

Chinese General Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (35): 4487-4493.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2025.0175
• Original Research·Appropriate Technology Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2025-03-10
Revised:2025-08-15
Published:2025-12-15
Online:2025-10-15
Contact:
CHEN Weigang
通讯作者:
陈卫刚
作者简介:作者贡献:
张卉进行研究设计、研究实施、数据收集、统计分析、论文撰写和定稿;骆苗苗参与研究构思、论文写作指导和定稿;于晓杭参与数据分析、论文起草和定稿;林欣、冶丽娜、唐旋、李加学、谢欣宇、赖力、冯燕、刘永辉参与研究实施、数据收集和整理、论文批判性审阅;陈卫刚负责研究设计和实施指导,数据解释与分析,对文章内容进行批判性审阅和修改,论文定稿。
基金资助:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2025.0175
| 一般资料 | 早期食管癌及癌前病变组(n=34) | 对照组(n=77) | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 2.333 | 0.127 | ||
| 男 | 21(61.8) | 34(44.2) | ||
| 女 | 13(39.2) | 40(55.8) | ||
| 年龄 | 18.985 | 0.001 | ||
| 18~<40岁 | 1(2.9) | 21(27.3) | ||
| 40~<60岁 | 11(32.4) | 36(46.8) | ||
| 60~<80岁 | 17(50.0) | 18(23.4) | ||
| ≥80岁 | 5(14.7) | 2(2.5) | ||
| 民族 | 1.940 | 0.164 | ||
| 汉族 | 29(85.3) | 72(93.5) | ||
| 其他民族 | 5(14.7) | 5(6.5) | ||
| BMI | 0.454 | 0.797 | ||
| 正常 | 17(50.0) | 35(45.5) | ||
| 超重 | 14(41.2) | 32(41.5) | ||
| 肥胖 | 3(8.8) | 10(13.0) | ||
| 学历水平 | 9.244 | 0.055 | ||
| 小学 | 11(32.4) | 13(16.9) | ||
| 初中 | 10(29.1) | 15(19.5) | ||
| 高中 | 4(11.8) | 19(24.6) | ||
| 大学 | 6(17.6) | 10(13.0) | ||
| 大学本科以上 | 3(8.8) | 20(26.0) | ||
| 一级亲属是否患肿瘤 | 0.08 | 0.928 | ||
| 否 | 24(70.6) | 55(71.4) | ||
| 是 | 10(29.4) | 22(28.6) | ||
| 一级亲属是否患食管癌 | 0.64 | 0.830 | ||
| 否 | 30(88.2) | 69(89.6) | ||
| 是 | 4(11.8) | 8(10.4) | ||
| 是否口腔炎症 | 0.105 | 0.746 | ||
| 否 | 27(79.4) | 59(76.6) | ||
| 是 | 7(20.6) | 18(23.4) | ||
| 是否牙齿缺失 | 4.527 | 0.033 | ||
| 否 | 9(26.5) | 37(48.1) | ||
| 是 | 25(63.5) | 40(51.9) | ||
Table 1 Comparison of general information between the early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions group and the control group
| 一般资料 | 早期食管癌及癌前病变组(n=34) | 对照组(n=77) | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 2.333 | 0.127 | ||
| 男 | 21(61.8) | 34(44.2) | ||
| 女 | 13(39.2) | 40(55.8) | ||
