

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (13): 1618-1623.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.341
Special Issue: 社区卫生服务最新研究合集
• Original Research·Primary Health Services • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2021-08-19
Revised:2021-11-25
Published:2021-12-23
Online:2022-04-22
Contact:
Xuejiao ZHU
About author:
通讯作者:
朱雪娇
作者简介:基金资助:
| 项目 | 例数 | 服务体验得分 | F(t)值 | P值 | 项目 | 例数 | 服务体验得分 | F(t)值 | P值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | -2.640a | 0.009 | 合并其他疾病 | -2.253a | 0.025 | ||||||
| 男 | 264 | -1.74±0.80 | 否 | 313 | -1.71±0.76 | ||||||
| 女 | 261 | -1.56±0.75 | 是 | 212 | -1.55±0.80 | ||||||
| 年龄(岁) | 1.418 | 0.227 | 签约时长(年) | 3.528 | 0.002 | ||||||
| ≤59 | 38 | -1.64±0.77 | <1 | 4 | -1.70±0.88 | ||||||
| 60~69 | 153 | -1.73±0.73 | 1 | 26 | -1.99±0.67 | ||||||
| 70~79 | 213 | -1.61±0.77 | 2 | 49 | -1.97±0.74 | ||||||
| 80~89 | 109 | -1.65±0.83 | 3 | 73 | -1.75±0.81 | ||||||
| ≥90 | 12 | -1.23±1.02 | 4 | 64 | -1.48±0.76 | ||||||
| 文化程度 | 0.999 | 0.408 | 5 | 54 | -1.63±0.68 | ||||||
| 小学及以下 | 155 | -1.72±0.78 | ≥6 | 255 | -1.56±0.79 | ||||||
| 初中 | 185 | -1.64±0.77 | 更换服务团队 | 2.014a | 0.045 | ||||||
| 高中或中专 | 119 | -1.64±0.71 | 否 | 345 | -1.60±0.80 | ||||||
| 大专 | 33 | -1.59±0.95 | 是 | 180 | -1.74±0.73 | ||||||
| 本科及以上 | 33 | -1.43±0.85 | 接受的服务内容项目数(项) | 22.010 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 月收入(元) | 2.618 | 0.051 | 1 | 18 | -1.99±0.74 | ||||||
| ≤1 000 | 6 | -2.16±0.92 | 2 | 83 | -2.15±0.79 | ||||||
| 1 001~3 000 | 56 | -1.86±0.79 | 3 | 187 | -1.80±0.69 | ||||||
| 3 001~5 000 | 280 | -1.62±0.75 | 4 | 147 | -1.40±0.68 | ||||||
| ≥5 001 | 183 | -1.60±0.81 | 5 | 85 | -1.25±0.73 | ||||||
| 医疗费用支付方式 | 5.385 | 0.005 | 6 | 5 | -0.58±0.29 | ||||||
| 全自费 | 3 | -2.20±0.96 | 接受的服务方式种类数(种) | 12.240 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 部分自费 | 517 | -1.65±0.77 | 1 | 92 | -2.03±0.83 | ||||||
| 公费 | 5 | -0.60±0.34 | 2 | 235 | -1.71±0.74 | ||||||
| 生活自理能力评分(分) | 1.216 | 0.303 | 3 | 159 | -1.46±0.69 | ||||||
| 1 | 1 | 0.00±0.00 | 4 | 35 | -1.18±0.75 | ||||||
| 2 | 2 | -1.40±1.27 | 5 | 2 | -0.98±0.81 | ||||||
| 3 | 21 | -1.62±0.81 | 6 | 2 | -0.13±0.18 | ||||||
| 4 | 69 | -1.68±0.82 | 利用的智慧医疗项目数(项) | 8.123 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 5 | 432 | -1.65±0.77 | 1 | 256 | -1.78±0.77 | ||||||
| 患病数量(种) | 0.198 | 0.821 | 2 | 267 | -1.52±0.77 | ||||||
