

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (05): 554-56.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.320
Special Issue: 脑健康最新研究合辑
• Original Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
The Effect of Longitudinal Trajectories of Triglyceride-glucose Index on the New-onset Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases
1. Cardiovascular Department,Luanzhou People's Hospital,Luanzhou 063700,China
2.Graduate School,North China University of Science and Technology,Tangshan 063000,China
3.Cardiovascular Department,Kailuan General Hospital,Tangshan 063000,China
*Corresponding author:WU Yuntao,Chief physician,Master supervisor;E-mail:wyt0086@163.com
Received:2021-06-21
Revised:2021-09-04
Published:2022-02-15
Online:2022-01-29
通讯作者:
吴云涛
基金资助:CLC Number:
CAO Zhiwei, LIU Qian, LI Jing, ZHANG Jing, JI Meiling, LIU Liwei, SONG Mingzhu, SUN Junyan, WU Yuntao.
The Effect of Longitudinal Trajectories of Triglyceride-glucose Index on the New-onset Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(05): 554-56.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.320
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(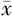 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 男性〔n(%)〕 | BMI (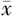 ±s,kg/m2) ±s,kg/m2) | 心率(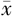 ±s,次/min) ±s,次/min) | TyG2006 (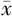 ±s) ±s) | TyG2008 (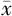 ±s) ±s) | TyG2010 (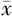 ±s) ±s) | HDL-C (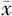 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | LDL-C (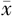 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | UA (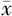 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低-稳定组 | 13 150 | 52.4±12.9 | 8 887(67.58) | 23.61±3.02 | 72±10 | 7.93±0.36 | 7.95±0.36 | 8.02±0.37 | 1.72±0.53 | 2.32±0.78 | 276.98±75.22 |
| 中低-稳定组 | 28 488 | 53.5±12.0 | 22 024(77.31) | 25.19±3.15 | 73±10 | 8.61±0.41 | 8.64±0.38 | 8.65±0.39 | 1.55±0.50 | 2.67±1.03 | 290.55±86.15 |
| 中高-稳定组 | 10 808 | 53.3±11.0 | 8 906(82.40) | 26.41±3.13 | 75±10 | 9.36±0.49 | 9.35±0.46 | 9.36±0.49 | 1.44±0.53 | 2.75±0.88 | 312.88±97.14 |
| 高-稳定组 | 1 812 | 52.0±9.6 | 1 565(86.37) | 26.66±3.05 | 77±11 | 10.08±0.60 | 10.36±0.62 | 10.30±0.66 | 1.37±0.51 | 2.64±1.05 | 326.59±109.93 |
| 检验统计量值 | 34.82 | 892.08a | 1 793.54 | 315.31 | 29 511.00 | 34 717.20 | 29 712.90 | 707.13 | 534.91 | 435.35 | |
| P值 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
Table 1 Comparison of basic characteristics of participants in different TyG index trajectory groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(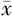 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 男性〔n(%)〕 | BMI (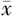 ±s,kg/m2) ±s,kg/m2) | 心率(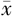 ±s,次/min) ±s,次/min) | TyG2006 (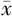 ±s) ±s) | TyG2008 (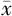 ±s) ±s) | TyG2010 (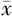 ±s) ±s) | HDL-C (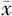 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | LDL-C (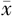 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | UA (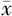 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低-稳定组 | 13 150 | 52.4±12.9 | 8 887(67.58) | 23.61±3.02 | 72±10 | 7.93±0.36 | 7.95±0.36 | 8.02±0.37 | 1.72±0.53 | 2.32±0.78 | 276.98±75.22 |
| 中低-稳定组 | 28 488 | 53.5±12.0 | 22 024(77.31) | 25.19±3.15 | 73±10 | 8.61±0.41 | 8.64±0.38 | 8.65±0.39 | 1.55±0.50 | 2.67±1.03 | 290.55±86.15 |
| 中高-稳定组 | 10 808 | 53.3±11.0 | 8 906(82.40) | 26.41±3.13 | 75±10 | 9.36±0.49 | 9.35±0.46 | 9.36±0.49 | 1.44±0.53 | 2.75±0.88 | 312.88±97.14 |
| 高-稳定组 | 1 812 | 52.0±9.6 | 1 565(86.37) | 26.66±3.05 | 77±11 | 10.08±0.60 | 10.36±0.62 | 10.30±0.66 | 1.37±0.51 | 2.64±1.05 | 326.59±109.93 |
| 检验统计量值 | 34.82 | 892.08a | 1 793.54 | 315.31 | 29 511.00 | 34 717.20 | 29 712.90 | 707.13 | 534.91 | 435.35 | |
