

Chinese General Practice ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (15): 1885-1891.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0856
Special Issue: 内分泌代谢性疾病最新文章合辑; 脑健康最新研究合辑
• Original Research·Clucose Fluctuation • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2022-12-05
Revised:2022-12-27
Published:2023-05-20
Online:2022-12-20
Contact:
YANG Xiaopeng
通讯作者:
杨霄鹏
作者简介:基金资助:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0856
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄〔M(P25,P75),岁〕 | 性别(男/女) | BMI( | 吸烟史〔n(%)〕 | 饮酒史〔n(%)〕 | 高血压史〔n(%)〕 | 冠心病史〔n(%)〕 | 空腹血糖〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | TG〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | TC( | HDL-C( |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低梗死负担组 | 95 | 65(57,73) | 52/43 | 24.8±2.8 | 16(16.8) | 17(17.9) | 31(32.6) | 20(21.1) | 5.42(4.94,6.20) | 1.61(1.23,1.88) | 3.87±0.90 | 1.63±0.78 |
| 高梗死负担组 | 45 | 70(63,75) | 23/22 | 25.4±2.3 | 10(22.2) | 11(24.4) | 21(46.7) | 12(26.7) | 5.63(5.07,7.53) | 1.57(1.36,1.86) | 3.65±1.12 | 1.89±1.11 |
| 检验统计量值 | -1.804 | 0.161a | -1.310b | 0.584a | 0.819a | 2.576a | 0.546a | -1.638 | -0.422 | 1.180b | -1.410b | |
| P值 | 0.071 | 0.688 | 0.192 | 0.445 | 0.366 | 0.108 | 0.460 | 0.101 | 0.673 | 0.242 | 0.163 | |
| 组别 | LDL-C( | HbA1c〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | Hcy〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | CRP〔M(P25,P75),mg/L〕 | SD( | %CV〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | LAGE〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | TIR〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | ||||
| 低梗死负担组 | 2.25±0.65 | 8.13(7.14,9.65) | 10.60(8.30,13.55) | 2.44(0.80,4.58) | 2.80±0.37 | 26.37(21.77,29.02) | 9.95(6.18,12.35) | 60.00(49.27,72.38) | ||||
| 高梗死负担组 | 2.08±0.83 | 8.76(7.30,9.72) | 10.70(9.10,13.70) | 2.83(1.10,5.91) | 3.15±0.59 | 31.17(26.51,36.85) | 10.51(6.75,13.36) | 42.70(35.40,51.21) | ||||
| 检验统计量值 | 1.231b | -0.814 | -0.768 | -1.068 | -3.664b | -4.897 | -1.064 | 6.588 | ||||
| P值 | 0.222 | 0.416 | 0.442 | 0.286 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.287 | <0.001 |
Table 1 Comparison of clinical data between high and low RSSI infarct burden groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄〔M(P25,P75),岁〕 | 性别(男/女) | BMI( | 吸烟史〔n(%)〕 | 饮酒史〔n(%)〕 | 高血压史〔n(%)〕 | 冠心病史〔n(%)〕 | 空腹血糖〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | TG〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | TC( | HDL-C( |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低梗死负担组 | 95 | 65(57,73) | 52/43 | 24.8±2.8 | 16(16.8) | 17(17.9) | 31(32.6) | 20(21.1) | 5.42(4.94,6.20) | 1.61(1.23,1.88) | 3.87±0.90 | 1.63±0.78 |
| 高梗死负担组 | 45 | 70(63,75) | 23/22 | 25.4±2.3 | 10(22.2) | 11(24.4) | 21(46.7) | 12(26.7) | 5.63(5.07,7.53) | 1.57(1.36,1.86) | 3.65±1.12 | 1.89±1.11 |
| 检验统计量值 | -1.804 | 0.161a | -1.310b | 0.584a | 0.819a | 2.576a | 0.546a | -1.638 | -0.422 | 1.180b | -1.410b | |
