

Chinese General Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (35): 4449-4456.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0692
• Original Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-10-08
Revised:2025-01-22
Published:2025-12-15
Online:2025-10-15
Contact:
LI Chengyi
通讯作者:
李成贻
作者简介:作者贡献:
周倩梅提出主要研究目标,负责研究的构思与设计,研究的实施,撰写论文;缪卡莉、钟永鸣进行数据的收集与整理,统计学处理,图、表的绘制与展示;张辅满、张哲进行论文的修订;李成贻负责文章的质量控制与审查,对文章整体负责,监督管理。
基金资助:CLC Number:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0692
| 组别 | 蛋白水平(n=60) | mRNA相对表达水平(n=30) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas6 | AXL | Gas6 | AXL | |
| 乳腺癌组织 | 0.076(0.070,0.098) | 0.104(0.082,0.123) | 0.709(0.615,0.959) | 7.940(3.045,18.112) |
| 癌旁组织 | 0.098(0.084,0.117) | 0.078(0.070,0.091) | 1.127(0.846,1.287) | 1.388(0.260,4.555) |
| Z值 | 4.719 | 5.610 | 3.651 | 4.741 |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Table 1 Comparison of Gas6 and AXL protein and mRNA expression in breast cancer tissue and adjacent normal tissue
| 组别 | 蛋白水平(n=60) | mRNA相对表达水平(n=30) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas6 | AXL | Gas6 | AXL | |
| 乳腺癌组织 | 0.076(0.070,0.098) | 0.104(0.082,0.123) | 0.709(0.615,0.959) | 7.940(3.045,18.112) |
| 癌旁组织 | 0.098(0.084,0.117) | 0.078(0.070,0.091) | 1.127(0.846,1.287) | 1.388(0.260,4.555) |
| Z值 | 4.719 | 5.610 | 3.651 | 4.741 |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 项目 | 蛋白水平(n=60) | mRNA表达水平(n=30) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数 | 平均光密度值 | Z(H)值 | P值 | 例数 | 相对表达量 | Z(H)值 | P值 | |
| 年龄 | -0.444 | 0.657 | -0.518 | 0.647 | ||||
| <55岁 | 30 | 0.081(0.069,0.098) | 17 | 0.716(0.654,1.048) | ||||
| ≥50岁 | 30 | 0.075(0.071,0.098) | 13 | 0.633(0.565,0.908) | ||||
| Ki-67 | -0.260 | 0.795 | -0.674 | 0.527 | ||||
| <14% | 13 | 0.076(0.068,0.096) | 6 | 0.826(0.642,1.004) | ||||
| ≥14% | 47 | 0.076(0.070,0.098) | 24 | 0.708(0.597,0.866) | ||||
