

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (02): 153-158.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.223
Special Issue: 高血压最新文章合辑
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
TG/HDL-C Ratio and ba-PWV in Patients with Essential Hypertension
1.Department of Hypertension,Beijing Anzhen Hospital,Capital Medical University,Beijing 100029,China
2.Department of Hypertension Research,Beijing Anzhen Hospital,Capital Medical University/Beijing Institute of Heart Lung and Blood Vessel Diseases,Beijing 100029,China
*Corresponding author:CHENG Wenli,Professor,Chief physician;E-mail:chengwenli2000@163.com
Received:2021-05-27
Revised:2021-09-22
Published:2022-01-15
Online:2021-12-29
通讯作者:
程文立
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZENG Rong, ZHENG Keyang, YAN Jiafu, WANG Zuoguang, CHENG Wenli.
TG/HDL-C Ratio and ba-PWV in Patients with Essential Hypertension [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(02): 153-158.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.223
| 项目 | 低分位组(n=219) | 高分位组(n=220) | 检验统计量值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性〔n(%)〕 | 118(53.9) | 149(67.7) | 8.82a | 0.003 |
年龄(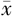 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 54.8±13.9 | 50.3±13.0 | 11.96b | <0.001 |
BMI(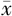 ±s,kg/m2) ±s,kg/m2) | 26.1±3.7 | 28.4±4.0 | 36.72b | <0.001 |
| 糖尿病史〔n(%)〕 | 56(25.6) | 75(34.1) | 3.80a | 0.051 |
| 高脂血症史〔n(%)〕 | 150(68.5) | 200(90.9) | 34.11a | <0.001 |
| 吸烟史〔n(%)〕 | 68(31.1) | 97(44.1) | 7.95a | 0.005 |
| 饮酒史〔n(%)〕 | 41(18.7) | 36(16.4) | 0.42a | 0.516 |
| 血肌酐〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 78.0(64.0,95.2) | 91.0(76.0,111.5) | -2.03c | 0.043 |
总胆固醇(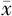 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | 4.5±1.1 | 4.7±1.2 | 5.29b | 0.022 |
| TG〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 1.0(0.8,1.3) | 2.3(1.8,3.2) | -13.11c | <0.001 |
LDL-C(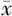 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | 2.8±0.8 | 2.8±0.8 | 0.49b | 0.482 |
HDL-C(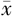 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | 1.2±0.5 | 0.9±0.2* | 84.19b | <0.001 |
| 血尿酸〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 334.6(265.0,413.7) | 412.2(322.0,479.2) | -4.53c | <0.001 |
空腹血糖( ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | 5.6±1.0 | 6.0±1.7 | 10.80b | <0.001 |
| TG/HDL-C比值〔M(P25,P75)〕 | 0.9(0.6,1.2) | 2.4(1.8,3.6) | -13.53c | <0.001 |
Table 1 Comparison of general data and blood biochemical indices between two groups of patients with essential hypertension with low or high TG/HDL-C ratio
| 项目 | 低分位组(n=219) | 高分位组(n=220) | 检验统计量值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性〔n(%)〕 | 118(53.9) | 149(67.7) | 8.82a | 0.003 |
年龄(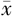 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 54.8±13.9 | 50.3±13.0 | 11.96b | <0.001 |
BMI(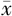 ±s,kg/m2) ±s,kg/m2) | 26.1±3.7 | 28.4±4.0 | 36.72b | <0.001 |
| 糖尿病史〔n(%)〕 | 56(25.6) | 75(34.1) | 3.80a | 0.051 |
| 高脂血症史〔n(%)〕 | 150(68.5) | 200(90.9) | 34.11a | <0.001 |
| 吸烟史〔n(%)〕 | 68(31.1) | 97(44.1) | 7.95a | 0.005 |
| 饮酒史〔n(%)〕 | 41(18.7) | 36(16.4) | 0.42a | 0.516 |
| 血肌酐〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 78.0(64.0,95.2) | 91.0(76.0,111.5) | -2.03c | 0.043 |
总胆固醇(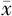 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | 4.5±1.1 | 4.7±1.2 | 5.29b | 0.022 |
| TG〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 1.0(0.8,1.3) | 2.3(1.8,3.2) | -13.11c | <0.001 |
