

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (01): 70-78.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.322
Special Issue: 内分泌代谢性疾病最新文章合辑; 社区卫生服务最新研究合辑
• Original Research·Community-based Diabetes Management • Previous Articles Next Articles
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Behaviors of Monitoring to Prevent Chronic Diabetic Complications among Type 2 Diabetes Patients Involved in Community-based Management
1.West China School of Nursing,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610041,China
2.West China Hospital,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610041,China
3.Department of Oncology,Mianyang Central Hospital,Mianyang 621000,China
4.Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery,Yichang Central People's Hospital,Yichang 443003,China
*Corresponding author:LIU Suzhen,Professor,Master supervisor;E-mail:yly90777@163.com
Received:2021-06-16
Revised:2021-11-14
Published:2022-01-05
Online:2021-12-29
通讯作者:
刘素珍
CLC Number:
JIANG Yuan, JIANG Lingjun, LIU Suzhen, LI Hang.
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Behaviors of Monitoring to Prevent Chronic Diabetic Complications among Type 2 Diabetes Patients Involved in Community-based Management [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(01): 70-78.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.322
| 一般情况 | 例数 | 一般情况 | 例数 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 在职 | ||||
| 男 | 375(47.8) | 是 | 129(16.4) | ||
| 女 | 410(52.2) | 否 | 656(83.6) | ||
| 年龄(岁) | 家庭人均月收入(元) | ||||
| <60 | 153(19.5) | ≤1 800 | 58(7.4) | ||
| 60~80 | 500(63.7) | 1 801~2 800 | 220(28.0) | ||
| >80 | 132(16.8) | 2 801~5 000 | 375(47.8) | ||
| 民族 | >5 000 | 132(16.8) | |||
| 汉族 | 779(99.2) | 医保类型 | |||
| 少数民族 | 6(0.8) | 社会基本医疗保险 | 33(4.2) | ||
| 受教育程度 | 社会基本医疗保险+特殊疾病门诊医疗 | 369(47.0) | |||
| 初中及以下 | 313(39.9) | 社会基本医疗保险+特殊疾病门诊医疗+其他补充医疗保险 | 364(46.4) | ||
| 高中/中专 | 231(29.4) | 公费医疗 | 19(2.4) | ||
| 大专及以上 | 241(30.7) | 饮酒 | |||
| 居住形式 | 是 | 86(11.0) | |||
| 独居 | 29(3.7) | 否 | 699(89.0) | ||
| 与非配偶居住 | 61(7.8) | 吸烟 | |||
| 与配偶及他人居住 | 260(33.1) | 是 | 110(14.0) | ||
| 仅与配偶居住 | 435(55.4) | 否 | 675(86.0) | ||
| 配偶 | |||||
| 有 | 712(90.7) | ||||
| 无 | 73(9.3) | ||||
Table 1 Socio-demographic data of type 2 diabetes patients involved in community-based management
| 一般情况 | 例数 | 一般情况 | 例数 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 在职 | ||||
| 男 | 375(47.8) | 是 | 129(16.4) | ||
| 女 | 410(52.2) | 否 | 656(83.6) | ||
| 年龄(岁) | 家庭人均月收入(元) | ||||
| <60 | 153(19.5) | ≤1 800 | 58(7.4) | ||
| 60~80 | 500(63.7) | 1 801~2 800 | 220(28.0) | ||
| >80 | 132(16.8) | 2 801~5 000 | 375(47.8) | ||
| 民族 | >5 000 | 132(16.8) | |||
| 汉族 | 779(99.2) | 医保类型 | |||
| 少数民族 | 6(0.8) | 社会基本医疗保险 | 33(4.2) | ||
| 受教育程度 | 社会基本医疗保险+特殊疾病门诊医疗 | 369(47.0) | |||
| 初中及以下 | 313(39.9) | 社会基本医疗保险+特殊疾病门诊医疗+其他补充医疗保险 | 364(46.4) | ||
| 高中/中专 | 231(29.4) | 公费医疗 | 19(2.4) | ||
| 大专及以上 | 241(30.7) | 饮酒 | |||
| 居住形式 | 是 | 86(11.0) | |||
| 独居 | 29(3.7) | 否 | 699(89.0) | ||
| 与非配偶居住 | 61(7.8) | 吸烟 | |||
| 与配偶及他人居住 | 260(33.1) | 是 | 110(14.0) | ||
| 仅与配偶居住 | 435(55.4) | 否 | 675(86.0) | ||
| 配偶 | |||||
| 有 | 712(90.7) | ||||
| 无 | 73(9.3) | ||||
| 慢性并发症类型 | 例数 | <5年 | 5~10年 | >10年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高血压 | 534 | 106(19.8) | 200(37.5) | 228(42.7) |
| 高脂血症 | 362 | 94(25.9) | 157(43.4) | 111(30.7) |