| P值 | 0.071 | 0.688 | 0.192 | 0.445 | 0.366 | 0.108 | 0.460 | 0.101 | 0.673 | 0.242 | 0.163 | |
| 组别 | LDL-C( | HbA1c〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | Hcy〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | CRP〔M(P25,P75),mg/L〕 | SD( | %CV〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | LAGE〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | TIR〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | ||||
| 低梗死负担组 | 2.25±0.65 | 8.13(7.14,9.65) | 10.60(8.30,13.55) | 2.44(0.80,4.58) | 2.80±0.37 | 26.37(21.77,29.02) | 9.95(6.18,12.35) | 60.00(49.27,72.38) | ||||
| 高梗死负担组 | 2.08±0.83 | 8.76(7.30,9.72) | 10.70(9.10,13.70) | 2.83(1.10,5.91) | 3.15±0.59 | 31.17(26.51,36.85) | 10.51(6.75,13.36) | 42.70(35.40,51.21) | ||||
| 检验统计量值 | 1.231b | -0.814 | -0.768 | -1.068 | -3.664b | -4.897 | -1.064 | 6.588 | ||||
| P值 | 0.222 | 0.416 | 0.442 | 0.286 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.287 | <0.001 |
| 变量 | rs值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|
| SD | 0.272 | 0.001 |
| %CV | 0.391 | <0.001 |
| LAGE | 0.041 | 0.628 |
| TIR | -0.325 | <0.001 |
Table 2 Spearman correlation analysis of GV and cognitive function(assessed using the MoCA score)
| 变量 | rs值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|
| SD | 0.272 | 0.001 |
| %CV | 0.391 | <0.001 |
| LAGE | 0.041 | 0.628 |
| TIR | -0.325 | <0.001 |
| 变量 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | 1.435 | 0.568 | 2.527 | 0.011 | 4.201 | (1.380,12.788) |
| %CV | 0.197 | 0.054 | 3.659 | <0.001 | 1.218 | (1.096,1.354) |
| TIR | -0.144 | 0.031 | -4.583 | <0.001 | 0.866 | (0.814,0.921) |
Table 3 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of the influencing factors of infarct burden in patients with RSSI and T2DM
| 变量 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | 1.435 | 0.568 | 2.527 | 0.011 | 4.201 | (1.380,12.788) |
| %CV | 0.197 | 0.054 | 3.659 | <0.001 | 1.218 | (1.096,1.354) |
| TIR | -0.144 | 0.031 | -4.583 | <0.001 | 0.866 | (0.814,0.921) |
| 变量 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | 1.081 | 0.480 | 2.252 | 0.024 | 2.947 | (1.150,7.548) |
| %CV | 0.161 | 0.047 | 3.437 | 0.001 | 1.174 | (1.072,1.287) |
| TIR | -0.047 | 0.020 | -2.360 | 0.018 | 0.954 | (0.917,0.992) |
Table 4 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of the influencing factors of cognitive impairment in patients with RSSI and T2DM
| 变量 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | 1.081 | 0.480 | 2.252 | 0.024 | 2.947 | (1.150,7.548) |
| %CV | 0.161 | 0.047 | 3.437 | 0.001 | 1.174 | (1.072,1.287) |
| TIR | -0.047 | 0.020 | -2.360 | 0.018 | 0.954 | (0.917,0.992) |
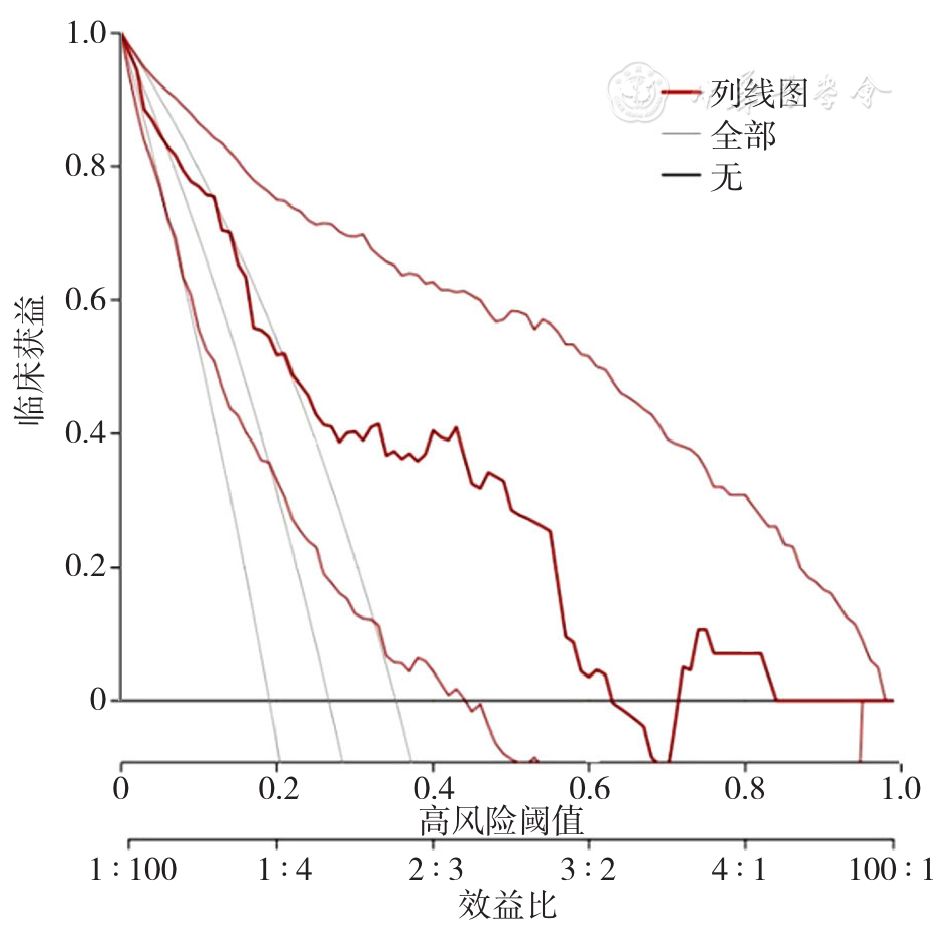
Figure 3 Internal validation of the DCA clinical benefit of the nomogram prediction model for the risk of cognitive impairment in patients with RSSI and T2DM
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会,朱大龙. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 国际内分泌代谢杂志,2021,41(5):482-548.