LDL-C(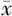 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | 2.8±0.8 | 2.8±0.8 | 0.49b | 0.482 |
HDL-C(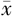 ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | 1.2±0.5 | 0.9±0.2* | 84.19b | <0.001 |
| 血尿酸〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 334.6(265.0,413.7) | 412.2(322.0,479.2) | -4.53c | <0.001 |
空腹血糖( ±s,mmol/L) ±s,mmol/L) | 5.6±1.0 | 6.0±1.7 | 10.80b | <0.001 |
| TG/HDL-C比值〔M(P25,P75)〕 | 0.9(0.6,1.2) | 2.4(1.8,3.6) | -13.53c | <0.001 |
| 项目 | 低分位组(n=219) | 高分位组(n=220) | 检验统计量值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
24 h平均收缩压(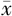 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 126.1±14.4 | 133.3±14.0 | 28.07b | <0.001 |
24 h平均舒张压(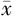 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 77.2±11.1 | 82.5±12.4 | 22.36b | <0.001 |
24 h平均心率(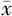 ±s,次/分) ±s,次/分) | 67.7±9.1 | 69.4±9.1 | 3.84b | 0.051 |
日间平均收缩压(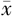 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 128.5±14.3 | 134.8±14.1 | 21.50b | <0.001 |
日间平均舒张压(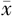 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 79.1±11.2 | 84.3±12.6 | 20.62b | <0.001 |
日间平均心率(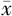 ±s,次/分) ±s,次/分) | 70.8±9.9 | 72.3±10.0 | 2.69b | 0.101 |
夜间平均收缩压(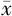 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 121.5±16.5 | 130.3±16.8 | 30.40b | <0.001 |
夜间平均舒张压(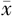 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 73.0±11.8 | 79.0±13.2 | 24.97b | <0.001 |
夜间平均心率(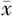 ±s,次/分) ±s,次/分) | 61.6±8.6 | 63.8±8.9 | 6.95b | 0.009 |
| 收缩压夜间下降率〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | 6.0(0.7,10.8) | 3.9(-1.0,9.0) | 2.34c | 0.020 |
| 舒张压夜间下降率〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | 7.6(2.8,12.9) | 6.3(1.3,11.2) | 1.33c | 0.183 |
| 勺型血压〔n(%)〕 | 55(25.1) | 38(17.3) | 4.04a | 0.044 |
ba-PWV(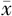 ±s,cm/s) ±s,cm/s) | 1 588.4±309.6 | 1 654.6±368.8 | 4.14 | 0.042 |
Table 2 Comparison of ambulatory blood pressure parameters and ba-PWV between two groups of patients with essential hypertension with low or high TG/HDL-C ratio
| 项目 | 低分位组(n=219) | 高分位组(n=220) | 检验统计量值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
24 h平均收缩压(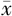 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 126.1±14.4 | 133.3±14.0 | 28.07b | <0.001 |
24 h平均舒张压(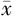 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 77.2±11.1 | 82.5±12.4 | 22.36b | <0.001 |
24 h平均心率(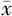 ±s,次/分) ±s,次/分) | 67.7±9.1 | 69.4±9.1 | 3.84b | 0.051 |
日间平均收缩压(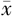 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 128.5±14.3 | 134.8±14.1 | 21.50b | <0.001 |
日间平均舒张压(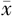 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 79.1±11.2 | 84.3±12.6 | 20.62b | <0.001 |
日间平均心率(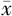 ±s,次/分) ±s,次/分) | 70.8±9.9 | 72.3±10.0 | 2.69b | 0.101 |
夜间平均收缩压(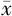 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 121.5±16.5 | 130.3±16.8 | 30.40b | <0.001 |
夜间平均舒张压(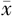 ±s,mm Hg) ±s,mm Hg) | 73.0±11.8 | 79.0±13.2 | 24.97b | <0.001 |
夜间平均心率(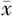 ±s,次/分) ±s,次/分) | 61.6±8.6 | 63.8±8.9 | 6.95b | 0.009 |