| 1 | 278 | -1.63±0.76 | 3 | 2 | -1.03±1.45 | ||||||
| 2 | 211 | -1.66±0.80 | |||||||||
| 3 | 36 | -1.72±0.81 | |||||||||
Table 1 Experience of integrated medical-elderly-nursing services in community-dwelling chronic disease patients by personal characteristics
| 项目 | 例数 | 服务体验得分 | F(t)值 | P值 | 项目 | 例数 | 服务体验得分 | F(t)值 | P值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | -2.640a | 0.009 | 合并其他疾病 | -2.253a | 0.025 | ||||||
| 男 | 264 | -1.74±0.80 | 否 | 313 | -1.71±0.76 | ||||||
| 女 | 261 | -1.56±0.75 | 是 | 212 | -1.55±0.80 | ||||||
| 年龄(岁) | 1.418 | 0.227 | 签约时长(年) | 3.528 | 0.002 | ||||||
| ≤59 | 38 | -1.64±0.77 | <1 | 4 | -1.70±0.88 | ||||||
| 60~69 | 153 | -1.73±0.73 | 1 | 26 | -1.99±0.67 | ||||||
| 70~79 | 213 | -1.61±0.77 | 2 | 49 | -1.97±0.74 | ||||||
| 80~89 | 109 | -1.65±0.83 | 3 | 73 | -1.75±0.81 | ||||||
| ≥90 | 12 | -1.23±1.02 | 4 | 64 | -1.48±0.76 | ||||||
| 文化程度 | 0.999 | 0.408 | 5 | 54 | -1.63±0.68 | ||||||
| 小学及以下 | 155 | -1.72±0.78 | ≥6 | 255 | -1.56±0.79 | ||||||
| 初中 | 185 | -1.64±0.77 | 更换服务团队 | 2.014a | 0.045 | ||||||
| 高中或中专 | 119 | -1.64±0.71 | 否 | 345 | -1.60±0.80 | ||||||
| 大专 | 33 | -1.59±0.95 | 是 | 180 | -1.74±0.73 | ||||||
| 本科及以上 | 33 | -1.43±0.85 | 接受的服务内容项目数(项) | 22.010 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 月收入(元) | 2.618 | 0.051 | 1 | 18 | -1.99±0.74 | ||||||
| ≤1 000 | 6 | -2.16±0.92 | 2 | 83 | -2.15±0.79 | ||||||
| 1 001~3 000 | 56 | -1.86±0.79 | 3 | 187 | -1.80±0.69 | ||||||
| 3 001~5 000 | 280 | -1.62±0.75 | 4 | 147 | -1.40±0.68 | ||||||
| ≥5 001 | 183 | -1.60±0.81 | 5 | 85 | -1.25±0.73 | ||||||
| 医疗费用支付方式 | 5.385 | 0.005 | 6 | 5 | -0.58±0.29 | ||||||
| 全自费 | 3 | -2.20±0.96 | 接受的服务方式种类数(种) | 12.240 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 部分自费 | 517 | -1.65±0.77 | 1 | 92 | -2.03±0.83 | ||||||
| 公费 | 5 | -0.60±0.34 | 2 | 235 | -1.71±0.74 | ||||||
| 生活自理能力评分(分) | 1.216 | 0.303 | 3 | 159 | -1.46±0.69 | ||||||
| 1 | 1 | 0.00±0.00 | 4 | 35 | -1.18±0.75 | ||||||
| 2 | 2 | -1.40±1.27 | 5 | 2 | -0.98±0.81 | ||||||
| 3 | 21 | -1.62±0.81 | 6 | 2 | -0.13±0.18 | ||||||
| 4 | 69 | -1.68±0.82 | 利用的智慧医疗项目数(项) | 8.123 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 5 | 432 | -1.65±0.77 | 1 | 256 | -1.78±0.77 | ||||||
| 患病数量(种) | 0.198 | 0.821 | 2 | 267 | -1.52±0.77 | ||||||
| 1 | 278 | -1.63±0.76 | 3 | 2 | -1.03±1.45 | ||||||
| 2 | 211 | -1.66±0.80 | |||||||||
| 3 | 36 | -1.72±0.81 | |||||||||
