

Chinese General Practice ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (01): 91-97.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0346
• Original Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2023-03-13
Revised:2023-08-30
Published:2024-01-05
Online:2023-10-23
Contact:
TIAN Chaowei
通讯作者:
田朝伟
作者简介:基金资助:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0346
| 分层 | TC | LDL-C | HDL-C | 非HDL-C | TG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 理想水平 | — | <2.6(100) | — | <3.4(130) | — |
| 合适水平 | <5.2(200) | <3.4(130) | — | <4.1(160) | <1.7(150) |
| 边缘水平 | ≥5.2(200)且<6.2(240) | ≥3.4(130)且<4.1(160) | — | ≥4.1(160)且<4.9(190) | ≥1.7(150)且<2.3(200) |
| 升高 | ≥6.2(240) | ≥4.1(160) | — | ≥4.9(190) | ≥2.3(200) |
| 降低 | — | — | <1.0(40) | — | — |
Table 1 Chinese lipid stratification standard
| 分层 | TC | LDL-C | HDL-C | 非HDL-C | TG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 理想水平 | — | <2.6(100) | — | <3.4(130) | — |
| 合适水平 | <5.2(200) | <3.4(130) | — | <4.1(160) | <1.7(150) |
| 边缘水平 | ≥5.2(200)且<6.2(240) | ≥3.4(130)且<4.1(160) | — | ≥4.1(160)且<4.9(190) | ≥1.7(150)且<2.3(200) |
| 升高 | ≥6.2(240) | ≥4.1(160) | — | ≥4.9(190) | ≥2.3(200) |
| 降低 | — | — | <1.0(40) | — | — |
| 项目 | 生存组(n=3 176) | 死亡组(n=287) | χ2(Z)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女) | 1 320/1 856 | 166/121 | 28.470a | <0.001 |
| 体育锻炼情况[例(%)] | 28.791a | <0.001 | ||
| 经常锻炼 | 2 006(63.16) | 138(48.08) | ||
| 偶尔锻炼 | 513(16.15) | 55(19.16) | ||
| 不锻炼 | 657(20.69) | 94(32.75) | ||
| 吸烟情况[例(%)] | 5.053a | 0.080 | ||
| 从不吸烟 | 2 724(85.77) | 233(81.18) | ||
| 已戒烟 | 154(4.85) | 21(7.32) | ||
| 吸烟 | 298(9.38) | 33(11.50) | ||
| 饮酒情况[例(%)] | 4.572a | 0.206 | ||
| 从不饮酒 | 2 857(89.96) | 259(90.24) | ||
| 偶尔饮酒 | 230(7.24) | 15(5.23) | ||
| 经常饮酒 | 34(1.07) | 4(1.39) | ||
| 每天饮酒 | 55(1.73) | 9(3.14) | ||
| 高血压及糖尿病患病情况[例(%)] | 15.719a | 0.001 | ||
| 否 | 1 046(32.93) | 65(22.65) | ||
| 高血压 | 1 443(45.43) | 139(48.43) | ||
| 糖尿病 | 172(5.42) | 19(6.62) | ||
| 高血压合并糖尿病 | 515(16.22) | 64(22.30) | ||
| 血脂异常情况[例(%)] | 28.132a | <0.001 | ||
| 血脂正常 | 621(19.55) | 56(19.51) | ||
| 混合型血脂紊乱 | 1 692(53.27) | 141(49.13) | ||
| 高甘油三酯症 | 200(6.30) | 8(2.79) | ||
| 高胆固醇血症 | 516(16.25) | 50(17.42) | ||
| 脂蛋白紊乱 | 147(4.63) | 32(11.15) | ||
| BMI[M(P25,P75)] | 23.6(21.6,25.7) | 23.3(20.8,26.0) | -2.091b | 0.037 |
| 腰围[M(P25,P75),cm] | 84.0(78.0,89.5) | 85.0(79.0,91.0) | -2.391b | 0.017 |
| TC[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 5.54(4.83,6.31) | 5.38(4.62,6.12) | -2.392b | 0.017 |
| TG[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 1.58(1.15,2.23) | 1.47(1.09,1.99) | -2.242b | 0.025 |
| LDL-C[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 3.60(2.89,4.29) | 3.41(2.76,4.16) | -2.099b | 0.036 |
| HDL-C[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 1.24(1.06,1.49) | 1.14(0.94,1.41) | -4.218b | <0.001 |
| 空腹血糖水平[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 5.41(5.02,6.02) | 5.50(5.06,6.43) | -2.105b | 0.035 |