| 心血管疾病 | 212 | 68(32.1) | 94(44.3) | 50(23.6) |
| 脑血管疾病 | 129 | 54(41.9) | 55(42.6) | 20(15.5) |
| 眼部疾病 | 194 | 108(55.7) | 70(36.0) | 16(8.3) |
| 肾脏疾病 | 80 | 42(52.5) | 34(42.5) | 4(5.0) |
| 周围神经病变 | 90 | 54(60.0) | 33(36.7) | 3(3.3) |
| 下肢血管病变 | 29 | 19(65.5) | 8(27.6) | 2(6.9) |
Table 2 The diagnosis time of chronic diabetic complications among type 2 diabetes patients involved in community-based management
| 慢性并发症类型 | 例数 | <5年 | 5~10年 | >10年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高血压 | 534 | 106(19.8) | 200(37.5) | 228(42.7) |
| 高脂血症 | 362 | 94(25.9) | 157(43.4) | 111(30.7) |
| 心血管疾病 | 212 | 68(32.1) | 94(44.3) | 50(23.6) |
| 脑血管疾病 | 129 | 54(41.9) | 55(42.6) | 20(15.5) |
| 眼部疾病 | 194 | 108(55.7) | 70(36.0) | 16(8.3) |
| 肾脏疾病 | 80 | 42(52.5) | 34(42.5) | 4(5.0) |
| 周围神经病变 | 90 | 54(60.0) | 33(36.7) | 3(3.3) |
| 下肢血管病变 | 29 | 19(65.5) | 8(27.6) | 2(6.9) |
| 自我检测 | 自我检测频率〔n(%)〕 | 平均得分(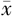 ±s,分) ±s,分) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 从不 | 偶尔 | 有时 | 经常 | 总是 | ||
| 按医生要求测血糖 | 145(18.5) | 158(20.1) | 246(31.4) | 176(22.4) | 60(7.6) | 2.81±1.20 |
| 记录血糖检测结果 | 159(20.3) | 154(19.6) | 240(30.6) | 172(21.9) | 60(7.6) | 2.81±1.20 |
| 按医生要求测量血压 | 167(21.3) | 95(12.1) | 218(27.8) | 220(28.0) | 85(10.8) | 2.95±1.30 |
| 记录血压测量结果 | 184(23.4) | 91(11.6) | 213(27.2) | 212(27.0) | 85(10.8) | 2.90±1.32 |
| 检查双足外观/感觉/温度 | 161(20.5) | 200(25.5) | 268(34.1) | 136(17.3) | 20(2.6) | 2.90±1.32 |
| 触摸足背动脉搏动 | 603(76.8) | 120(15.3) | 49(6.3) | 12(1.5) | 1(0.1) | 1.33±0.67 |
| 观察异常表现 | 83(10.6) | 202(25.7) | 346(44.1) | 127(16.2) | 27(3.4) | 2.76±0.96 |
Table 3 The frequency and score of self-observation behavior among type 2 diabetes patients involved in community-based management
| 自我检测 | 自我检测频率〔n(%)〕 | 平均得分(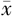 ±s,分) ±s,分) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 从不 | 偶尔 | 有时 | 经常 | 总是 | ||
| 按医生要求测血糖 | 145(18.5) | 158(20.1) | 246(31.4) | 176(22.4) | 60(7.6) | 2.81±1.20 |
| 记录血糖检测结果 | 159(20.3) | 154(19.6) | 240(30.6) | 172(21.9) | 60(7.6) | 2.81±1.20 |
| 按医生要求测量血压 | 167(21.3) | 95(12.1) | 218(27.8) | 220(28.0) | 85(10.8) | 2.95±1.30 |
| 记录血压测量结果 | 184(23.4) | 91(11.6) | 213(27.2) | 212(27.0) | 85(10.8) | 2.90±1.32 |
| 检查双足外观/感觉/温度 | 161(20.5) | 200(25.5) | 268(34.1) | 136(17.3) | 20(2.6) | 2.90±1.32 |
| 触摸足背动脉搏动 | 603(76.8) | 120(15.3) | 49(6.3) | 12(1.5) | 1(0.1) | 1.33±0.67 |
| 观察异常表现 | 83(10.6) | 202(25.7) | 346(44.1) | 127(16.2) | 27(3.4) | 2.76±0.96 |
| 筛查项目 | 检测行为频率〔n(%)〕 | 平均得分(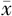 ±s,分) ±s,分) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1次/3~6个月或1次/年 | 1次/ ≥2年 | 确诊后查过1次 | 从未查过或不清楚 | ||
| HbA1c | 608(77.5) | 82(10.5) | 72(9.1) | 23(2.9) | 3.62±0.77 |
| 血脂 | 639(81.4) | 81(10.3) | 58(7.4) | 7(0.9) | 3.72±0.63 |
| 心电图 | 612(78.0) | 86(11.0) | 60(7.6) | 27(3.4) | 3.63±0.77 |
| 肾脏病变 | 606(77.2) | 69(8.8) | 69(8.8) | 41(5.2) | 3.58±0.86 |
| 视网膜病变 | 95(12.1) | 63(8.0) | 282(35.9) | 345(44.0) | 1.88±0.99 |
| 周围神经病变 | 47(6.0) | 36(4.6) | 151(19.2) | 551(70.2) | 1.46±0.84 |
| 下肢血管病变 | 46(5.9) | 38(4.8) | 158(20.1) | 543(69.2) | 1.47±0.84 |
Table 4 The frequency and score of performing screening tests for chronic diabetic complications among type 2 diabetes patients involved in community-based management