| 年龄 | 18.985 | 0.001 | ||
| 18~<40岁 | 1(2.9) | 21(27.3) | ||
| 40~<60岁 | 11(32.4) | 36(46.8) | ||
| 60~<80岁 | 17(50.0) | 18(23.4) | ||
| ≥80岁 | 5(14.7) | 2(2.5) | ||
| 民族 | 1.940 | 0.164 | ||
| 汉族 | 29(85.3) | 72(93.5) | ||
| 其他民族 | 5(14.7) | 5(6.5) | ||
| BMI | 0.454 | 0.797 | ||
| 正常 | 17(50.0) | 35(45.5) | ||
| 超重 | 14(41.2) | 32(41.5) | ||
| 肥胖 | 3(8.8) | 10(13.0) | ||
| 学历水平 | 9.244 | 0.055 | ||
| 小学 | 11(32.4) | 13(16.9) | ||
| 初中 | 10(29.1) | 15(19.5) | ||
| 高中 | 4(11.8) | 19(24.6) | ||
| 大学 | 6(17.6) | 10(13.0) | ||
| 大学本科以上 | 3(8.8) | 20(26.0) | ||
| 一级亲属是否患肿瘤 | 0.08 | 0.928 | ||
| 否 | 24(70.6) | 55(71.4) | ||
| 是 | 10(29.4) | 22(28.6) | ||
| 一级亲属是否患食管癌 | 0.64 | 0.830 | ||
| 否 | 30(88.2) | 69(89.6) | ||
| 是 | 4(11.8) | 8(10.4) | ||
| 是否口腔炎症 | 0.105 | 0.746 | ||
| 否 | 27(79.4) | 59(76.6) | ||
| 是 | 7(20.6) | 18(23.4) | ||
| 是否牙齿缺失 | 4.527 | 0.033 | ||
| 否 | 9(26.5) | 37(48.1) | ||
| 是 | 25(63.5) | 40(51.9) | ||
| 一般资料 | 早期食管癌及癌前病变组(n=34) | 反流性食管炎组(n=150) | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 2.579 | 0.108 | ||
| 男 | 21(61.8) | 113(75.3) | ||
| 女 | 13(39.2) | 37(24.7) | ||
| 年龄 | 25.669 | 0.001 | ||
| 18~<40岁 | 1(2.9) | 20(13.3) | ||
| 40~<60岁 | 11(32.4) | 84(56.0) | ||
| 60~<80岁 | 17(50.0) | 45(30.0) | ||
| ≥80岁 | 5(14.7) | 1(0.7) | ||
| 民族 | 3.708 | 0.054 | ||
| 汉族 | 29(85.3) | 142(94.7) | ||
| 其他民族 | 5(14.7) | 8(5.3) | ||
| BMI | 6.483 | 0.039 | ||
| 正常 | 17(50.0) | 43(28.7) | ||
| 超重 | 14(41.2) | 76(50.7) | ||
| 肥胖 | 3(8.8) | 31(20.6) | ||
| 学历水平 | 5.440 | 0.245 | ||
| 小学 | 11(32.4) | 27(18.0) | ||
| 初中 | 10(29.1) | 41(27.3) | ||
| 高中 | 4(11.8) | 31(20.7) | ||
| 大学 | 6(17.6) | 24(16.0) | ||
| 大学本科以上 | 3(8.8) | 27(18.0) | ||
| 一级亲属是否患肿瘤 | 0.021 | 0.886 | ||
| 否 | 24(70.6) | 104(69.3) | ||
| 是 | 10(29.4) | 46(30.7) | ||
| 一级亲属是否患食管癌 | 0.502 | 0.479 | ||
| 否 | 30(88.2) | 125(83.3) | ||
| 是 | 4(11.8) | 25(16.7) | ||
| 是否口腔炎症 | 5.004 | 0.025 | ||
| 否 | 27(79.4) | 108(72.0) | ||
| 是 | 7(20.6) | 42(28.0) | ||
| 是否牙齿缺失 | 1.118 | 0.290 | ||
| 否 | 9(26.5) | 54(36.0) | ||