|
| [11] |
中国研究型医院学会脑小血管病专业委员会《中国脑小血管病诊治专家共识2021》编写组. 中国脑小血管病诊治专家共识2021[J]. 中国卒中杂志,2021,16(7):716-726.
|
| [12] |
车艺玮,苗延巍,蒋玉涵,等. 系统性红斑狼疮患者脑小血管病变的MRI初步研究[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志,2020,31(4):234-237,247. DOI:10.12117/jccmi.2020.04.002.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [1] | ZHAO Xiaoqing, GUO Tongtong, ZHANG Xinyi, LI Linhong, ZHANG Ya, JI Lihong, DONG Zhiwei, GAO Qianqian, CAI Weiqing, ZHENG Wengui, JING Qi. Construction and Validation of a Risk Prediction Model for Cognitive Impairment in Community-dwelling Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2776-2783. |
| [2] | SHI Jiarui, WANG Zili, ZHANG Xueqing, SONG Yulei, XU Guihua, BAI Yamei. The Current Status of Initial Cognitive Screening Services in Community-based Cognitive Services Centers in Nanjing [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2784-2790. |
| [3] | LI Bing, XI Zhi, WANG Yang, XIU Jiaqi, GUO Qiancheng, YU Chenchen, SUN Siyu, YANG Xiaopeng. Association of Blood Pressure Variability and Systemic Immune-inflammation Index with Intracranial Arterial Negative Remodeling in Patients with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1751-1757. |
| [4] | ZHAO Xinrui, HUANG Li, CAO Lichun, QU Huichao, ZHANG Meilin, LIU Huan. Status and Influencing Factors of Reversible and Potentially Reversible Cognitive Frailty among the Community-dwelling Elderly [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(07): 824-830. |
| [5] | YUAN Yiqing, CHEN Honglin. Research Progress on Stigma of Cognitive Disorders [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(05): 631-638. |
| [6] | GU Shanye, ZHOU Ziyi, CAI Yefeng. Study on Risk Prediction of Non-dementia Vascular Cognitive Impairment in Glycolipid Metabolic Diseases [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(35): 4412-4416. |
| [7] | QIN Yali, CHEN Jing, LI Jun, WANG Mingdong, OU Weizheng, QIU Jiyao, PENG Yanqing. Construction and Validation of a Predictive Model of Influencing Factors for Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Based on the LASSO-Logistic Regression Model [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(30): 3776-3783. |
| [8] | XIAO Yuqian, BAI Yanjie, WANG Yan, SUN Kexin, WAN Jun, CHEN Shuying, CHEN Limin. Research Progress of Astrocyte-derived Extracellular Vesicles in Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(20): 2551-2556. |
| [9] | XU Yunjia, SHU Biyun, ZHENG Yongtao, CHEN Ting, LAI Fenhua, NI Mengjiao, LUO Xiulan, WU Hengjing. Risk Factors and Predictive Model of Long-term Bedridden Risk of Falls in Super-aged Population Based on Competing Risk Model Analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(18): 2192-2197. |
| [10] | ZHOU Lulu, LU Yuan, ZHANG Yi, GAO Xin, LIU Fang, CHENG Yuan, FENG Yuqin, YU Dehua. Analysis of Social Support and Related Factors of Family Caregivers of Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(16): 1977-1983. |
| [11] | DU Jin, ZHANG Hongyu, QIAO Yuchen, LIU Yifan, LI Luling. Action Research on Constructing a Welfare Pluralism System for the Elderly with Dementia: Taking the Elderly Health Social Work Service of Beijing X Hospital as an Example [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(13): 1651-1660. |
| [12] | ZHANG Min, LU Yuan, GAO Song, MA Jia, LIU Yalin, ZHAI Jiayi, YU Dehua. Analysis on the Perceptions Toward Mild Cognitive Impairment and Medical Willingness among Population Aged over 55 Years in Shanghai Based on a Proactive Health Perspective [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(10): 1208-1214. |
| [13] | WU Shuqin, WANG Yuanhan, ZHENG Kaiyuan, HAN Hongjuan, KANG Jinxiu, YU Hongmei. Prognosis and Influencing Factors of Patients with Malignant Melanoma [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(08): 942-947. |
| [14] | TANG Can, LI Xiangyang, LI Jing, QIN Haoran, ZHU Hong. The Value of Nomogram Established by Serological Indicators and Tumor Diameter to Predict the Risk of Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(36): 4514-4520. |
| [15] | JIAN Qiufeng, XU Ronghua, YAO Qian, ZHOU Yuanyuan. A Meta-analysis of the Prevalence and Influencing Factors of Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment in Chinese Elderly Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(32): 4070-4079. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||