| 筛查项目 | 检测行为频率〔n(%)〕 | 平均得分(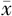 ±s,分) ±s,分) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1次/3~6个月或1次/年 | 1次/ ≥2年 | 确诊后查过1次 | 从未查过或不清楚 | ||
| HbA1c | 608(77.5) | 82(10.5) | 72(9.1) | 23(2.9) | 3.62±0.77 |
| 血脂 | 639(81.4) | 81(10.3) | 58(7.4) | 7(0.9) | 3.72±0.63 |
| 心电图 | 612(78.0) | 86(11.0) | 60(7.6) | 27(3.4) | 3.63±0.77 |
| 肾脏病变 | 606(77.2) | 69(8.8) | 69(8.8) | 41(5.2) | 3.58±0.86 |
| 视网膜病变 | 95(12.1) | 63(8.0) | 282(35.9) | 345(44.0) | 1.88±0.99 |
| 周围神经病变 | 47(6.0) | 36(4.6) | 151(19.2) | 551(70.2) | 1.46±0.84 |
| 下肢血管病变 | 46(5.9) | 38(4.8) | 158(20.1) | 543(69.2) | 1.47±0.84 |
| 特征 | 例数 | 自我观测行为 | 专项筛查行为 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 得分 | F(t)值 | P值 | 得分 | F(t)值 | P值 | |||
| 糖尿病确诊时间(年) | 20.017 | <0.001 | 31.525 | <0.001 | ||||
| <5 | 226 | 2.31±0.79 | 2.53±0.59 | |||||
| 5~10 | 331 | 2.44±0.82 | 2.82±0.55 | |||||
| >10 | 228 | 2.78±0.84 | 2.93±0.51 | |||||
| 糖尿病家族史 | 1.936 | 0.145 | 1.150 | 0.317 | ||||
| 是 | 165 | 2.42±0.79 | 2.74±0.60 | |||||
| 否 | 606 | 2.53±0.84 | 2.78±0.60 | |||||
| 不清楚 | 14 | 2.23±0.95 | 2.57±0.63 | |||||
| 最近一次检测空腹血糖水平(mmol/L) | 0.568a | 0.570 | 0.966a | 0.334 | ||||
| <7.0 | 470 | 2.51±0.81 | 2.79±0.56 | |||||
| ≥7.0 | 315 | 2.48±0.88 | 2.75±0.59 | |||||
| 最近一次检测HbA1c水平 | 3.541 | 0.029 | 100.591 | <0.001 | ||||
| <7.0% | 452 | 2.60±0.84 | 2.86±0.49 | |||||
| ≥7.0% | 252 | 2.63±0.88 | 2.85±0.54 | |||||
| 不清楚 | 81 | 2.34±0.84 | 2.01±0.51 | |||||
| 治疗方案 | 10.015 | <0.001 | 5.340 | 0.001 | ||||
| 生活方式干预 | 12 | 2.39±0.98 | 2.26±0.66 | |||||
| 口服降糖药 | 576 | 2.49±0.83 | 2.79±0.56 | |||||
| 胰岛素 | 24 | 2.67±0.86 | 2.94±0.62 | |||||
| 降糖药+胰岛素 | 173 | 2.89±0.89 | 2.85±0.58 | |||||
| 慢性并发症罹患情况 | 10.227 | <0.001 | 14.973 | <0.001 | ||||
| 无慢性并发症 | 103 | 2.28±0.79 | 2.47±0.67 | |||||
| 仅有代谢综合征 | 198 | 2.47±0.62 | 2.67±0.62 | |||||
| 仅有慢性并发症 | 49 | 2.42±0.90 | 2.95±0.62 | |||||
| 代谢综合征+慢性并发症 | 435 | 2.72±0.86 | 2.86±0.51 | |||||
| 医保类型 | 4.682 | 0.003 | 5.060 | 0.002 | ||||
| 社会基本医疗保险 | 33 | 2.48±0.92 | 2.50±0.63 | |||||
| 社会基本医疗保险+糖尿病特殊门诊补贴 | 369 | 2.48±0.96 | 2.72±0.53 | |||||
| 社会基本医疗保险+糖尿病特殊门诊补贴+其他补充医疗保险 | 364 | 2.67±0.84 | 2.83±0.59 | |||||
| 公费医疗 | 19 | 3.02±0.84 | 2.92±0.59 | |||||
| 对自我检测异常情况的处理 | 110.583 | <0.001 | - | - | ||||
| 及时就医 | 276 | 3.09±0.77 | - | |||||
| 继续观察 | 370 | 2.52±0.68 | - | |||||
| 自行增减药物 | 6 | 2.10±0.81 | - | |||||
| 未做处理 | 133 | 1.72±0.71 | - | |||||
| 参加专项筛查的原因 | - | - | 54.458 | <0.001 | ||||
| 主动筛查 | 78 | - | 3.48±0.51 | |||||
| 医生推荐 | 614 | - | 2.71±0.48 | |||||
| 身体不适 | 83 | - | 2.62±0.72 | |||||
| 例行检查 | 10 | - | 2.30±0.75 | |||||
| 对专项筛查结果的处理 | - | - | 8.173 | <0.001 | ||||
| 主动复查后处理 | 11 | - | 3.29±0.37 | |||||
| 就医及遵医处理 | 389 | - | 3.04±0.47 | |||||
| 有异常自行服药 | 7 | - | 2.27±0.48 | |||||
| 未做处理 | 378 | - | 2.49±0.52 | |||||
Table 5 Comparison of scores of self-observation behavior and performing screening tests for chronic diabetic complications among type 2 diabetes patients by illness- and treatment-related factors
| 特征 | 例数 | 自我观测行为 | 专项筛查行为 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 得分 | F(t)值 | P值 | 得分 | F(t)值 | P值 | |||
| 糖尿病确诊时间(年) | 20.017 | <0.001 | 31.525 | <0.001 | ||||
| <5 | 226 | 2.31±0.79 | 2.53±0.59 | |||||
| 5~10 | 331 | 2.44±0.82 | 2.82±0.55 | |||||
| >10 | 228 | 2.78±0.84 | 2.93±0.51 | |||||
| 糖尿病家族史 | 1.936 | 0.145 | 1.150 | 0.317 | ||||
| 是 | 165 | 2.42±0.79 | 2.74±0.60 | |||||