| 是 | 25(63.5) | 96(64.0) | ||
Table 2 Comparison of general information between the early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions group and reflux esophagitis group
| 一般资料 | 早期食管癌及癌前病变组(n=34) | 反流性食管炎组(n=150) | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 2.579 | 0.108 | ||
| 男 | 21(61.8) | 113(75.3) | ||
| 女 | 13(39.2) | 37(24.7) | ||
| 年龄 | 25.669 | 0.001 | ||
| 18~<40岁 | 1(2.9) | 20(13.3) | ||
| 40~<60岁 | 11(32.4) | 84(56.0) | ||
| 60~<80岁 | 17(50.0) | 45(30.0) | ||
| ≥80岁 | 5(14.7) | 1(0.7) | ||
| 民族 | 3.708 | 0.054 | ||
| 汉族 | 29(85.3) | 142(94.7) | ||
| 其他民族 | 5(14.7) | 8(5.3) | ||
| BMI | 6.483 | 0.039 | ||
| 正常 | 17(50.0) | 43(28.7) | ||
| 超重 | 14(41.2) | 76(50.7) | ||
| 肥胖 | 3(8.8) | 31(20.6) | ||
| 学历水平 | 5.440 | 0.245 | ||
| 小学 | 11(32.4) | 27(18.0) | ||
| 初中 | 10(29.1) | 41(27.3) | ||
| 高中 | 4(11.8) | 31(20.7) | ||
| 大学 | 6(17.6) | 24(16.0) | ||
| 大学本科以上 | 3(8.8) | 27(18.0) | ||
| 一级亲属是否患肿瘤 | 0.021 | 0.886 | ||
| 否 | 24(70.6) | 104(69.3) | ||
| 是 | 10(29.4) | 46(30.7) | ||
| 一级亲属是否患食管癌 | 0.502 | 0.479 | ||
| 否 | 30(88.2) | 125(83.3) | ||
| 是 | 4(11.8) | 25(16.7) | ||
| 是否口腔炎症 | 5.004 | 0.025 | ||
| 否 | 27(79.4) | 108(72.0) | ||
| 是 | 7(20.6) | 42(28.0) | ||
| 是否牙齿缺失 | 1.118 | 0.290 | ||
| 否 | 9(26.5) | 54(36.0) | ||
| 是 | 25(63.5) | 96(64.0) | ||
| 细胞学诊断 | 金标准 | 合计 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鳞状细胞癌/腺癌细胞 | 高级别上皮内瘤变 | 低级别上皮内瘤变 | 非典型鳞状细胞 | 炎细胞 | 区域水肿/细胞增生 | 正常细胞 | ||
| 癌细胞 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 鳞状上皮内高度病变 | 1 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 27 |
| 鳞状上皮内低级别病变 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 12 |
| 非典型鳞状细胞 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 12 | 7 | 53 | 20 | 101 |
| 鳞状细胞增生/炎细胞 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 55 | 46 | 111 |
| 无上皮内病变及恶性细胞 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| 合计 | 4 | 19 | 11 | 20 | 15 | 115 | 77 | 261 |
Table 3 Comparison of cytological findings with gastroscopic and histopathological findings