| 自变量 | b(95%CI) | SE | b' | t值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(以男为参照) | ||||||
| 女 | 0.175(0.048,0.302) | 0.064 | 0.112 | 2.713 | 0.007 | |
| 月收入(以实际值纳入) | 0.115(0.021,0.210) | 0.048 | 0.100 | 2.409 | 0.016 | |
| 医疗费用支付方式(公费)a | 0.785(0.178,1.392) | 0.309 | 0.098 | 2.540 | 0.011 | |
| 患病数量(以实际值纳入) | -0.111(-0.208,-0.013) | 0.050 | -0.088 | -2.227 | 0.026 | |
| 更换服务团队(以否为参照) | ||||||
| 是 | -0.128(-0.251,-0.004) | 0.063 | -0.078 | -2.030 | 0.043 | |
| 接受的服务内容项目数(以实际值纳入) | 0.254(0.196,0.313) | 0.030 | 0.350 | 8.518 | <0.001 | |
| 接受的服务方式种类数(以实际值纳入) | 0.178(0.107,0.248) | 0.036 | 0.199 | 4.944 | <0.001 | |
| 常量 | -3.348(-3.809,-2.887) | 0.235 | - | -14.271 | <0.001 | |
Table 2 Multiple linear regression analysis of the factors affecting community-dwelling chronic disease patients' experience of integrated medical-elderly-nursing services
| 自变量 | b(95%CI) | SE | b' | t值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(以男为参照) | ||||||
| 女 | 0.175(0.048,0.302) | 0.064 | 0.112 | 2.713 | 0.007 | |
| 月收入(以实际值纳入) | 0.115(0.021,0.210) | 0.048 | 0.100 | 2.409 | 0.016 | |
| 医疗费用支付方式(公费)a | 0.785(0.178,1.392) | 0.309 | 0.098 | 2.540 | 0.011 | |
| 患病数量(以实际值纳入) | -0.111(-0.208,-0.013) | 0.050 | -0.088 | -2.227 | 0.026 | |
| 更换服务团队(以否为参照) | ||||||
| 是 | -0.128(-0.251,-0.004) | 0.063 | -0.078 | -2.030 | 0.043 | |
| 接受的服务内容项目数(以实际值纳入) | 0.254(0.196,0.313) | 0.030 | 0.350 | 8.518 | <0.001 | |
| 接受的服务方式种类数(以实际值纳入) | 0.178(0.107,0.248) | 0.036 | 0.199 | 4.944 | <0.001 | |
| 常量 | -3.348(-3.809,-2.887) | 0.235 | - | -14.271 | <0.001 | |
| 项目 | 适配标准 | 本模型结果 | 结果判定 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绝对拟合度指数 | ||||
| χ2值 | P<0.05 | 194.479(P<0.001) | 良好 | |
| RMSEA | <0.08为适配合理,<0.05为适配良好 | 0.07 | 合理 | |
| SRMR | <0.08 | 0.05 | 良好 | |
| GFI | >0.90 | 0.95 | 良好 | |
| AGFI | >0.90 | 0.92 | 良好 | |
| 增值适配度指数 | ||||
| NFI | >0.90 | 0.92 | 良好 | |
| RFI | >0.90 | 0.90 | 良好 | |
| IFI | >0.90 | 0.95 | 良好 | |
| CFI | >0.90 | 0.95 | 良好 | |
| 简约适配度指数 | ||||
| PNFI | >0.50 | 0.70 | 良好 | |
| PGFI | >0.50 | 0.72 | 良好 | |
| χ2/df | >1~<5 | 3.30 | 良好 | |
Table 3 Goodness of fit indices for the verification model of the influencing factors of the experience of integrated medical-elderly-nursing services in community-dwelling chronic disease patients
| 项目 | 适配标准 | 本模型结果 | 结果判定 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绝对拟合度指数 | ||||
| χ2值 | P<0.05 | 194.479(P<0.001) | 良好 | |
| RMSEA | <0.08为适配合理,<0.05为适配良好 | 0.07 | 合理 | |