| 否 | 606 | 2.53±0.84 | 2.78±0.60 | |||||
| 不清楚 | 14 | 2.23±0.95 | 2.57±0.63 | |||||
| 最近一次检测空腹血糖水平(mmol/L) | 0.568a | 0.570 | 0.966a | 0.334 | ||||
| <7.0 | 470 | 2.51±0.81 | 2.79±0.56 | |||||
| ≥7.0 | 315 | 2.48±0.88 | 2.75±0.59 | |||||
| 最近一次检测HbA1c水平 | 3.541 | 0.029 | 100.591 | <0.001 | ||||
| <7.0% | 452 | 2.60±0.84 | 2.86±0.49 | |||||
| ≥7.0% | 252 | 2.63±0.88 | 2.85±0.54 | |||||
| 不清楚 | 81 | 2.34±0.84 | 2.01±0.51 | |||||
| 治疗方案 | 10.015 | <0.001 | 5.340 | 0.001 | ||||
| 生活方式干预 | 12 | 2.39±0.98 | 2.26±0.66 | |||||
| 口服降糖药 | 576 | 2.49±0.83 | 2.79±0.56 | |||||
| 胰岛素 | 24 | 2.67±0.86 | 2.94±0.62 | |||||
| 降糖药+胰岛素 | 173 | 2.89±0.89 | 2.85±0.58 | |||||
| 慢性并发症罹患情况 | 10.227 | <0.001 | 14.973 | <0.001 | ||||
| 无慢性并发症 | 103 | 2.28±0.79 | 2.47±0.67 | |||||
| 仅有代谢综合征 | 198 | 2.47±0.62 | 2.67±0.62 | |||||
| 仅有慢性并发症 | 49 | 2.42±0.90 | 2.95±0.62 | |||||
| 代谢综合征+慢性并发症 | 435 | 2.72±0.86 | 2.86±0.51 | |||||
| 医保类型 | 4.682 | 0.003 | 5.060 | 0.002 | ||||
| 社会基本医疗保险 | 33 | 2.48±0.92 | 2.50±0.63 | |||||
| 社会基本医疗保险+糖尿病特殊门诊补贴 | 369 | 2.48±0.96 | 2.72±0.53 | |||||
| 社会基本医疗保险+糖尿病特殊门诊补贴+其他补充医疗保险 | 364 | 2.67±0.84 | 2.83±0.59 | |||||
| 公费医疗 | 19 | 3.02±0.84 | 2.92±0.59 | |||||
| 对自我检测异常情况的处理 | 110.583 | <0.001 | - | - | ||||
| 及时就医 | 276 | 3.09±0.77 | - | |||||
| 继续观察 | 370 | 2.52±0.68 | - | |||||
| 自行增减药物 | 6 | 2.10±0.81 | - | |||||
| 未做处理 | 133 | 1.72±0.71 | - | |||||
| 参加专项筛查的原因 | - | - | 54.458 | <0.001 | ||||
| 主动筛查 | 78 | - | 3.48±0.51 | |||||
| 医生推荐 | 614 | - | 2.71±0.48 | |||||
| 身体不适 | 83 | - | 2.62±0.72 | |||||
| 例行检查 | 10 | - | 2.30±0.75 | |||||
| 对专项筛查结果的处理 | - | - | 8.173 | <0.001 | ||||
| 主动复查后处理 | 11 | - | 3.29±0.37 | |||||
| 就医及遵医处理 | 389 | - | 3.04±0.47 | |||||
| 有异常自行服药 | 7 | - | 2.27±0.48 | |||||
| 未做处理 | 378 | - | 2.49±0.52 | |||||
| 变量 | 赋值 |
|---|---|
| 性别 | 男=0,女=1 |
| 年龄(岁) | <60=0,0;60~80=1,0;>80=0,1 |
| 民族 | 汉族=0,少数民族=1 |
| 受教育程度 | 初中及以下=0,0,0;高中=1,0,0;专科=0,1,0;本科及以上=0,0,1 |
| 居住形式 | 独居=0,0,0;与非配偶居住=1,0,0;与配偶及他人居住=0,1,0;仅与配偶居住=0,0,1 |
| 有无配偶 | 有=0,无=1 |
| 在职 | 是=0,否=1 |
| 家庭人均月收入 | ≤1 800=0,0,0;1 801~2 800=1,0,0;2 801~5 000=0,1,0;>5 000=0,0,1 |
| 医保类型 | 社会基本医疗保险=0,0,0;社会基本医疗保险+特殊疾病门诊医疗=1,0,0;社会基本医疗保险+特殊疾病门诊医疗+其他补充医保=0,1,0;公费医疗=0,0,1 |
| 饮酒 | 是=0,否=1 |
| 吸烟 | 是=0,否=1 |
| 糖尿病家族史 | 否=0,0;是=1,0;不清楚=0,1 |
| 糖尿病确诊时间(年) | <5=0,0;5~10=1,0;>10=0,1 |
| 最近一次检测HbA1c水平 | <7.0%=0,0;≥7.0%=1,0;不清楚=0,1 |
| 糖尿病治疗方案 | 生活方式干预=0,0,0;口服降糖药=1,0,0;胰岛素=0,1,0;降糖药+胰岛素=0,0,1 |
| 罹患慢性并发症的种类 | 未罹患慢性并发症=0,0,0;仅有代谢综合征=1,0,0;代谢综合征+慢性并发症=0,1,0;仅有慢性并发症=0,0,1 |
| 对自我观测异常情况的处理 | 未做处理=0,0,0;继续观察=1,0,0;自行增减药量=0,1,0;及时就医=0,0,1 |
| 参加专项筛查的原因 | 主动筛查=0,0,0;医生推荐=1,0,0;身体不适=0,1,0;例行体检=0,0,1 |
| 对专项筛查结果的处理 | 未做处理=0,0,0;就医及遵医嘱处理=1,0,0;有异常自行服药=0,1,0;主动复查后处理=0,0,1 |
Table 6 Dummy variable setting for independent variables of multiple linear regression analysis
| 变量 | 赋值 |
|---|---|
| 性别 | 男=0,女=1 |
| 年龄(岁) | <60=0,0;60~80=1,0;>80=0,1 |
| 民族 | 汉族=0,少数民族=1 |
| 受教育程度 | 初中及以下=0,0,0;高中=1,0,0;专科=0,1,0;本科及以上=0,0,1 |
| 居住形式 | 独居=0,0,0;与非配偶居住=1,0,0;与配偶及他人居住=0,1,0;仅与配偶居住=0,0,1 |
| 有无配偶 | 有=0,无=1 |
| 在职 | 是=0,否=1 |
| 家庭人均月收入 | ≤1 800=0,0,0;1 801~2 800=1,0,0;2 801~5 000=0,1,0;>5 000=0,0,1 |
| 医保类型 | 社会基本医疗保险=0,0,0;社会基本医疗保险+特殊疾病门诊医疗=1,0,0;社会基本医疗保险+特殊疾病门诊医疗+其他补充医保=0,1,0;公费医疗=0,0,1 |
| 饮酒 | 是=0,否=1 |
| 吸烟 | 是=0,否=1 |
| 糖尿病家族史 | 否=0,0;是=1,0;不清楚=0,1 |
| 糖尿病确诊时间(年) | <5=0,0;5~10=1,0;>10=0,1 |
| 最近一次检测HbA1c水平 | <7.0%=0,0;≥7.0%=1,0;不清楚=0,1 |
