GUO Qingge, LI Xiaohuan, MA Jianjun, YANG Hongqi, SHI Xiaoxue, FAN Yongyan, YANG Dawei, GUO Dashuai, DONG Linrui, GU Qi, LI Dongsheng. Predictive Value of Machine Learning Based on Retinal Structural Changes for Early Parkinson's Disease Diagnosis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(09): 1102-1108. |
| [11] | WANG Kai, XU Baichao, WANG Zhaoxin, SU Jianjiao. Effects of Combined Motion Intervention on Body Composition, Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Cardiopulmonary Fitness of Obese Female Adolescents [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(09): 1109-1117. |
| [12] | XUE Shan, LI Laiyou, LIANG Junli, JIN Yinghui, WEI Shuyan. The Efficacy and Safety of Home Enteral Nutrition in Patients with Esophageal Cancer: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(20): 2540-2547. |
| [13] | WANG Qiuqin, ZHANG Yutong, XU Yuchen, BAI Yamei, CHEN Hua, JIANG Rongrong, YAN Shuxia, WANG Qing, XU Guihua, XIE Ying, QIAO Chun, YANG Juan. Short-term Clinical Effect of Guasha Combined with Drug Therapy on Idiopathic Parkinson's Disease [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(17): 2155-2161. |
| [14] | ZHANG Yutong, WANG Qiuqin, XU Yuchen, WENG Heng, LIANG Yongqi, WANG Lulu, WANG Qing, XU Guihua. Factors Affecting Pain in Patients with Parkinson's Disease: a Systematic Review [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(14): 1766-1774. |
| [15] | LIU Yanhui, CHEN Shuchun. Interpretation and Clinical Significance of the Definition and Diagnostic Criteria for Sarcopenic Obesity: ESPEN and EASO Consensus Statement [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(12): 1422-1428. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||