| SRMR | <0.08 | 0.05 | 良好 | |
| GFI | >0.90 | 0.95 | 良好 | |
| AGFI | >0.90 | 0.92 | 良好 | |
| 增值适配度指数 | ||||
| NFI | >0.90 | 0.92 | 良好 | |
| RFI | >0.90 | 0.90 | 良好 | |
| IFI | >0.90 | 0.95 | 良好 | |
| CFI | >0.90 | 0.95 | 良好 | |
| 简约适配度指数 | ||||
| PNFI | >0.50 | 0.70 | 良好 | |
| PGFI | >0.50 | 0.72 | 良好 | |
| χ2/df | >1~<5 | 3.30 | 良好 | |
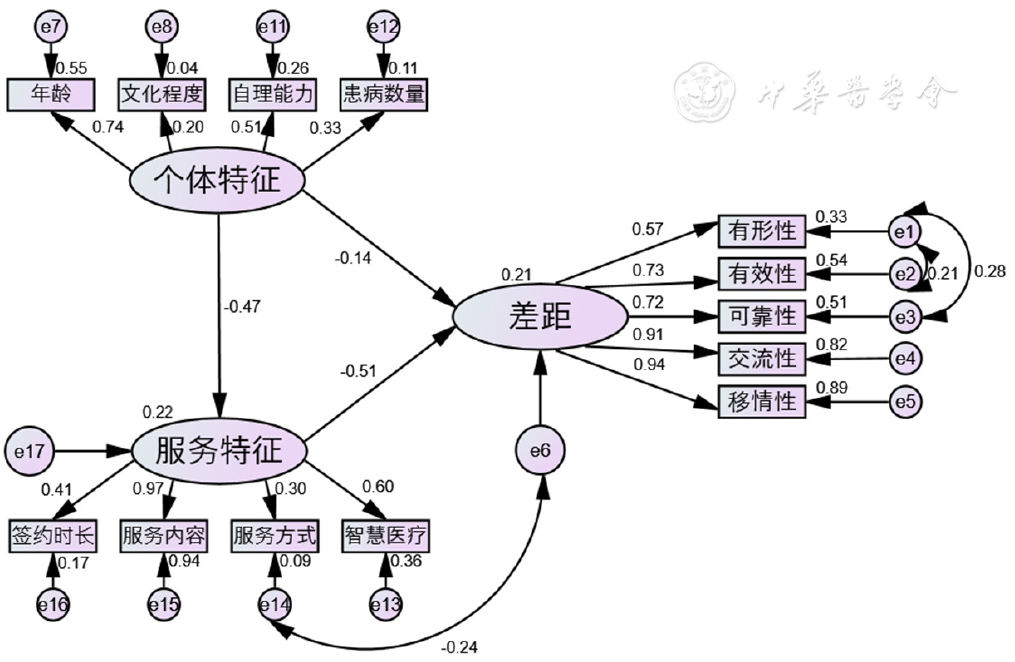
Figure 1 A structural equation model of the influencing factors of the experience of integrated medical-elderly-nursing services in community-dwelling chronic disease patients
| [1] |
浙江省统计局. 浙江统计年鉴2020[M]. 北京:中国统计出版社,2020.
|
| [2] |
杭州市人民政府. 杭州市人民政府办公厅关于推进医养护一体化智慧医疗服务的实施意见[EB/OL].(2014-05-30)[2021-08-16].
|
| [3] |
杭州市人民政府. 杭州市人民政府办公厅关于印发杭州市医养护一体化签约服务实施方案(试行)的通知[EB/OL].(2014-09-03)[2021-08-16].
|
| [4] |
魏雅宁. 杭州:重点人群家庭医生签约覆盖率达82.04%[EB/OL].(2019-01-26)[2021-08-16].
|
| [5] |
杨旻,朱雪娇,徐玛瑙. 杭州市社区慢性病患者医养护一体化服务体验的现况研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(10):1232-1237. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.224.
|
| [6] |
汪冬晓. 杭州市"医养护一体化"综合服务质量及影响因素研究[D]. 杭州:浙江财经大学,2016.
|
| [7] |
陈育蕾. 浙江省医养护一体化服务质量发展状况调查与分析[M]. 北京:电子工业出版社,2020:112-113.
|
| [8] |
杨旻,朱雪娇,章琛越,等. 基于实施性研究的整合性理论框架医养护一体化服务实施影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(4):505-509. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.210.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
胡赛. SERVQUAL量表用于我国社区卫生服务质量评价的适用性研究[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学,2018.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
倪云潮,周培森,李章平,等. 浙江省家庭医生签约居民续签意愿及影响因素调查[J]. 中国农村卫生事业管理,2020,40(8):552-556.
|
| [13] |
杭州市人民政府. 杭州市医养护一体化智慧医疗服务促进办法[EB/OL].(2015-04-13)[2021-08-16].
|
| [14] |
云美丽. 我国公众基本医疗卫生服务获得感的生成逻辑、影响因素和提升路径[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古大学,2019.
|
| [15] |
陈楚媛,沈勤,陈巧玲,等. 杭州市居家老年人家庭型医养护一体化服务利用情况及影响因素研究[J]. 护理学杂志,2019,34(21):64-67. DOI:10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2019.21.064.
|
| [16] |
杭州市卫生计生委. 关于印发杭州市家庭病床服务规范(试行)的通知[EB/OL].(2014-11-24)[2021-08-16].
|
| [17] |
刘金玲. 杭州市居家老年人健康状况与家庭型医养护一体化服务需求的调查研究[D]. 杭州:浙江中医药大学,2017.
|
| [18] |
黄志杰,王皓翔,周志衡,等. 远程动态血压监测下综合干预在社区高血压管理中的应用效果及影响因素研究[J].中国全科医学,2018,21(19):2343-2347. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.17-9572.2018.19.015.
|
| [19] |
何炜,滕建荣,周智林,等. 杭州智慧医疗探索及其思考[J]. 中华医院管理杂志,2017,33(2):125-127.
|
| [20] |
国务院办公厅. 关于切实解决老年人运用智能技术困难实施方案的通知[EB/OL].(2020-11-15)[2021-08-16].