| 糖尿病治疗方案 | 生活方式干预=0,0,0;口服降糖药=1,0,0;胰岛素=0,1,0;降糖药+胰岛素=0,0,1 |
| 罹患慢性并发症的种类 | 未罹患慢性并发症=0,0,0;仅有代谢综合征=1,0,0;代谢综合征+慢性并发症=0,1,0;仅有慢性并发症=0,0,1 |
| 对自我观测异常情况的处理 | 未做处理=0,0,0;继续观察=1,0,0;自行增减药量=0,1,0;及时就医=0,0,1 |
| 参加专项筛查的原因 | 主动筛查=0,0,0;医生推荐=1,0,0;身体不适=0,1,0;例行体检=0,0,1 |
| 对专项筛查结果的处理 | 未做处理=0,0,0;就医及遵医嘱处理=1,0,0;有异常自行服药=0,1,0;主动复查后处理=0,0,1 |
| 自变量 | b(95%CI) | SE | b' | t值 | P值 | 共线性诊断 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 容差 | ViF | |||||||
| 糖尿病确诊时间(年) | ||||||||
| 5~10 | -0.062(-0.183,0.058) | 0.061 | -0.036 | -1.013 | 0.311 | 0.666 | 1.502 | |
| >10 | 0.150(0.010,0.290) | 0.071 | 0.079 | 2.097 | 0.036 | 0.586 | 1.705 | |
| 慢性并发症罹患情况 | ||||||||
| 仅有代谢综合征 | 0.199(0.032,0.367) | 0.085 | 0.101 | 2.335 | 0.020 | 0.447 | 2.237 | |
| 代谢综合征+慢性并发症 | 0.283(0.129,0.437) | 0.078 | 0.164 | 3.606 | <0.001 | 0.404 | 2.467 | |
| 仅有慢性并发症 | 0.009(-0.229,0.248) | 0.122 | 0.003 | 0.078 | 0.938 | 0.698 | 1.433 | |
| 对自我观测异常情况的处理 | ||||||||
| 继续观察 | 0.743(0.603,0.883) | 0.071 | 0.433 | 10.442 | <0.001 | 0.487 | 2.052 | |
| 及时就医 | 1.276(1.127,1.426) | 0.076 | 0.711 | 16.798 | <0.001 | 0.467 | 2.141 | |
| 自行增减药物 | 0.350(-0.235,0.935) | 0.298 | 0.036 | 1.174 | 0.241 | 0.912 | 1.096 | |
Table 7 Multiple linear regression analysis of factors affecting self-observation behaviors for chronic diabetic complications among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus involved in community-based management
| 自变量 | b(95%CI) | SE | b' | t值 | P值 | 共线性诊断 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 容差 | ViF | |||||||
| 糖尿病确诊时间(年) | ||||||||
| 5~10 | -0.062(-0.183,0.058) | 0.061 | -0.036 | -1.013 | 0.311 | 0.666 | 1.502 | |
| >10 | 0.150(0.010,0.290) | 0.071 | 0.079 | 2.097 | 0.036 | 0.586 | 1.705 | |
| 慢性并发症罹患情况 | ||||||||
| 仅有代谢综合征 | 0.199(0.032,0.367) | 0.085 | 0.101 | 2.335 | 0.020 | 0.447 | 2.237 | |
| 代谢综合征+慢性并发症 | 0.283(0.129,0.437) | 0.078 | 0.164 | 3.606 | <0.001 | 0.404 | 2.467 | |
| 仅有慢性并发症 | 0.009(-0.229,0.248) | 0.122 | 0.003 | 0.078 | 0.938 | 0.698 | 1.433 | |
| 对自我观测异常情况的处理 | ||||||||
| 继续观察 | 0.743(0.603,0.883) | 0.071 | 0.433 | 10.442 | <0.001 | 0.487 | 2.052 | |
| 及时就医 | 1.276(1.127,1.426) | 0.076 | 0.711 | 16.798 | <0.001 | 0.467 | 2.141 | |
| 自行增减药物 | 0.350(-0.235,0.935) | 0.298 | 0.036 | 1.174 | 0.241 | 0.912 | 1.096 | |
| 自变量 | b(95%CI) | SE | b' | t值 | P值 | 共线性诊断 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 容差 | ViF | |||||||
| 糖尿病确诊时间(年) | ||||||||
| 5~10 | 0.185(0.115,0.255) | 0.036 | 0.160 | 5.180 | <0.001 | 0.661 | 1.513 | |
| >10 | 0.262(0.181,0.342) | 0.041 | 0.209 | 6.379 | <0.001 | 0.591 | 1.693 | |
| 最近一次检测HbA1c水平 | ||||||||
| >7.0% | -0.038(-0.102,0.025) | 0.032 | -0.031 | -1.185 | 0.236 | 0.896 | 1.115 | |
| 不清楚 | -0.655(-0.756,-0.554) | 0.052 | -0.348 | -12.722 | <0.001 | 0.840 | 0.184 | |
| 慢性并发症罹患情况 | ||||||||
| 仅有代谢综合征 | 0.117(0.020,0.214) | 0.049 | 0.089 | 2.372 | 0.018 | 0.447 | 2.239 | |
| 仅有慢性并发症 | 0.315(0.176,0.454) | 0.071 | 0.135 | 4.449 | <0.001 | 0.687 | 1.456 | |
| 代谢综合征+慢性并发症 | 0.211(0.121,0.300) | 0.046 | 0.184 | 4.601 | <0.001 | 0.396 | 2.526 | |
| 参加专项筛查的原因 | ||||||||
| 医生推荐 | -0.570(-0.667,-0.472) | -0.050 | -0.413 | -11.445 | <0.001 | 0.486 | 2.059 | |
| 身体不适 | -0.532(-0.663,-0.402) | 0.067 | -0.287 | -7.993 | <0.001 | 0.489 | 0.046 | |
| 例行体检 | -0.470(-0.744,-0.196) | 0.139 | -0.903 | -3.371 | 0.001 | 0.838 | 1.193 | |