| 红细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×1012/L] | 4.50(4.22,4.83) | 4.42(4.09,4.81) | -2.764b | 0.006 |
| 血红蛋白水平[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 131(123,140) | 129(115,137) | -4.067b | <0.001 |
| 白细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 6.7(5.7,7.9) | 7.0(5.9,8.6) | -3.146b | 0.002 |
| 血小板计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 238(202,280) | 227(187,282) | -1.990b | 0.047 |
| 血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶水平[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 16.5(12.0,22.0) | 14.3(10.6,20.7) | -2.996b | 0.003 |
| 血清天冬氨酸氨基转移酶水平[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 20.0(17.2,23.6) | 19.8(16.3,24.0) | -0.587b | 0.557 |
| 总胆红素水平[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 10.6(8.5,13.3) | 10.5(7.6,13.8) | -0.554b | 0.579 |
| 血清肌酐水平[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 75.4(64.5,89.2) | 86.4(72.9,104.6) | -7.821b | <0.001 |
| 血尿氮素水平[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 5.38(4.61,6.31) | 5.67(4.81,7.29) | -4.401b | <0.001 |
Table 2 Comparison of baseline physical examination data between the survival group and death group of elderly physical examination residents
| 项目 | 生存组(n=3 176) | 死亡组(n=287) | χ2(Z)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女) | 1 320/1 856 | 166/121 | 28.470a | <0.001 |
| 体育锻炼情况[例(%)] | 28.791a | <0.001 | ||
| 经常锻炼 | 2 006(63.16) | 138(48.08) | ||
| 偶尔锻炼 | 513(16.15) | 55(19.16) | ||
| 不锻炼 | 657(20.69) | 94(32.75) | ||
| 吸烟情况[例(%)] | 5.053a | 0.080 | ||
| 从不吸烟 | 2 724(85.77) | 233(81.18) | ||
| 已戒烟 | 154(4.85) | 21(7.32) | ||
| 吸烟 | 298(9.38) | 33(11.50) | ||
| 饮酒情况[例(%)] | 4.572a | 0.206 | ||
| 从不饮酒 | 2 857(89.96) | 259(90.24) | ||
| 偶尔饮酒 | 230(7.24) | 15(5.23) | ||
| 经常饮酒 | 34(1.07) | 4(1.39) | ||
| 每天饮酒 | 55(1.73) | 9(3.14) | ||
| 高血压及糖尿病患病情况[例(%)] | 15.719a | 0.001 | ||
| 否 | 1 046(32.93) | 65(22.65) | ||
| 高血压 | 1 443(45.43) | 139(48.43) | ||
| 糖尿病 | 172(5.42) | 19(6.62) | ||
| 高血压合并糖尿病 | 515(16.22) | 64(22.30) | ||
| 血脂异常情况[例(%)] | 28.132a | <0.001 | ||
| 血脂正常 | 621(19.55) | 56(19.51) | ||
| 混合型血脂紊乱 | 1 692(53.27) | 141(49.13) | ||
| 高甘油三酯症 | 200(6.30) | 8(2.79) | ||
| 高胆固醇血症 | 516(16.25) | 50(17.42) | ||
| 脂蛋白紊乱 | 147(4.63) | 32(11.15) | ||
| BMI[M(P25,P75)] | 23.6(21.6,25.7) | 23.3(20.8,26.0) | -2.091b | 0.037 |
| 腰围[M(P25,P75),cm] | 84.0(78.0,89.5) | 85.0(79.0,91.0) | -2.391b | 0.017 |
| TC[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 5.54(4.83,6.31) | 5.38(4.62,6.12) | -2.392b | 0.017 |
| TG[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 1.58(1.15,2.23) | 1.47(1.09,1.99) | -2.242b | 0.025 |
| LDL-C[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 3.60(2.89,4.29) | 3.41(2.76,4.16) | -2.099b | 0.036 |
| HDL-C[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 1.24(1.06,1.49) | 1.14(0.94,1.41) | -4.218b | <0.001 |
| 空腹血糖水平[M(P25,P75),mmol/L] | 5.41(5.02,6.02) | 5.50(5.06,6.43) | -2.105b | 0.035 |
| 红细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×1012/L] | 4.50(4.22,4.83) | 4.42(4.09,4.81) | -2.764b | 0.006 |