| 组织学分级 | 0.477a | 0.788 | 0.353a | 0.765 | ||||
| Ⅰ级 | 7 | 0.084(0.073,0.104) | 3 | 0.820(0.563,0.973) | ||||
| Ⅱ级 | 25 | 0.076(0.070,0.099) | 2 | 0.698(0.626,1.107) | ||||
| Ⅲ级 | 28 | 0.074(0.069,0.097) | 25 | 0.734(0.597,0.866) | ||||
| 雌激素受体 | -1.056 | 0.291 | -1.566 | 0.124 | ||||
| 阴性 | 24 | 0.074(0.068,0.093) | 12 | 0.821(0.700,0.979) | ||||
| 阳性 | 36 | 0.078(0.068,0.093) | 18 | 0.654(0.583,0.982) | ||||
| 孕激素受体 | -0.513 | 0.608 | -0.146 | 0.902 | ||||
| 阴性 | 33 | 0.076(0.071,0.099) | 17 | 0.765(0.592,0.969) | ||||
| 阳性 | 27 | 0.076(0.079,0.097) | 13 | 0.698(0.629,0.967) | ||||
| 人表皮生长因子受体2(HER2) | -1.102 | 0.270 | -0.550 | 0.602 | ||||
| 阴性 | 35 | 0.075(0.069,0.097) | 18 | 0.725(0.624,0.959) | ||||
| 阳性 | 25 | 0.085(0.072,0.105) | 12 | 0.699(0.591,1.004) | ||||
| 肿瘤最大直径 | -1.389 | 0.165 | -0.206 | 0.837 | ||||
| ≤2 cm | 27 | 0.084(0.070,0.104) | 15 | 0.733(0.594,1.051) | ||||
| >2 cm | 33 | 0.084(0.068,0.091) | 15 | 0.700(0.619,0.866) | ||||
| 腋窝淋巴结转移 | -1.215 | 0.224 | -2.037 | 0.042 | ||||
| 无 | 32 | 0.075(0.067,0.096) | 16 | 0.842(0.650,1.111) | ||||
| 有 | 28 | 0.077(0.072,0.099) | 14 | 0.654(0.667,0.741) | ||||
| 脉管癌栓侵犯 | -1.170 | 0.242 | -1.625 | 0.104 | ||||
| 无 | 50 | 0.075(0.068,0.098) | 27 | 0.716(0.619,0.950) | ||||
| 有 | 10 | 0.093(0.073,0.098) | 3 | 0.698(0.605,0.843) | ||||
| 分子分型 | 5.368a | 0.252 | 2.834a | 0.586 | ||||
| Luminal A型 | 12 | 0.081(0.073,0.103) | 6 | 0.777(0.634,1.267) | ||||
| Luminal B型(HER-2阴性) | 12 | 0.072(0.069,0.094) | 6 | 0.638(0.589,0.814) | ||||
| Luminal B型(HER-2阳性) | 12 | 0.093(0.071,0.118) | 6 | 0.612(0.412,0.817) | ||||
| 三阴性型 | 12 | 0.071(0.066,0.094) | 6 | 0.816(0.682,0.959) | ||||
| HER-2型 | 12 | 0.079(0.072,0.101) | 6 | 0.821(0.673,1.070) | ||||
| 临床分期 | 3.537a | 0.171 | 8.011a | 0.018 | ||||
| Ⅰ期 | 18 | 0.081(0.070,0.106) | 8 | 0.885(0.538,1.126) | ||||
| Ⅱ期 | 32 | 0.073(0.067,0.097) | 15 | 0.716(0.657,0.989) | ||||