| 对专项筛查结果的处理 | ||||||||
| 就医及遵医嘱处理 | 0.098( -0.112,0.685) | 0.039 | 0.045 | 2.237 | 0.233 | 0.678 | 2.045 | |
| 异常自行服药 | -0.063(-0.257,0.131) | 0.099 | -0.017 | -0.639 | 0.523 | 0.941 | 1.062 | |
| 主动复查后处理 | 0.352(0.292,0.413) | 0.031 | 0.309 | 11.492 | <0.001 | 0.865 | 1.156 | |
Table 8 Multiple linear regression analysis of factors affecting the performing of screening tests for chronic diabetic complications among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus involved in community-based management
| 自变量 | b(95%CI) | SE | b' | t值 | P值 | 共线性诊断 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 容差 | ViF | |||||||
| 糖尿病确诊时间(年) | ||||||||
| 5~10 | 0.185(0.115,0.255) | 0.036 | 0.160 | 5.180 | <0.001 | 0.661 | 1.513 | |
| >10 | 0.262(0.181,0.342) | 0.041 | 0.209 | 6.379 | <0.001 | 0.591 | 1.693 | |
| 最近一次检测HbA1c水平 | ||||||||
| >7.0% | -0.038(-0.102,0.025) | 0.032 | -0.031 | -1.185 | 0.236 | 0.896 | 1.115 | |
| 不清楚 | -0.655(-0.756,-0.554) | 0.052 | -0.348 | -12.722 | <0.001 | 0.840 | 0.184 | |
| 慢性并发症罹患情况 | ||||||||
| 仅有代谢综合征 | 0.117(0.020,0.214) | 0.049 | 0.089 | 2.372 | 0.018 | 0.447 | 2.239 | |
| 仅有慢性并发症 | 0.315(0.176,0.454) | 0.071 | 0.135 | 4.449 | <0.001 | 0.687 | 1.456 | |
| 代谢综合征+慢性并发症 | 0.211(0.121,0.300) | 0.046 | 0.184 | 4.601 | <0.001 | 0.396 | 2.526 | |
| 参加专项筛查的原因 | ||||||||
| 医生推荐 | -0.570(-0.667,-0.472) | -0.050 | -0.413 | -11.445 | <0.001 | 0.486 | 2.059 | |
| 身体不适 | -0.532(-0.663,-0.402) | 0.067 | -0.287 | -7.993 | <0.001 | 0.489 | 0.046 | |
| 例行体检 | -0.470(-0.744,-0.196) | 0.139 | -0.903 | -3.371 | 0.001 | 0.838 | 1.193 | |
| 对专项筛查结果的处理 | ||||||||
| 就医及遵医嘱处理 | 0.098( -0.112,0.685) | 0.039 | 0.045 | 2.237 | 0.233 | 0.678 | 2.045 | |
| 异常自行服药 | -0.063(-0.257,0.131) | 0.099 | -0.017 | -0.639 | 0.523 | 0.941 | 1.062 | |
| 主动复查后处理 | 0.352(0.292,0.413) | 0.031 | 0.309 | 11.492 | <0.001 | 0.865 | 1.156 | |
| [1] | LI X, XU Z, JI L,et al. Direct medical costs for patients with type 2 diabetes in 16 tertiary hospitals in urban China:a multicenter prospective cohort study[J]. J Diabetes Investing,2019,10(2):539-551. DOI:10.1111/jdi.12905. |
| [2] | WALKER I F, GARBE F, WRIGHT J,et al. The economic costs of cardiovascular disease,diabetes mellitus,and associated complications in South Asia:a systematic review[J]. Value Health Reg Issues,2018,15:12-26. DOI:10.1016/j.vhri.2017.05.003. |
| [3] | KHUNTI K, GAVIN J R, BOULTON A J M,et al. The Berlin Declaration:a call to improve early actions related to type 2 diabetes.Why is primary care important[J]. Prim Care Diabetes,2018,12(5):383-392. DOI:10.1016/j.pcd.2018.04.003. |
| [4] | AKRAM MU, KHALID S, KHAN S A. Identification and classification of microaneurysms for early detection of diabetic retinopathy[J]. Pattern Recogn,2013,46(1):107-116. |
| [5] | WENG J, JI L, JIA W,et al. Standards of care for type 2 diabetes in China[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev,2016,32(5):442-458. DOI:10.1002/dmrr.2827. |
| [6] | VALENCIA W M, FLOREZ H. How to prevent the microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes beyond glucose control[J]. BMJ,2017,356:i6505. DOI:10.1136/bmj.i6505. |
| [7] | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2018,10(1):4-67. |
| [8] | SCANLON P H. The English National Screening Programme for diabetic retinopathy 2003—2016[J]. Acta Diabetol,2017,54(6):515-525. DOI:10.1007/s00592-017-0974-1. |