| 血红蛋白水平[M(P25,P75),g/L] | 131(123,140) | 129(115,137) | -4.067b | <0.001 |
| 白细胞计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 6.7(5.7,7.9) | 7.0(5.9,8.6) | -3.146b | 0.002 |
| 血小板计数[M(P25,P75),×109/L] | 238(202,280) | 227(187,282) | -1.990b | 0.047 |
| 血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶水平[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 16.5(12.0,22.0) | 14.3(10.6,20.7) | -2.996b | 0.003 |
| 血清天冬氨酸氨基转移酶水平[M(P25,P75),U/L] | 20.0(17.2,23.6) | 19.8(16.3,24.0) | -0.587b | 0.557 |
| 总胆红素水平[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 10.6(8.5,13.3) | 10.5(7.6,13.8) | -0.554b | 0.579 |
| 血清肌酐水平[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 75.4(64.5,89.2) | 86.4(72.9,104.6) | -7.821b | <0.001 |
| 血尿氮素水平[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 5.38(4.61,6.31) | 5.67(4.81,7.29) | -4.401b | <0.001 |
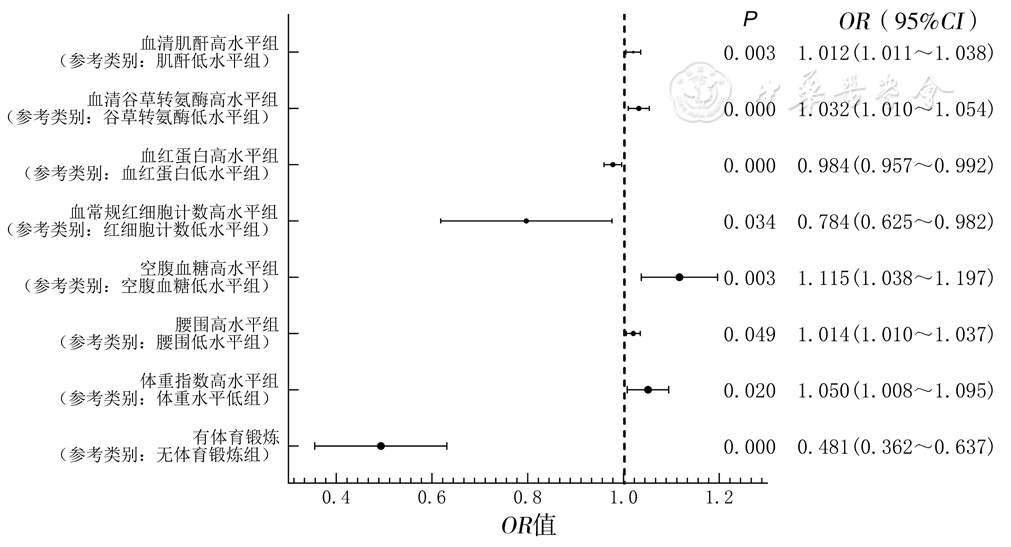
Figure 2 Cox proportional hazards regression model of factors influencing 5-year crude survival rate in elderly residents with hypertension and diabetes combined with dyslipidemia
| [1] |
王丽敏,陈志华,张梅,等. 中国老年人群慢性病患病状况和疾病负担研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2019,40(3):277-283. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.03.005.
|
| [2] |
范潇茹,陈莎,施予宁,等. 我国中老年人慢性病共病现状及其对卫生服务利用和医疗费用的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(19):2371-2378. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0220.
|
| [3] |
潘晔,刘志辉,胡倩倩,等. 中国老年人慢性病多病共存模式的研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2023,26(29):3608-3615. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0186.
|
| [4] |
章轶立,黄馨懿,齐保玉,等. 老年人共病研究的现实意义、内容方法与前景展望[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2023,23(7):862-868. DOI:10.7507/1672-2531.202302103.
|
| [5] |
国家心血管病中心国家基本公共卫生服务项目基层高血压管理办公室,国家基层高血压管理专家委员会. 国家基层高血压防治管理指南2020版[J]. 中国循环杂志,2021,36(3):209-220. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2021.03.001.
|
| [6] |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会,国家基层糖尿病防治管理办公室. 国家基层糖尿病防治管理指南(2022)[J]. 中华内科杂志,2022,61(3):249-262. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20220120-000063.
|
| [7] |
诸骏仁,高润霖,赵水平,等. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中国循环杂志,2016,31(10):937-953. DOI:CNKI:SUN:ZGXH.0.2016-10-002
|
| [8] |
国家卫生健康委. "健康中国2030"规划纲要[J]. 中国预防医学杂志,2019,20(8):770.
|
| [9] |
人民日报. 人均预期寿命已达77.93岁:我国主要健康指标居中高收入国家前列[EB/OL]. (2022-07-06)[2023-03-13].
|
| [10] |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 国际内分泌代谢杂志,2021,41(5):482-548. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn121383-20210825-08063.
|
| [11] |
邢辰. 《ISH2020国际高血压实践指南》全球首发[J]. 中华医学信息导报,2020,35(9):16. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-8039.2020.09.112.
|
| [12] |
国家心血管病中心. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2020[J]. 心肺血管病杂志,2021,40(9):885-889.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
毛娟娟,宣浩军,俞星飞,等. 乳腺癌患者病理分期和分子分型与肿瘤标志物及血脂水平的关系[J]. 现代实用医学,2021,33(6):774-775. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2021.06.034.