| P值 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| 因变量 | 模型 | 自变量 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | HR (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVD | 模型1 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 65.47 | <0.01 | 1.65(1.46,1.87) |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.78 | 0.07 | 129.49 | <0.01 | 2.18(1.91,2.50) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 1.13 | 0.10 | 123.47 | <0.01 | 3.08(2.53,3.76) | ||
| 模型2 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 15.49 | <0.01 | 1.29(1.14,1.46) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 19.03 | <0.01 | 1.40(1.20,1.63) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.56 | 0.11 | 24.50 | <0.01 | 1.76(1.41,2.20) | ||
| 模型3 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 10.09 | <0.01 | 1.25(1.09,1.44) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 7.79 | <0.01 | 1.31(1.08,1.59) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 8.61 | <0.01 | 1.57(1.16,2.13) | ||
| TyG2010 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 1.11 | 0.29 | 1.06(0.95,1.17) | ||
| 心肌梗死 | 模型1 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.66 | 0.15 | 20.67 | <0.01 | 1.94(1.46,2.59) |
| 中高-稳定组 | 1.11 | 0.16 | 51.00 | <0.01 | 3.04(2.24,4.12) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 1.26 | 0.23 | 29.76 | <0.01 | 3.51(2.24,5.51) | ||
| 模型2 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.39 | 0.15 | 6.59 | 0.01 | 1.48(1.10,1.98) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 14.03 | <0.01 | 1.91(1.36,2.69) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.71 | 0.26 | 7.53 | <0.01 | 2.03(1.22,3.36) | ||
| 模型3 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.38 | 0.16 | 5.51 | 0.02 | 1.47(1.07,2.02) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.64 | 0.22 | 8.69 | <0.01 | 1.89(1.24,2.89) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.69 | 0.34 | 4.05 | 0.04 | 1.99(1.02,3.90) | ||
| TyG2010 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.94 | 1.01(0.81,1.26) | ||
| 脑卒中 | 模型1 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.45 | 0.07 | 44.47 | <0.01 | 1.57(1.38,1.79) |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.68 | 0.08 | 80.58 | <0.01 | 1.98(1.70,2.29) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 1.06 | 0.11 | 88.85 | <0.01 | 2.89(2.32,3.60) | ||
| 模型2 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 8.77 | <0.01 | 1.23(1.07,1.42) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 7.78 | <0.01 | 1.27(1.07,1.50) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.49 | 0.13 | 14.76 | <0.01 | 1.63(1.27,2.08) | ||
| 模型3 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 5.18 | 0.02 | 1.19(1.03,1.39) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 2.40 | 0.12 | 1.18(0.96,1.46) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 4.49 | 0.03 | 1.44(1.03,2.02) | ||
| TyG2010 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 1.10 | 0.30 | 1.06(0.95,1.19) | ||
| 缺血性脑卒中 | 模型1 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.47 | 0.07 | 41.60 | <0.01 | 1.60(1.39,1.85) |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.73 | 0.08 | 81.26 | <0.01 | 2.08(1.78,2.44) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 1.14 | 0.12 | 93.42 | <0.01 | 3.13(2.49,3.95) | ||
| 模型2 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 8.67 | <0.01 | 1.25(1.08,1.45) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 10.21 | <0.01 | 1.35(1.12,1.60) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.57 | 0.13 | 18.53 | <0.01 | 1.77(1.37,2.30) | ||
| 模型3 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 4.59 | 0.03 | 1.19(1.02,1.41) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 2.83 | 0.09 | 1.21(0.97,1.52) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.40 | 0.18 | 4.95 | 0.03 | 1.50(1.05,2.14) | ||
| TyG2010 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 1.86 | 0.17 | 1.09(0.96,1.23) | ||