| 细胞学诊断 | 金标准 | 合计 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鳞状细胞癌/腺癌细胞 | 高级别上皮内瘤变 | 低级别上皮内瘤变 | 非典型鳞状细胞 | 炎细胞 | 区域水肿/细胞增生 | 正常细胞 | ||
| 癌细胞 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 鳞状上皮内高度病变 | 1 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 27 |
| 鳞状上皮内低级别病变 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 12 |
| 非典型鳞状细胞 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 12 | 7 | 53 | 20 | 101 |
| 鳞状细胞增生/炎细胞 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 55 | 46 | 111 |
| 无上皮内病变及恶性细胞 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| 合计 | 4 | 19 | 11 | 20 | 15 | 115 | 77 | 261 |
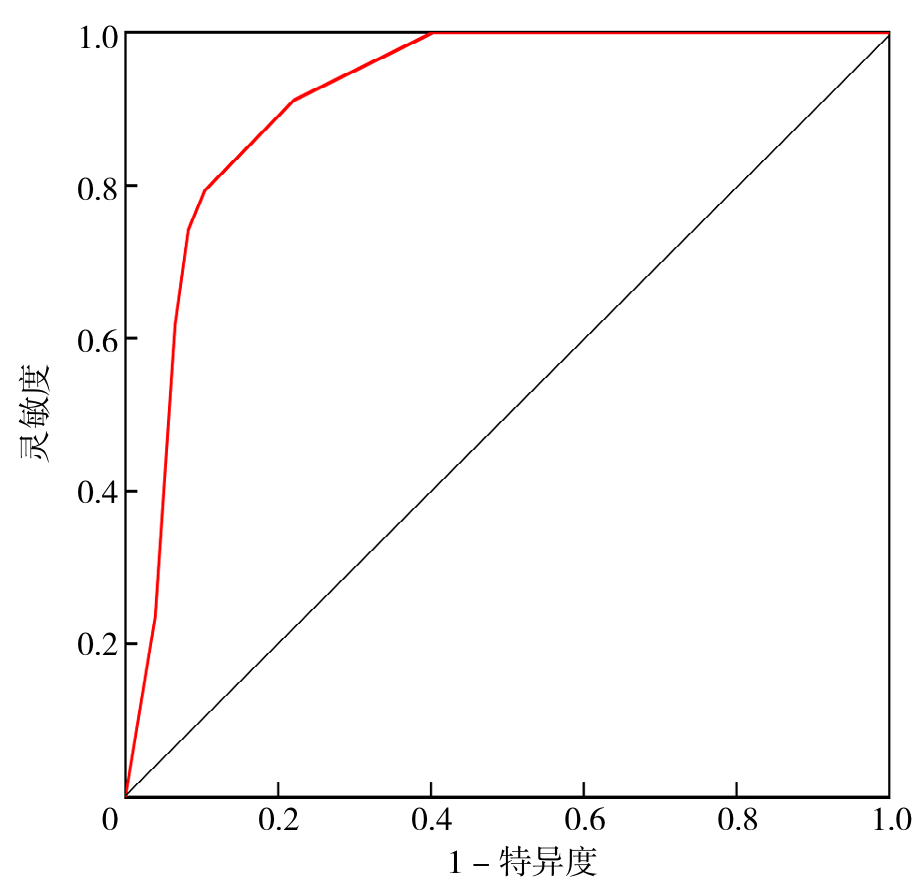
Figure 1 ROC curve for screening early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions in the early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesion group and the control group using a novel esophageal cell collector
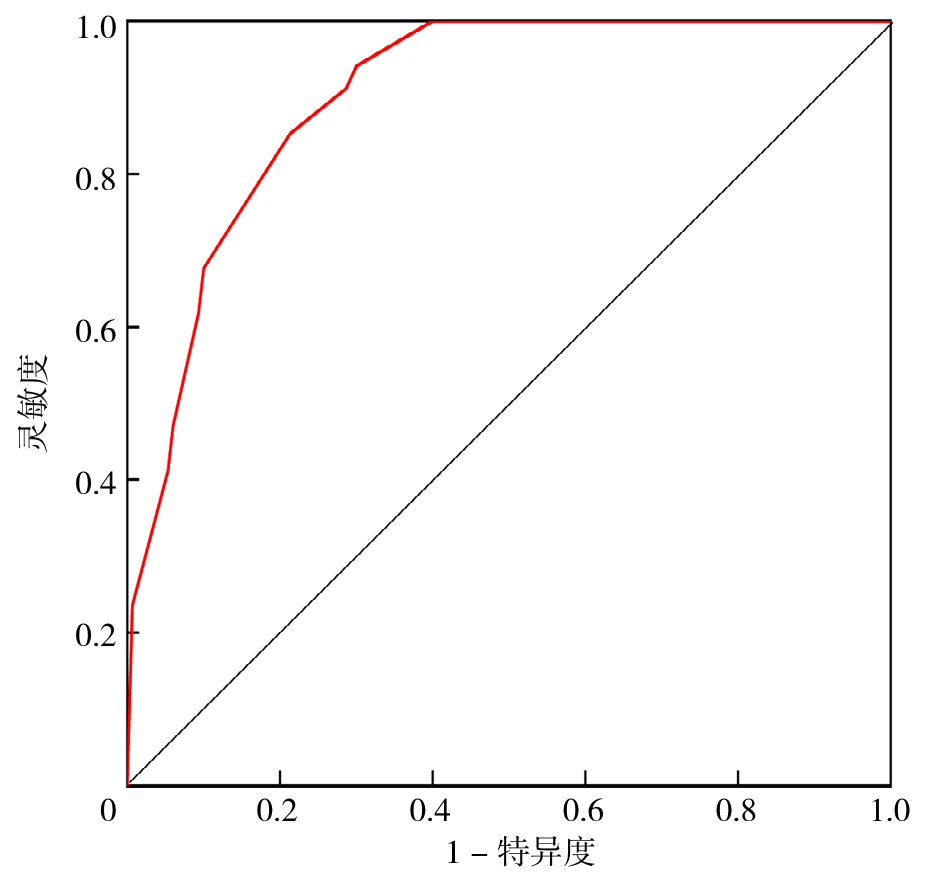
Figure 2 ROC curve for screening early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions in the early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesion group and the reflux esophagitis group using a novel esophageal cell collector
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
张正,张莉芳,刘彦廷,等. 《2022全球癌症统计报告》解读[J]. 中国医院统计,2024,31(5):393-400.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
陈志峰,董稚明. 食管-胃交界腺癌地域发病特点与思考[J]. 中国肿瘤临床,2011,38(1):57-60.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
王立东,宋昕,赵学科,等. 河南省食管癌高发现场防治和实验室研究60年回顾与展望[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版),2019,54(2):149-160.
|
| [12] |
沈琼. 食管细胞学诊断现况和展望[J]. 河南医药,1979(5):14-18,2.
|
| [13] |
丁源,朱铟楠,张婉月,等. 食管早癌筛查方法的研究进展[J]. 中华医学杂志,2023,103(26):2026-2030. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20230312-00380.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
蒋惠珊,高野,林寒,等. 人工智能食管细胞学风险预测模型在食管癌前病变中的构建和验证[J]. 中华消化内镜杂志,2024,41(10):762-767.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
康桂花. 胃镜检查的并发症及防治原则(附150例报告)[J]. 中国社区医师(医学专业),2012,14(7):248.