| Ⅲ期 | 10 | 0.077(0.074,0.102) | 7 | 0.594(0.577,0.618) | ||||
Table 2 Clinical information of breast cancer patients and intergroup comparison of average optical density values of Gas6 protein and Gas6 mRNA transcription levels
| 项目 | 蛋白水平(n=60) | mRNA表达水平(n=30) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数 | 平均光密度值 | Z(H)值 | P值 | 例数 | 相对表达量 | Z(H)值 | P值 | |
| 年龄 | -0.444 | 0.657 | -0.518 | 0.647 | ||||
| <55岁 | 30 | 0.081(0.069,0.098) | 17 | 0.716(0.654,1.048) | ||||
| ≥50岁 | 30 | 0.075(0.071,0.098) | 13 | 0.633(0.565,0.908) | ||||
| Ki-67 | -0.260 | 0.795 | -0.674 | 0.527 | ||||
| <14% | 13 | 0.076(0.068,0.096) | 6 | 0.826(0.642,1.004) | ||||
| ≥14% | 47 | 0.076(0.070,0.098) | 24 | 0.708(0.597,0.866) | ||||
| 组织学分级 | 0.477a | 0.788 | 0.353a | 0.765 | ||||
| Ⅰ级 | 7 | 0.084(0.073,0.104) | 3 | 0.820(0.563,0.973) | ||||
| Ⅱ级 | 25 | 0.076(0.070,0.099) | 2 | 0.698(0.626,1.107) | ||||
| Ⅲ级 | 28 | 0.074(0.069,0.097) | 25 | 0.734(0.597,0.866) | ||||
| 雌激素受体 | -1.056 | 0.291 | -1.566 | 0.124 | ||||
| 阴性 | 24 | 0.074(0.068,0.093) | 12 | 0.821(0.700,0.979) | ||||
| 阳性 | 36 | 0.078(0.068,0.093) | 18 | 0.654(0.583,0.982) | ||||
| 孕激素受体 | -0.513 | 0.608 | -0.146 | 0.902 | ||||
| 阴性 | 33 | 0.076(0.071,0.099) | 17 | 0.765(0.592,0.969) | ||||
| 阳性 | 27 | 0.076(0.079,0.097) | 13 | 0.698(0.629,0.967) | ||||
| 人表皮生长因子受体2(HER2) | -1.102 | 0.270 | -0.550 | 0.602 | ||||
| 阴性 | 35 | 0.075(0.069,0.097) | 18 | 0.725(0.624,0.959) | ||||
| 阳性 | 25 | 0.085(0.072,0.105) | 12 | 0.699(0.591,1.004) | ||||
| 肿瘤最大直径 | -1.389 | 0.165 | -0.206 | 0.837 | ||||
| ≤2 cm | 27 | 0.084(0.070,0.104) | 15 | 0.733(0.594,1.051) | ||||
| >2 cm | 33 | 0.084(0.068,0.091) | 15 | 0.700(0.619,0.866) | ||||
| 腋窝淋巴结转移 | -1.215 | 0.224 | -2.037 | 0.042 | ||||
| 无 | 32 | 0.075(0.067,0.096) | 16 | 0.842(0.650,1.111) | ||||
| 有 | 28 | 0.077(0.072,0.099) | 14 | 0.654(0.667,0.741) | ||||
| 脉管癌栓侵犯 | -1.170 | 0.242 | -1.625 | 0.104 | ||||