| 出血性脑卒中 | 模型1 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 3.32 | 0.07 | 1.36(0.98,1.88) |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 3.24 | 0.07 | 1.43(0.97,2.10) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.68 | 0.31 | 4.68 | 0.03 | 1.97(1.07,3.63) | ||
| 模型2 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.81 | 0.37 | 1.17(0.83,1.65) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | ~0.02 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.93 | 0.98(0.63,1.52) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.13 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.70 | 1.14(0.58,2.23) | ||
| 模型3 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 1.34 | 0.25 | 1.25(0.86,1.84) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.67 | 1.13(0.64,1.98) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.68 | 0.41 | 1.46(0.59,3.61) | ||
| TyG2010 | ~0.12 | 0.15 | 0.65 | 0.42 | 0.88(0.65,1.20) |
Table 2 Multivariate Cox regression analysis of the effect of different TyG index trajectory groups on CVD
| 因变量 | 模型 | 自变量 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | HR (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVD | 模型1 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 65.47 | <0.01 | 1.65(1.46,1.87) |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.78 | 0.07 | 129.49 | <0.01 | 2.18(1.91,2.50) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 1.13 | 0.10 | 123.47 | <0.01 | 3.08(2.53,3.76) | ||
| 模型2 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 15.49 | <0.01 | 1.29(1.14,1.46) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 19.03 | <0.01 | 1.40(1.20,1.63) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.56 | 0.11 | 24.50 | <0.01 | 1.76(1.41,2.20) | ||
| 模型3 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 10.09 | <0.01 | 1.25(1.09,1.44) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 7.79 | <0.01 | 1.31(1.08,1.59) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 8.61 | <0.01 | 1.57(1.16,2.13) | ||
| TyG2010 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 1.11 | 0.29 | 1.06(0.95,1.17) | ||
| 心肌梗死 | 模型1 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.66 | 0.15 | 20.67 | <0.01 | 1.94(1.46,2.59) |
| 中高-稳定组 | 1.11 | 0.16 | 51.00 | <0.01 | 3.04(2.24,4.12) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 1.26 | 0.23 | 29.76 | <0.01 | 3.51(2.24,5.51) | ||
| 模型2 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.39 | 0.15 | 6.59 | 0.01 | 1.48(1.10,1.98) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 14.03 | <0.01 | 1.91(1.36,2.69) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.71 | 0.26 | 7.53 | <0.01 | 2.03(1.22,3.36) | ||
| 模型3 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.38 | 0.16 | 5.51 | 0.02 | 1.47(1.07,2.02) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.64 | 0.22 | 8.69 | <0.01 | 1.89(1.24,2.89) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.69 | 0.34 | 4.05 | 0.04 | 1.99(1.02,3.90) | ||
| TyG2010 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.94 | 1.01(0.81,1.26) | ||
| 脑卒中 | 模型1 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.45 | 0.07 | 44.47 | <0.01 | 1.57(1.38,1.79) |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.68 | 0.08 | 80.58 | <0.01 | 1.98(1.70,2.29) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 1.06 | 0.11 | 88.85 | <0.01 | 2.89(2.32,3.60) | ||
| 模型2 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 8.77 | <0.01 | 1.23(1.07,1.42) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 7.78 | <0.01 | 1.27(1.07,1.50) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.49 | 0.13 | 14.76 | <0.01 | 1.63(1.27,2.08) | ||
| 模型3 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 5.18 | 0.02 | 1.19(1.03,1.39) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 2.40 | 0.12 | 1.18(0.96,1.46) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 4.49 | 0.03 | 1.44(1.03,2.02) | ||
| TyG2010 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 1.10 | 0.30 | 1.06(0.95,1.19) | ||
| 缺血性脑卒中 | 模型1 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.47 | 0.07 | 41.60 | <0.01 | 1.60(1.39,1.85) |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.73 | 0.08 | 81.26 | <0.01 | 2.08(1.78,2.44) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 1.14 | 0.12 | 93.42 | <0.01 | 3.13(2.49,3.95) | ||