|
| [21] |
方之瑜. 智慧城市背景下老年群体信息技术现状与能力培养[J]. 中国电化教育,2018,39(2):67-72.
|
| [1] | QIN Fengyin, ZHANG Qishan, LAI Jinjia, HUANG Yimin, HAN Guoyin, SUN Xinglan, WANG Fen, TAN Yibing. Current Status and Influencing Factors of the Intention to Screen for High-risk Stroke among Community Residents in Guangdong [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(34): 4283-4289. |
| [2] | HAO Aihua, ZENG Weilin, LI Guanhai, XIA Yinghua, CHEN Liang. Current Situation of the Construction of Family Doctor Team: an Investigation Based on the Perspective of General Practitioners [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(34): 4261-4268. |
| [3] | LI Dianjiang, PAN Enchun, SUN Zhongming, WEN Jinbo, WANG Miaomiao, WU Ming, SHEN Chong. The Current Status and Influencing Factors of Clinical Inertia in Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Community [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(34): 4296-4301. |
| [4] | LIN Kai, YAO Mi, CHEN Zhang, JI Xinxin, LIN Runqi, CHEN Yongsong, Sim MOIRA. Conceptual Framework and Responding Approach of Treatment Burden of Type 2 Diabetes: a Video Recording-based Analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(34): 4302-4307. |
| [5] | WANG Yue, CHEN Qing, LIU Lurong. Detection Rate of Depression and Its Influencing Factors in Chinese Elderly: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(34): 4329-4335. |
| [6] | YU Xinyan, ZHAO Jun, ZHAO Xiaoye, JIANG Qingru, CHEN Yatian, WANG Yan, ZHANG Haicheng. Application of Mobile Smart Healthcare in the Prevention and Control of Cardiovascular Diseases in Elderly Patients with Chronic Diseases in Primary Care [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(33): 4167-4172. |
| [7] | ZHOU Yuyu, GAO Chuan, CUI Puan, WANG Yaping, HE Zhong. Influencing Factors of Shared Decision Making between Doctors and Patients in Menopausal Hormone Therapy in Patients with Menopausal Syndrome [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(33): 4181-4186. |
| [8] | WANG Lina, GAO Pengfei, CAO Fan, GE Ying, YAN Wei, HE Daikun. Analysis of the Prevalence and Influencing Factors of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Different Gender Groups [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(33): 4143-4151. |
| [9] | LI Qianqian, CHEN Xunrui, ZHANG Wenying, YUAN Haihua, ZHANG Yanjie, JIANG Bin, LIU Feng. Demand and Influencing Factors for Community Health Services during Chemotherapy of Patients with Advanced Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(33): 4173-4180. |
| [10] | ZHANG Jin, DING Zhiguo, QI Shuo, LI Ying, LI Weiqiang, ZHANG Yuanyuan, ZHOU Tong. Relationship between Serum Thyroid Hormone Levels and Prognosis during Hospitalization in Heart Failure Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(33): 4125-4129. |
| [11] | LIANG Xuan, NA Feiyang, QIN Mengyao, YANG Hui, GUO Li, GUO Qi, REN Lei, CHEN De, LIU Donghai, ZHANG Rongfang. Clinical Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Bronchial Asthma Combined with Obstructive Sleep Apnea-hypopnea Syndrome in Children [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(33): 4225-4230. |
| [12] | GAO Dekang, WEI Shaohua, MA Xiaoming, DU Peng, XING Chungen, CAO Chun. Risk Factors for Loss of Skeletal Muscle Mass and Its Correlation with Complications after Major Hepatectomy for Liver Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(32): 4031-4037. |
| [13] | ZHANG Juan, LI Haifen, LI Xiaoman, YAO Miao, MA Huizhen, MA Qiang. Construction of Recurrence Risk Prediction Model for Diabetic Foot Ulcer on the Basis of Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machine and BP Neural Network Model [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(32): 4013-4019. |
| [14] | GAO Jing, ZHOU Shangcheng, GAO Sande, ZOU Guanyang, CHEN Yingyao. Health-related Quality of Life and Its Influencing Factors in Patients with Prevention of Disease in Traditionnal Chinese Medicine based on EQ-5D-5L Scale [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(32): 4043-4050. |
| [15] | WANG Minghuan, LI Yuhong, YU Min, WANG Yougang, YU Qiaozhi, YANG Fangfang, YUAN Dehui, ZHANG Liu. Effect of Allostatic Load on Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes of Women in Late Pregnancy [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(32): 4064-4069. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 498
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 1343
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||