| 收缩压夜间下降率〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | 6.0(0.7,10.8) | 3.9(-1.0,9.0) | 2.34c | 0.020 |
| 舒张压夜间下降率〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | 7.6(2.8,12.9) | 6.3(1.3,11.2) | 1.33c | 0.183 |
| 勺型血压〔n(%)〕 | 55(25.1) | 38(17.3) | 4.04a | 0.044 |
ba-PWV(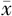 ±s,cm/s) ±s,cm/s) | 1 588.4±309.6 | 1 654.6±368.8 | 4.14 | 0.042 |
| 自变量 | β | 95%CI | SE | t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 61.71 | (-9.749,133.187) | 36.35 | 1.697 | 0.090 |
| 年龄 | 12.35 | (10.307,14.401) | 1.04 | 11.863 | <0.001 |
| BMI | -4.66 | (-11.503,2.182) | 3.48 | -1.339 | 0.181 |
| 吸烟史 | -10.49 | (-75.984,54.999) | 33.31 | -0.315 | 0.753 |
| 饮酒史 | 25.20 | (-51.478,101.883) | 39.01 | 0.646 | 0.519 |
| 血肌酐 | -0.18 | (-0.452,0.078) | 0.13 | -1.390 | 0.165 |
| 总胆固醇 | 2.30 | (-39.199,43.801) | 21.11 | 0.109 | 0.913 |
| LDL-C | 3.50 | (-50.003,57.016) | 27.22 | 0.129 | 0.898 |
| 血尿酸 | -0.15 | (-0.389,0.086) | 0.12 | -1.256 | 0.210 |
| 空腹血糖 | 20.69 | (1.532,39.854) | 9.74 | 2.123 | 0.034 |
| TG/HDL-C比值 | 20.99 | (6.176,35.810) | 7.53 | 2.785 | 0.006 |
| 24 h平均收缩压 | 7.57 | (5.656,9.493) | 0.97 | 7.761 | <0.001 |
Table 3 Multiple linear regression analysis of influencing factors of ba-PWV in patients with essential hypertension
| 自变量 | β | 95%CI | SE | t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 61.71 | (-9.749,133.187) | 36.35 | 1.697 | 0.090 |
| 年龄 | 12.35 | (10.307,14.401) | 1.04 | 11.863 | <0.001 |
| BMI | -4.66 | (-11.503,2.182) | 3.48 | -1.339 | 0.181 |
| 吸烟史 | -10.49 | (-75.984,54.999) | 33.31 | -0.315 | 0.753 |
| 饮酒史 | 25.20 | (-51.478,101.883) | 39.01 | 0.646 | 0.519 |
| 血肌酐 | -0.18 | (-0.452,0.078) | 0.13 | -1.390 | 0.165 |
| 总胆固醇 | 2.30 | (-39.199,43.801) | 21.11 | 0.109 | 0.913 |
| LDL-C | 3.50 | (-50.003,57.016) | 27.22 | 0.129 | 0.898 |
| 血尿酸 | -0.15 | (-0.389,0.086) | 0.12 | -1.256 | 0.210 |
| 空腹血糖 | 20.69 | (1.532,39.854) | 9.74 | 2.123 | 0.034 |
| TG/HDL-C比值 | 20.99 | (6.176,35.810) | 7.53 | 2.785 | 0.006 |
| 24 h平均收缩压 | 7.57 | (5.656,9.493) | 0.97 | 7.761 | <0.001 |
| [1] | YU Y,LI M H,HUANG X,et al. A U-shaped association between the LDL-cholesterol to HDL-cholesterol ratio and all-cause mortality in elderly hypertensive patients:a prospective cohort study[J]. Lipids Health Dis,2020,19(1):238. DOI:10.1186/s12944-020-01413-5. |
| [2] | LIN T,XIA X,YU J,et al. The predictive study of the relation between elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and mortality in peritoneal dialysis[J]. Lipids Health Dis,2020,19(1):51. DOI:10.1186/s12944-020-01240-8. |
| [3] | FAN J H,LIU Y Q,YIN S P,et al. Small dense LDL cholesterol is associated with metabolic syndrome traits independently of obesity and inflammation[J]. Nutr Metab(Lond),2019,16:7. DOI:10.1186/s12986-019-0334-y. |
| [4] | HO C I,CHEN J Y,CHEN S Y,et al. Relationship between TG/HDL-C ratio and metabolic syndrome risk factors with chronic kidney disease in healthy adult population[J]. Clin Nutr,2015,34(5):874-880. DOI:10.1016/j.clnu.2014.09.007. |
| [5] | SULTANI R,TONG D C,PEVERELLE M,et al. Elevated triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol(TG/HDL-C)ratio predicts long-term mortality in high-risk patients[J]. Heart Lung Circ,2020,29(3):414-421. DOI:10.1016/j.hlc.2019.03.019. |
| [6] | NUR ZATI IWANI A K,JALALUDIN M Y,WAN MOHD ZIN R M,et al. TG:HDL-C ratio is a good marker to identify children affected by obesity with increased cardiometabolic risk and insulin resistance[J]. Int J Endocrinol,2019,2019:8586167. DOI:10.1155/2019/8586167. |
| [7] | LEE J S,CHANG P Y,ZHANG Y,et al. Triglyceride and HDL-C dyslipidemia and risks of coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke by glycemic dysregulation status:the strong heart study[J]. Diabetes Care,2017,40(4):529-537. DOI:10.2337/dc16-1958. |