|
| [21] |
余珊,王志敏,殷红. 胃镜检查的并发症及防治[J]. 中国内镜杂志,2005,11(B11):220-221.
|
| [22] |
杨雅涵,管亦方,张小峰. 吸氧结合托下颌法对行无痛胃镜治疗患者呛咳、呼吸抑制的改善作用[J]. 齐鲁护理杂志,2022,28(11):62-64. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7256.2022.11.018.
|
| [23] |
|
| [1] | ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Huanyu, CHEN Kaiyue, LI Xiaohong, GUO Ying. Research on the Screening Effect and Strategy of Fasting Plasma Glucose and Glycosylated Hemoglobin for Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes Mellitus [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(32): 4055-4061. |
| [2] | ZHANG Jia, WANG Hairong, ZHAO Jing, SU Yifan. Influencing Factors of Screening Behavior of First-degree Relatives of Lung Cancer Patients Based on Logistic Regression and Decision Tree Model [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(31): 3961-3967. |
| [3] | XU Baichuan, WANG Yan, ZHANG Peng, LI Yiting, LIU Feilai, XIE Yang. Research and Analysis of Screening Tools for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Comorbidity Lung Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3847-3852. |
| [4] | MA Wenyuan, QI Shuo, SHANG Jianwei, CHEN Xiaoheng, LI Zhe, LI Huilong, HU Rui, LI Lu, SI Xinying, DING Zhiguo. Preliminary Development of a TCM Syndrome Evaluation Scale for Hashimoto's Thyroiditis with Normal Thyroid Function: Based on Expert Consultation and Clinical Survey [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(28): 3590-3600. |
| [5] | YU Wenhua, LI Jianguo, DUAN Wenyan, GAO Xuyan, LI Xiaxia, ZHANG Zilong, ZHANG Li, MA Lina. Reliability and Validity of the Function Impairment Screening Tool among Community-dwelling Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 3000-3004. |
| [6] | SHI Jiarui, WANG Zili, ZHANG Xueqing, SONG Yulei, XU Guihua, BAI Yamei. The Current Status of Initial Cognitive Screening Services in Community-based Cognitive Services Centers in Nanjing [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2784-2790. |
| [7] | LI Jia, TAN Wenbin. The Dilemma of Prevention and Treatment of Secondary Osteoporosis and Its Countermeasures [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2075-2081. |
| [8] | ZHANG Qi, HE Shen, LI Hua. Interpretation of Screening for Depression and Suicide Risk in Children and Adolescents: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement 2022 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(15): 1823-1830. |
| [9] | ZENG Yongtian, CHEN Riling, NONG Xueyan, LIU Zhou, LIANG Lizhong, ZHU Zijian. Clinical Research Progress and Challenges of Digital Therapeutics from Screening to Intervention in Autism Spectrum Disorder [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1702-1708. |
| [10] | WU Dadong, LIU Huimin, ZHANG Jiayi, LIU Siyuan, ZHAO Guanglin, JIN Shuyan, JIANG Lei. Application and Evaluation of the Mobile Platform for Perinatal Depression Screening and Intervention [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1773-1780. |
| [11] | ZHANG Yushuang, WU Zhongbing, HUANG Ming, JIA Lei, GAO Shuang, ZHAO Weipeng, LI Jing. Study on Metabolic Characteristics in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients with TCM Differentiation of Deficiency of Fluid and Blood Based on Non Target Metabolomics [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(12): 1513-1519. |
| [12] | CHI Xun, LIU Sisi, CHEN Qiao, HU Yue, WANG Weixian. The Suitability of Four Nutritional Screening Tools for Nutritional Screening in Patients with Cirrhosis: a Network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(11): 1395-1402. |
| [13] | SHU Ting, LAN Zhipeng, WU Xia, LUO Yingjuan, YANG Liu. Study on the Infection and Related Factors of High-risk HPV in Cervical Cancer Screening Women: Based on 450 000 Participants in Chengdu [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(02): 213-219. |
| [14] | ZHANG Shuo, ZHANG Long, ZHANG Yan, LI Jianping. Advances in Molecular Biotechnology for Diagnosing and Treating Familial Hypercholesterolemia [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(36): 4498-4504. |
| [15] | LI Yuan, MA Hongyang, LI Biao, YUE Anna, SHAO Yaqing, SUN Kangyun. Clinical Significance of Screening for Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Patients with Hypercholesterolemia [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(36): 4515-4521. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||