|
| [17] |
董娅. 血脂水平检测在治疗小细胞肺癌中的临床意义[D]. 青岛:青岛大学,2021.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
程兴浩. 血生化指标变化与结直肠癌相关性的回顾性研究[D]. 沈阳:中国医科大学,2021.
|
| [20] |
尹钟平. 乳腺癌术后患者的血脂对机体免疫状态及预后的影响[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2020.
|
| [21] | |
| [22] |
杨超,王晋伟,杨尧政,等. 贫血及慢性肾脏病对糖尿病人群心脑血管事件发生与死亡的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2018,50(3):495-500. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.03.017.
|
| [23] |
吕跃斌,殷召雪,罗杰斯,等. 中国长寿地区高龄老年人贫血及其3年死亡风险关系的研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2015,36(7):682-686. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2015.07.004.
|
| [24] |
郑刚. 红细胞分布宽度是预测心力衰竭和死亡危险的标记物[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2012,14(11):1219-1220. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-0126.2012.11.030.
|
| [1] | DAI Yuheng, GAO Chang, LIANG Xinxiu, LU Sha, HUA Wen, ZHENG Jusheng, HU Wensheng. Association of Gut Microbiota with Hypertensive Disorders in Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(02): 156-162. |
| [2] | ZHOU Xuan, ZHANG Dan. Construction of an Integrated Management Model for Geriatric Comorbidities under Medical Association Based on PDSA Theory [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(02): 192-200. |
| [3] | PAN Hongwei, LIU Li, MA Chao, DENG Guangpu, FANG Haoting, HUANG Shuwei, ZHU Hong. The Current Status and Influencing Factors of Treatment Adherence to National Chronic Disease Management Services for Hypertensive Population in a Community Healthcare Center in Guangzhou [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(01): 59-66. |
| [4] | LIU Zhigang, LIU Shimeng, ZHENG Lyuyun, XUE Wenjing, CAO Chenchen, LIU Jing, CHEN Yingyao. Second-line Medication Preference in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: a Study Based on a Discrete Choice Experiment [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(01): 67-73. |
| [5] | YAO lin, SHANG Danmei, ZHAO Hui, LIU Xinyu, LIU Yongwei, JIANG Yong. The Effect and Satisfaction of Mobile Network in the Hypertension Management of Community-dwelling Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(01): 85-90. |
| [6] | YANG Haiyan, LI Ting, JIN Guanghui, LU Xiaoqin. Barriers in Monitoring and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Based on the Perspective of General Practitioners: a Qualitative Research [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(01): 98-104. |
| [7] | ZHAO Yi, YANG Jingyuan, YANG Xing, ZHOU Quanxiang, JIANG Yun, HUANG Hui, ZHU Yujie. The Relationship between Multi-dimensional Frailty and Impairment of Activities of Daily Living in Rural Elderly [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(01): 79-84. |
| [8] | WANG Ruijie, LI Hongyu, SHI Hong. Association of Tooth Loss with Hearing Impairment in Chinese Older Adults Aged 65 Years and Above [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(01): 45-50. |
| [9] | ZHANG Qian, LI Shu, LI Pengmei. Interpretation of the 2023 AGS Beers Criteria: Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(35): 4372-4381. |
| [10] | CHU Xiaojing, LI Jun, FU Yanqin, LIU Danqing, LIU Aiping, ZHANG Yuanyuan. Effect of Human Body Composition and Serum Biochemical Indicators on the Accuracy of Flash Glucose Monitoring System [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(35): 4433-4438. |
| [11] | ZHONG Pingping, NAN Yayun, PENG Linlin, ZHOU Yuting, CHEN Qiong. A Bibliometrics Analysis of Polypharmacy in the Elderly from 2003 to 2022 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(35): 4404-4411. |
| [12] | CHEN Yanyan, SHI Min, WANG Yi, FU Jianfang, ZHANG Ying, LIU Xiangyang, ZHANG Weiqing, TA Shengjun, LIU Liwen, LI Zeping, ZHOU Jie, LI Xiaomiao. Correlation between Subclinical Left Ventricular Systolic Function and Diabetic Microvascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(35): 4412-4418. |
| [13] | XIE Xuemei, GAO Jing, BAI Dingxi, LU Xianying, HE Jiali, LI Yue. Current Status of Polypharmacy in the Elderly and Its Influencing Factors: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(35): 4394-4403. |
| [14] | XU Man, AN Zhuoling, ZHANG Yuhui, MA Zhuo. Current Situation of Potentially Inappropriate Medication in Older Cancer Patients and Strategies to Address It [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(35): 4382-4387. |
| [15] | LIU Yinghong, YANG Xiaojuan. Recent Advances in Clinical Management of Takayasu's Arteritis in Pregnancy [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(35): 4483-4486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||