| [9] | FOREMAN J, KEEL S, Dirani M. Adherence to diabetic eye examination guidelines in Australia:the National Eye Health Survey[J]. Med J Aust,2018,208(2):97. |
| [10] | 赵文惠,张金苹,帅瑛,等. 北京市社区2型糖尿病患者微血管并发症筛查率与糖尿病知识水平的关系[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2015,23(8):478-481. |
| [11] | LIU F, BAO Y, HU R,et al. Screening and prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetic outpatients:a randomized multicentre survey in 12 city hospitals of China[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev,2010,26(6):481-489. |
| [12] | 万霞,刘建平. 临床研究中的样本量估算:(2)观察性研究[J]. 中医杂志,2007,48(7):599-601. |
| [13] | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国血糖监测临床应用指南(2015年版)[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2015,7(10):603-613. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5809.2015.10.004. |
| [14] | 国家卫生健康委. 国家基本公共卫生服务规范(2011年版)[EB/OL]. (2011-05-24)[2021-07-12]. . |
| [15] | 满清霞. 894例2型糖尿病患者血糖控制效果及影响因素[J].中国卫生工程学,2018,17(4):545-547. |
| [16] | 赵璇,于梦根,于亚航,等. 卫生服务体系整合型改革中基层运行环境对糖尿病患者血糖控制的影响[J]. 中国卫生政策研究,2021,14(1):37-43. |
| [17] | KWASNY C, MANUWALD U, KUGLER J,et al. Systematic review of the epidemiology and natural history of the metabolic vascular syndrome and its coincidence with type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases in different european countries[J]. Horm Metab Res,2018,50(3):201-208. |
| [18] | 陈伟伟,高润霖,刘力生,等. 中国心血管病报告2013概要[J].中国循环杂志,2014,29(7):487-491. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2014.07.003. |
| [19] | 贺小宁,张雅雯,阮贞,等. 中国2型糖尿病患者慢性并发症患病率与次均医疗费用研究[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志,2019,35(3):200-205. |
| [20] | 倪云霞,刘素珍,李继平. 四川省城市社区糖尿病病人自我管理现状及相关因素分析[J]. 护理研究,2017,31(4):413-416. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6493.2017.04.008. |
| [21] | 汪星,张建凤,李志菊,等. 社区2型糖尿病患者自我管理行为现状调查[J]. 中国护理管理,2012,12(7):52-56. |
| [22] | SHEPPLER C R, LAMBERT W E, GARDINER S K,et al. Predicting adherence to diabetic eye examinations:development of the compliance with Annual Diabetic Eye Exams Survey[J]. Ophthalmology,2014,121(6):1212-1219. |
| [23] | KREFT D, MCGUINNESS M B, DOBLHAMMER G,et al. Diabetic retinopathy screening in incident diabetes mellitus type 2 in Germany between 2004 and 2013:a prospective cohort study based on health claims data[J]. PLoS One,2018,13(4):e0195426. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0195426. |
| [1] | HU Jieman, TAN Feixiang, YUAN Anxin, CHEN Shiyu, TANG Chulei, YIN Yueheng, BA Lei, XU Qin. Analysis of the Trajectory of Postoperative Frailty and Influencing Factors in Patients with Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3276-3282. |
| [2] | CHOU Xintong, PENG Hanyu, MA Hui, ZHANG Zhen, SU Xian, QIU Hongyan. Maternal Preferences in Contraceptive Decision-making: an Analysis of Influencing Factors [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3294-3299. |
| [3] | WEI Jiaohua, PENG Huiru, PENG Jianye, TAN Wenting, HUANG Jine, FANG Li. Expression of the Serum MOTS-c and Its Correlation with Atrial Remodeling in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3271-3276. |
| [4] | YU Zizi, LIU Duli, LI Ximin, RUAN Chunyi, YIN Xiangyang, CAI Le. Analysis of the Prevalence and Self-management of Hypertension and Its Influencing Factors in Rural [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3137-3143. |