| 无 | 50 | 0.075(0.068,0.098) | 27 | 0.716(0.619,0.950) | ||||
| 有 | 10 | 0.093(0.073,0.098) | 3 | 0.698(0.605,0.843) | ||||
| 分子分型 | 5.368a | 0.252 | 2.834a | 0.586 | ||||
| Luminal A型 | 12 | 0.081(0.073,0.103) | 6 | 0.777(0.634,1.267) | ||||
| Luminal B型(HER-2阴性) | 12 | 0.072(0.069,0.094) | 6 | 0.638(0.589,0.814) | ||||
| Luminal B型(HER-2阳性) | 12 | 0.093(0.071,0.118) | 6 | 0.612(0.412,0.817) | ||||
| 三阴性型 | 12 | 0.071(0.066,0.094) | 6 | 0.816(0.682,0.959) | ||||
| HER-2型 | 12 | 0.079(0.072,0.101) | 6 | 0.821(0.673,1.070) | ||||
| 临床分期 | 3.537a | 0.171 | 8.011a | 0.018 | ||||
| Ⅰ期 | 18 | 0.081(0.070,0.106) | 8 | 0.885(0.538,1.126) | ||||
| Ⅱ期 | 32 | 0.073(0.067,0.097) | 15 | 0.716(0.657,0.989) | ||||
| Ⅲ期 | 10 | 0.077(0.074,0.102) | 7 | 0.594(0.577,0.618) | ||||
| 项目 | 例数 | 平均光密度值 | Z(H)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乳腺癌分子分型 | 250.598a | <0.001 | ||
| Luminal A型 | 627 | 9.615(9.120,10.013) | ||
| Luminal B型 | 441 | 8.885(8.345,9.457) | ||
| 三阴性型 | 402 | 9.472(8.875,10.084) | ||
| HER-2型 | 209 | 8.995(8.637,9.464) | ||
| 正常乳腺组织 | 122 | 9.845(9.452,10.175) | ||
| 原发肿瘤分期 | 17.251a | 0.002 | ||
| T1期 | 452 | 9.517(8.934,9.971) | ||
| T2期 | 761 | 9.305(8.736,9.856) | ||
| T3期 | 104 | 9.349(8.823,9.935) | ||
| T4期 | 9 | 9.308(8.921,9.690) | ||
| 组织学分级 | 41.496a | <0.001 | ||
| Ⅰ期 | 148 | 9.556(9.071,10.191) | ||
| Ⅱ期 | 675 | 9.527(8.977,9.930) | ||
| Ⅲ期 | 906 | 9.218(8.642,9.846) | ||
| 是否接受化疗 | -2.970 | 0.003 | ||
| 否 | 1 408 | 9.423(8.853,9.913) | ||
| 是 | 393 | 9.228(8.704,9.872) | ||
| 绝经状态 | -0.816 | 0.415 | ||
| 绝经前 | 399 | 9.346(8.844,9.912) | ||
| 绝经后 | 1 402 | 9.374(8.816,9.902) | ||
| 区域淋巴结分期 | 8.400a | 0.038 | ||
| N0期 | 888 | 9.472(8.834,9.958) | ||
| N1期 | 570 | 9.281(8.765,9.828) | ||
| N2期 | 184 | 9.329(8.876,9.718) | ||
| N3期 | 91 | 9.318(8.875,9.923) | ||
| 是否接受内分泌治疗 | -0.106 | 0.916 | ||
| 否 | 707 | 9.358(8.786,9.952) | ||