| 模型2 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 8.67 | <0.01 | 1.25(1.08,1.45) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 10.21 | <0.01 | 1.35(1.12,1.60) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.57 | 0.13 | 18.53 | <0.01 | 1.77(1.37,2.30) | ||
| 模型3 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 4.59 | 0.03 | 1.19(1.02,1.41) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 2.83 | 0.09 | 1.21(0.97,1.52) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.40 | 0.18 | 4.95 | 0.03 | 1.50(1.05,2.14) | ||
| TyG2010 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 1.86 | 0.17 | 1.09(0.96,1.23) | ||
| 出血性脑卒中 | 模型1 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 3.32 | 0.07 | 1.36(0.98,1.88) |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 3.24 | 0.07 | 1.43(0.97,2.10) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.68 | 0.31 | 4.68 | 0.03 | 1.97(1.07,3.63) | ||
| 模型2 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.81 | 0.37 | 1.17(0.83,1.65) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | ~0.02 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.93 | 0.98(0.63,1.52) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.13 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.70 | 1.14(0.58,2.23) | ||
| 模型3 | 中低-稳定组 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 1.34 | 0.25 | 1.25(0.86,1.84) | |
| 中高-稳定组 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.67 | 1.13(0.64,1.98) | ||
| 高-稳定组 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.68 | 0.41 | 1.46(0.59,3.61) | ||
| TyG2010 | ~0.12 | 0.15 | 0.65 | 0.42 | 0.88(0.65,1.20) |
| [1] | 李镒冲,刘世炜,曾新颖,等. 1990—2016年中国及省级行政区心血管病疾病负担报告[J]. 中国循环杂志,2019,34(8):729-740. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2019.08.001. |
| [2] | 胡盛寿,高润霖,刘力生,等.《中国心血管病报告2018》概要[J]. 中国循环杂志,2019,34(3):209-220. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2019.03.001. |
| [3] | HAN C, LIU F C, YANG X L,et al. Ideal cardiovascular health and incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease among Chinese adults:the China-PAR project[J]. Sci China Life Sci,2018,61(5):504-514. DOI:10.1007/s11427-018-9281-6. |
| [4] | ORMAZABAL V, NAIR S, ELFEKY O,et al. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2018,17(1):122. DOI:10.1186/s12933-018-0762-4. |
| [5] | ZHANG M, WANG B Y, LIU Y,et al. Cumulative increased risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus with increasing triglyceride glucose index in normal-weight people:the Rural Chinese Cohort Study[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2017,16(1):30. DOI:10.1186/s12933-017-0514-x. |
| [6] | SU W Y, CHEN S C, HUANG Y T,et al. Comparison of the effects of fasting glucose,hemoglobin A1c,and triglyceride-glucose index on cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(11):E2838. DOI:10.3390/nu11112838. |
| [7] | SÁNCHEZ-GARCÍA A, RODRÍGUEZ-GUTIÉRREZ R, MANCILLAS-ADAME L,et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the triglyceride and glucose index for insulin resistance: a systematic review[J]. Int J Endocrinol,2020,2020:4678526. DOI:10.1155/2020/4678526. |
| [8] | IRACE C, CARALLO C, SCAVELLI F B,et al. Markers of insulin resistance and carotid atherosclerosis. A comparison of the homeostasis model assessment and triglyceride glucose index[J]. Int J Clin Pract,2013,67(7):665-672. DOI:10.1111/ijcp.12124. |
| [9] | ZHAO S, YU S K, CHI C,et al. Association between macro- and microvascular damage and the triglyceride glucose index in community-dwelling elderly individuals:the Northern Shanghai Study[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2019,18(1):95. DOI:10.1186/s12933-019-0898-x. |
| [10] | SÁNCHEZ-ÍÑIGO L, NAVARRO-GONZÁLEZ D, FERNÁNDEZ-MONTERO A,et al. The TyG index may predict the development of cardiovascular events[J]. Eur J Clin Invest,2016,46(2):189-197. DOI:10.1111/eci.12583. |