| [5] | FAN Boyang, ZHANG Yu, SUN Wenning, ZHANG Huifang, WANG Yingjie, ZHANG Ao, ZHAO Yang, WANG Haipeng. Study of Behavioral Intention and Influencing Factors of Integrated Medical and Preventive Care Provided by Grassroots Doctors for Patients with Chronic Diseases [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3144-3150. |
| [6] | WANG Rupeng, NAN Jing, HU Yiran, YANG Shenghua, JIN Zening. Predictive Value of the Triglyceride-Glucose Body Mass Index for Slow Flow/No-reflow Phenomenon in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Acute Myocardial Infarction Undergoing Emergency Percutaneous Coronary Intervention [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 2985-2992. |
| [7] | WU Yue, WANG Xuetong, KE Bilian. Evaluation of Vision-related Quality of Life in Myopic Macular Degeneration Patients with Low Vision and Associated Factors [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2908-2914. |
| [8] | DING Zijun, ZHOU Nannan, LUO Xing, LUO Jieyu, HAO Wenjuan, ZHANG Chunjiang, JIN Xin, ZHAO Dan. Cognitive Impairment in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis and Its Influencing Factors: a Multicenter Cross-sectional Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2885-2893. |
| [9] | WEI Xiaoxia, CHEN Nuo, WANG Juanjuan, ZHU Jingfen. The Effects of Depression and Anxiety on Smoking Behavior among Vocational School Students [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2826-2832. |
| [10] | ZHAO Xiaoqing, GUO Tongtong, ZHANG Xinyi, LI Linhong, ZHANG Ya, JI Lihong, DONG Zhiwei, GAO Qianqian, CAI Weiqing, ZHENG Wengui, JING Qi. Construction and Validation of a Risk Prediction Model for Cognitive Impairment in Community-dwelling Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2776-2783. |
| [11] | HAO Aihua, ZENG Ziying, JIN Aiqiong, TANG Lingling, ZHENG Zique, MA Jingtai, ZHAO Jianguo, ZENG Weilin, XIAO Jianpeng, NIE Hui, YANG Ying. Analysis of Factors Influencing Avoidable Hospitalization for Elderly Hypertensive Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2370-2375. |
| [12] | JING Tao, DAI Yongmei, LUO Jianying, LUO Wei, JI Yelinfan, PENG Chi, ZHANG Cuijun, CAO Yanjun, ZHENG Qing, HUANG Yu, SHEN Hejun. The Body Mass Index, Dietary Knowledge Acquisition Level, Sedentary Time and Influencing Factors among Chinese High School Students [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(16): 2025-2032. |
| [13] | HUANG Zhijie, MAI Zhihua, WANG Haoxiang, HE Yuming, DENG Qiaoyan, DAI Ranran, ZHOU Zhiheng. Multimorbidity of Hypertension, Diabetes, and Dyslipidemia and Influencing Factors of Family Function among the Elderly [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(16): 2001-2010. |
| [14] | ZHAO Can, SHEN Ying, XI Qian, PENG Houxuan, QIN Jinqiong, WANG Xuan, ZHENG Yanping, QIN Li, ZUO Yanli. The Hospitalization Spending and Associated Factors in Inpatients with Multimorbidity in Township Health Centers in Guangxi [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(16): 2039-2049. |
| [15] | SHENG Jingyu, LIU Fanfan, MA Mei, TIAN Lin, LIU Yutong, LIU Fengmin, GAO Shan, YU Chunquan. Association between Blood Urea Nitrogen to Serum Albumin Ratio and Carotid Plaque in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(15): 1831-1839. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||