| 是 | 1 094 | 9.371(8.877,9.883) | ||
| 是否接受放疗 | -1.744 | 0.081 | ||
| 否 | 718 | 9.454(8.918,9.903) | ||
| 是 | 1 083 | 9.327(8.756,9.905) | ||
Table 3 Clinical information of breast cancer patients and intergroup comparison of average optical density values of Gas6 mRNA transcription levels in the METABRIC
| 项目 | 例数 | 平均光密度值 | Z(H)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乳腺癌分子分型 | 250.598a | <0.001 | ||
| Luminal A型 | 627 | 9.615(9.120,10.013) | ||
| Luminal B型 | 441 | 8.885(8.345,9.457) | ||
| 三阴性型 | 402 | 9.472(8.875,10.084) | ||
| HER-2型 | 209 | 8.995(8.637,9.464) | ||
| 正常乳腺组织 | 122 | 9.845(9.452,10.175) | ||
| 原发肿瘤分期 | 17.251a | 0.002 | ||
| T1期 | 452 | 9.517(8.934,9.971) | ||
| T2期 | 761 | 9.305(8.736,9.856) | ||
| T3期 | 104 | 9.349(8.823,9.935) | ||
| T4期 | 9 | 9.308(8.921,9.690) | ||
| 组织学分级 | 41.496a | <0.001 | ||
| Ⅰ期 | 148 | 9.556(9.071,10.191) | ||
| Ⅱ期 | 675 | 9.527(8.977,9.930) | ||
| Ⅲ期 | 906 | 9.218(8.642,9.846) | ||
| 是否接受化疗 | -2.970 | 0.003 | ||
| 否 | 1 408 | 9.423(8.853,9.913) | ||
| 是 | 393 | 9.228(8.704,9.872) | ||
| 绝经状态 | -0.816 | 0.415 | ||
| 绝经前 | 399 | 9.346(8.844,9.912) | ||
| 绝经后 | 1 402 | 9.374(8.816,9.902) | ||
| 区域淋巴结分期 | 8.400a | 0.038 | ||
| N0期 | 888 | 9.472(8.834,9.958) | ||
| N1期 | 570 | 9.281(8.765,9.828) | ||
| N2期 | 184 | 9.329(8.876,9.718) | ||
| N3期 | 91 | 9.318(8.875,9.923) | ||
| 是否接受内分泌治疗 | -0.106 | 0.916 | ||
| 否 | 707 | 9.358(8.786,9.952) | ||
| 是 | 1 094 | 9.371(8.877,9.883) | ||
| 是否接受放疗 | -1.744 | 0.081 | ||
| 否 | 718 | 9.454(8.918,9.903) | ||
| 是 | 1 083 | 9.327(8.756,9.905) | ||
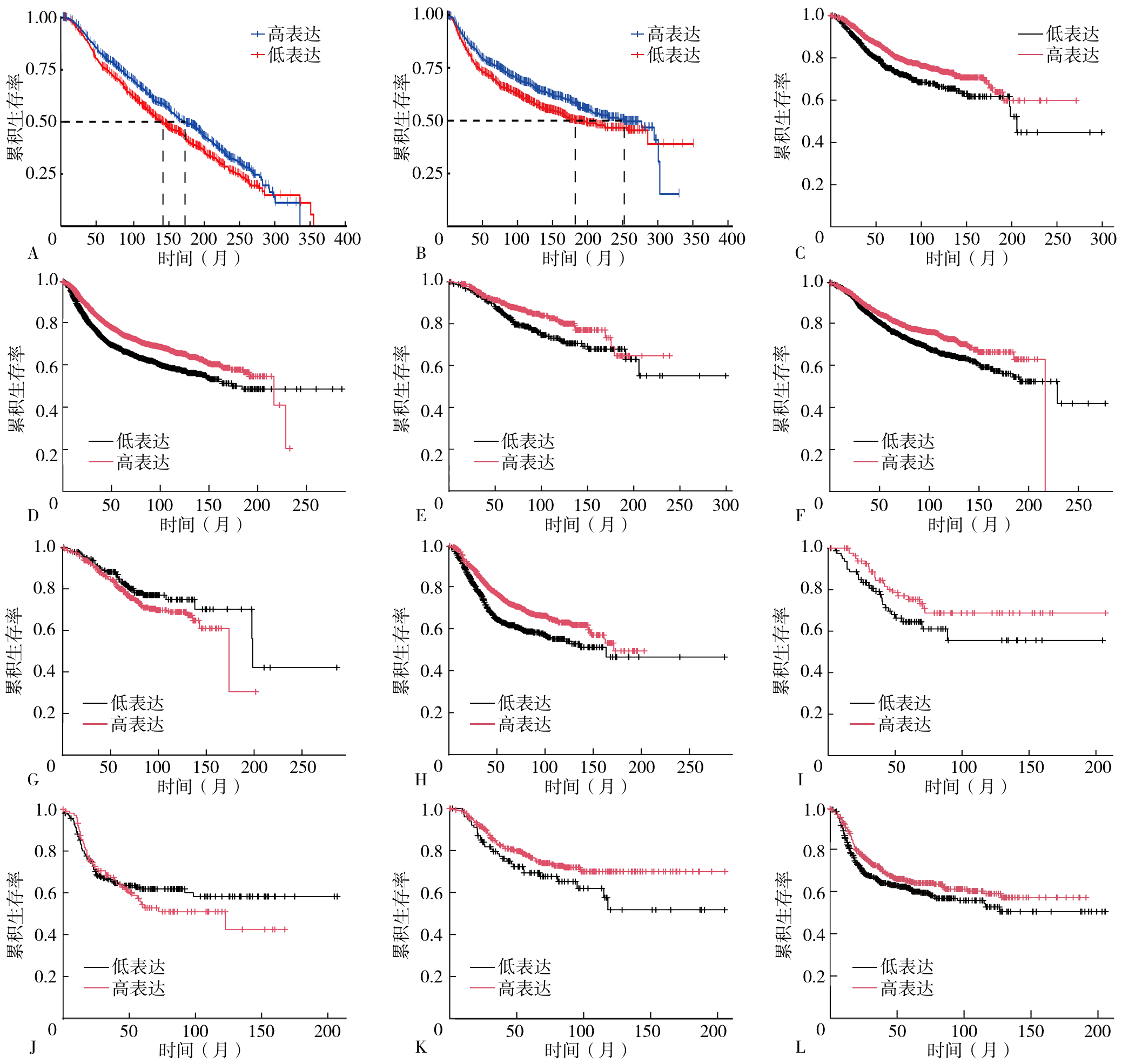
Figure 2 Survival curves analysis of high and low Gas6 mRNA expression groups in breast cancer patients based on the METABRIC database and Kaplan-Meier Plotter
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
张明帅,朱丽萍,欧江华,等. Axl及其配体在乳腺癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志,2014,19(1):29-33.