| [11] | WANG A X, TIAN X, ZUO Y T,et al. Change in triglyceride-glucose index predicts the risk of cardiovascular disease in the general population:a prospective cohort study[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2021,20(1):113. DOI:10.1186/s12933-021-01305-7. |
| [12] | NAGIN D S, TREMBLAY R E. Analyzing developmental trajectories of distinct but related behaviors:a group-based method[J]. Psychol Methods,2001,6(1):18-34. DOI:10.1037/1082-989x.6.1.18. |
| [13] | WU S L, AN S S, LI W J,et al. Association of trajectory of cardiovascular health score and incident cardiovascular disease[J]. JAMA Netw Open,2019,2(5):e194758. DOI:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.4758. |
| [14] | 崔皓哲,马向明,刘倩,等. 腹型肥胖与甘油三酯的交互作用对非酒精性脂肪性肝病发病的影响[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2020,36(6):1314-1319. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.06.025. |
| [15] | 崔皓哲,孙苗苗,梁明杨,等. 胆石症对心血管疾病发病的影响[J]. 肝胆胰外科杂志,2020,32(1):19-25. DOI:10.11952/j.issn.1007-1954.2020.01.005. |
| [16] | 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组.中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018[J]. 中华神经科杂志,2018,51(9):666-682. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2018.09.004. |
| [17] | 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组.中国脑出血诊治指南(2019)[J]. 中华神经科杂志,2019,52(12):994-1005. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2019.12.003. |
| [18] | THYGESEN K, ALPERT J S, JAFFE A S,et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018)[J]. Circulation,2018,138(20): e618-651. DOI:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000617. |
| [19] | 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会,高血压联盟(中国,中华医学会心血管病学分会,中国医师协会高血压专业委员会,等.中国高血压防治指南( 2018年修订版)[J]. 中国心血管杂志,2019,24(1):24-56. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2019.01.002. |
| [20] | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2018,10(1):4-67. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5809.2018.01.003. |
| [21] | NAGIN D S, ODGERS C L. Group-based trajectory modeling in clinical research[J]. Annu Rev Clin Psychol,2010,6:109-138. DOI:10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.121208.131413. |
| [22] | JONES B L, NAGIN D S, ROEDER K. A SAS procedure based on mixture models for estimating developmental trajectories[J]. Sociol Methods Res,2001,29(3):374-393. DOI:10.1177/0049124101029003005. |
| [23] | LI S S, GUO B X, CHEN H N,et al. The role of the triglyceride (triacylglycerol) glucose index in the development of cardiovascular events:a retrospective cohort analysis[J]. Sci Rep,2019,9(1):7320. DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-43776-5. |
| [24] | JANUS A, SZAHIDEWICZ-KRUPSKA E, MAZUR G,et al. Insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction constitute a common therapeutic target in cardiometabolic disorders[J]. Mediators Inflamm,2016,2016:3634948. DOI:10.1155/2016/3634948. |
| [25] | MONTAGNANI M, GOLOVCHENKO I, KIM I,et al. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase enhances mitogenic actions of insulin in endothelial cells[J]. J Biol Chem,2002,277(3):1794-1799. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M103728200. |
| [26] | KIM J A, MONTAGNANI M, KOH K K,et al. Reciprocal relationships between insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction:molecular and pathophysiological mechanisms[J]. Circulation,2006,113(15):1888-1904. DOI:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.563213. |
| [27] | ZHOU Y T, GRAYBURN P, KARIM A,et al. Lipotoxic heart disease in obese rats:implications for human obesity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2000,97(4):1784-1789. DOI:10.1073/pnas.97.4.1784. |
| [28] | 张坚,满青青,王春荣,等.中国18岁及以上人群血脂水平及分布特征[J]. 中华预防医学杂志,2005,39(5):302-305. DOI:10.3760/j:issn:0253-9624.2005.05.003. |
| [29] | 戴璟,闵杰青,杨云娟.中国九省市成年人血脂异常流行特点研究[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2018,46(2):114-118. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758. |
| [30] | 中国成人血脂异常防治指南修订联合委员会.中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中国循环杂志,2016,31(10):937-950. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614. |