|
| [5] |
张明帅,朱丽萍,齐新,等. 新疆维、汉民族乳腺良恶性病变组织中Axl及其配体蛋白Gas6的表达与临床意义[J]. 新疆医科大学学报,2014,37(1):20-23,28.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [1] | NONG Jingtang, YANG Chengmin, MO Shenglong, LU Zhicheng, TANG Lina, JIAN Chongdong, SHANG Jingwei. Research Progress on Prognostic Biomarkers after Cerebral Infarction: Mechanisms and Clinical Applications [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(29): 3711-3720. |
| [2] | LI Yibing, JIA Hongbo, FAN Xiaonong, ZHAO Wenjun, LIU Wei, GE Wenyi, LI Songjiao, LEI Kangchen, ZHANG Menglong, ZHANG Weiwei, CHEN Yang, LI Li. Comprehensive Evaluation of Prognostic Factors Affecting Dysphagia after Stroke: an Umbrella Review [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(29): 3631-3637. |
| [3] | XU Yanpeng, HUANG Pe, ZHANG Pingping, LUO Yan, SHI Xiaoqi, WU Liusong, CHEN Yan, HE Zhixu. Expression of β-Adrenergic Receptors in Acute T-cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Its Clinical Significance [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3391-3398. |
| [4] | YANG Chen, CHEN Tong, ZHANG Lifang, ZHANG Hongxu, LI Pengfei, ZHANG Xuejuan. Prognostic Impact of Dapagliflozin in Elderly Breast Cancer Survivors with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Type 2 Diabetes [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 3053-3058. |
| [5] | CHEN Fei, WANG Jinying, YU Haibo, LI Xin, ZHANG Jiajia, SHEN Man, ZHAN Xiaokai, TANG Ran, FAN Sibin, ZHAO Fengyi, ZHANG Tianyu, HUANG Zhongxia. Significance of Elevated Urinary NGAL, TIM-1, VCAM-1 and Activin A in Patients with New Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2740-2749. |
| [6] | LUO Yunzhao, JIANG Hongchuan, XU Feng. Predicting Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy in Breast Cancer Using Deep Learning on Primary Core Needle Biopsy Slides [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2407-2413. |
| [7] | DENG Yaqian, CAO Chunli, MA Jinmei, LI Wenxiao, XU Zelin, CHENG Jing, LI Jun. Predictive Value of S-Detect Combined with Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging Quantification in Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis of Breast Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2149-2155. |
| [8] | CAO Gan, DENG Yifan, HE Shenghu, ZHANG Jing. Study on the Correlation between the Lactate Dehydrogenase-to-albumin Ratio and Prognosis in Patients with Acute ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction after Emergency PCI [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(15): 1878-1883. |
| [9] | ZHANG Shujing, SUN Lixin, CAO Yuqing. Comparative Study on the Clinicopathological Features and Prognostic between HPV-related and Non-HPV-related Cervical Adenocarcinoma [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1758-1764. |
| [10] | WU Mengjuan, ZHANG Tao, GAO Chunjie, ZHAO Ting, WANG Lei. Joint-modeling of Estradiol Levels and Survival Data of Breast Cancer Patients in the Case-cohort Design [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1765-1772. |
| [11] | HE Yun, FAN Huanfang, MA Pan, XU Shaoqing, YANG Liu, JIN Mingzhe, ZHANG Mingrui, CHEN Jiaqi. Effect of Postoperative Upper Extremity Lymphedema after Breast Cancer Treated with Different Acupuncture and Moxibustion Therapies: a Network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1788-1794. |
| [12] | WANG Dexiang, YUAN Jiawen, LU Qinyun, HANG Yuhao, LU Jun, CHENG Lu. Influences of Treatment Timing of the TCM prescription Qingfei Huayu Tongfu Formula on the Therapeutic Effect and Prognosis of Sepsis-related Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(12): 1500-1505. |
| [13] | LI Qiujing, SHANG Na, GAO Qian, YANG Li, GUO Shubin. Predictive Value of Abdominal CT Based-skeletal Muscle Mass Combined with Critical Illness Score for Prognosis in Older Patients with Intra-abdominal Sepsis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(12): 1459-1464. |
| [14] | ZHANG Pei, YANG Meng, GAO Chunlin, XIA Zhengkun. Study on the Intervention and Prognosis of Modified Lifting Powder on Acute Kidney Injury and Acute Kidney Disease in Children [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(11): 1376-1382. |
| [15] | WANG Yiquan, CHEN Wanjia, LIU Wangyi, ZHANG Luyun, DENG Yueyi. The Prognosis of Stage 4 Chronic Kidney Diseasetreated with Fermented Cordyceps Sinensis Powder: Based on a Retrospective Cohort Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(09): 1084-1091. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||