| [1] | XU Baichuan, WANG Yan, ZHANG Peng, LI Yiting, LIU Feilai, XIE Yang. Research and Analysis of Screening Tools for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Comorbidity Lung Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(30): 3847-3852. |
| [2] | SHAO Xiaoying, SHAO Jie, ZHU Yan, SHAO Jinling, SHANG Ling, WU Zhenlian, ZHAO Yu, ZHANG Jiacai. Analysis of the Current Status of Iron Deficiency and Factors Affecting Iron Deficiency Anemia among Children Aged 6-36 Months in Guizhou Province [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3368-3374. |
| [3] | ZHOU Sheng, DENG Changsheng, ZOU Guanyang, SONG Jianping. Research Progress on the Pathogenesis of Complications of Malaria in Cardiovascular Diseases [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(27): 3466-3472. |
| [4] | XIANG Xinyue, ZHANG Bingqing, OUYANG Yuqin, TANG Wenjuan, FENG Wenhuan. Impact of Short-term Medical Weight Loss on Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Patients with Obesity [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3229-3239. |
| [5] | LIU Yinyin, SUI Hongping, LI Tingting, JIANG Tongtong, SHI Tieying, XIA Yunlong. Advances in Risk Prediction Models for Cardiotoxicity Associated with Breast Cancer Treatment [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 3072-3078. |
| [6] | ZHOU Qian, WU Xiaomin, WANG Baohua, YAN Ruohan, YU Miao, WU Jing. Study on Nomogram Prediction Model for Risk of Gastric Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2870-2877. |
| [7] | GUO Shengteng, ZHANG Fenfen, WAN Di, YU Dongmei, WANG Qinghua. Risk Factors for Severe Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Acute Lung Injury: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(20): 2546-2554. |
| [8] | PAN Yaojia, FU Fanglin, HAN Zheng, SUN Meng, GU Huaicong, WANG Weiqiang. Correlation of the Type of Obesity with the Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity: a Study in Male and Female Middle-aged Residents in Anhui Province [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(18): 2285-2293. |
| [9] | CHEN Qiaoqiao, SU Ping, ZHAO Yingying, PANG Jinhong, SHI Jie, WANG Yaqian, LI Qiuchun, HE Ruiyan, WANG Yue, CHEN Xueyu, QIAO Junpeng, CHI Weiwei. Association between Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Incident Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity in the Elderly: a Prospective Cohort Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(18): 2270-2277. |
| [10] | HAN Zheng, SUN Meng, FU Fanglin, PAN Yaojia, WANG Weiqiang. A Study on the Relationship between the Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity in Individuals Aged 50 and Above [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(18): 2278-2284. |
| [11] | ZHANG Bingqing, WANG Zhongkai, WU Changyong, SUN Huang, LI Ruijie, LIU Wenjie, LUO Yihua, ZHENG Lihui, PENG Yunzhu. Changes and Trend Prediction in the Global Burden of Congenital Heart Defects, 1990-2021 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(18): 2253-2261. |
| [12] | AN Qinyu, WANG Yiying, ZHANG Xiaodan, ZHANG Tianlin, ZHAN Qingqing, ZHANG Fuyan, LIU Tao, WU Yanli. Prospective Cohort Study of the Impact of Socioeconomic Status and Healthy Lifestyle on Cardiovascular Disease [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(16): 2017-2024. |
| [13] | NIE Yuanyuan, FANG Da, XU Hao, YANG Donghui, BI Yan, GU Tianwei. Clinical Characteristics and Cardiovascular Disease Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Populations with Different Liver Fibrosis Risks [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(15): 1847-1854. |
| [14] | WANG Xiaoyu, FENG Zhenzhen, WANG Jun, GUO Xiaochuan, LI Jiansheng. Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: a Systematic Review [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(12): 1527-1537. |
| [15] | KONG Xiaoqian, WANG Jingyi, WANG Li, MAO Ting, XIA Wenjing, SHI Yan. The Real Experience of Elderly People in Rural Areas Who Witnessed Acute Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Events: a Qualitative Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(11): 1342-1346. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||