| [8] | GHARIPOUR M,SADEGHI M,NEZAFATI P,et al. Cardiovascular disease risk assessment:triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein versus metabolic syndrome criteria[J]. J Res Health Sci,2019,19(2):e00442. |
| [9] | SINGH-MANOUX A,FAYOSSE A,SABIA S,et al. Clinical,socioeconomic,and behavioural factors at age 50 years and risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity and mortality:a cohort study[J]. PLoS Med,2018,15(5):e1002571. DOI:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002571. |
| [10] | CWYNAR M,GASOWSKI J,GRYGLEWSKA B,et al. Insulin resistance and renal sodium handling influence arterial stiffness in hypertensive patients with prevailing sodium intake[J]. Am J Hypertens,2019,32(9):848-857. DOI:10.1093/ajh/hpz063. |
| [11] | URUSKA A,ZOZULINSKA-ZIOLKIEWICZ D,NIEDZWIECKI P,et al. TG/HDL-C ratio and visceral adiposity index may be useful in assessment of insulin resistance in adults with type 1 diabetes in clinical practice[J]. J Clin Lipidol,2018,12(3):734-740. DOI:10.1016/j.jacl.2018.01.005. |
| [12] | BEHIRY E G,EL NADY N M,ABDEL HAIE O M,et al. Evaluation of TG-HDL ratio instead of HOMA ratio as insulin resistance marker in overweight and children with obesity[J]. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets,2019,19(5):676-682. DOI:10.2174/1871530319666190121123535. |
| [13] | HILL M A,YANG Y,ZHANG L P,et al. Insulin resistance,cardiovascular stiffening and cardiovascular disease[J]. Metabolism,2021,119:154766. DOI:10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154766. |
| [14] | WEN J H,ZHONG Y Y,WEN Z G,et al. Triglyceride to HDL-C ratio and increased arterial stiffness in apparently healthy individuals[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med,2015,8(3):4342-4348. DOI:10.4239/wjd.v10.i2.63 |
| [15] | ZHAO W W,GONG W,WU N,et al. Association of lipid profiles and the ratios with arterial stiffness in middle-aged and elderly Chinese[J]. Lipids Health Dis,2014,13:37. DOI:10.1186/1476-511X-13-37. |
| [16] | CAO X,WANG D L,ZHOU J S,et al. Comparison of lipoprotein derived indices for evaluating cardio-metabolic risk factors and subclinical organ damage in middle-aged Chinese adults[J]. Clin Chim Acta,2017,475:22-27. DOI:10.1016/j.cca.2017.09.014. |
| [17] | SHIMIZU Y,NAKAZATO M,SEKITA T,et al. Association of arterial stiffness and diabetes with triglycerides-to-HDL cholesterol ratio for Japanese men:the Nagasaki Islands Study[J]. Atherosclerosis,2013,228(2):491-495. DOI:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.03.021. |
| [18] | 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会,高血压联盟(中国),中华医学会心血管病学分会,等. 中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版)[J]. 中国心血管杂志,2019,24(1):24-56. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2019.01.002. |
| [19] | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2021,13(4):315-409. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20210221-00095. |
| [20] | 诸骏仁,高润霖,赵水平,等. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中国循环杂志,2016,31(10):937-953. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2016.10.001. |
| [21] | URBINA E M,KHOURY P R,MCCOY C E,et al. Triglyceride to HDL-C ratio and increased arterial stiffness in children,adolescents,and young adults[J]. Pediatrics,2013,131(4):e1082-1090. DOI:10.1542/peds.2012-1726. |
| [22] | MENG C C,SUN M,WANG Z X,et al. Insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function are associated with arterial stiffness in individuals without hypertension[J]. J Diabetes Res,2013,2013:151675. DOI:10.1155/2013/151675. |
| [23] | ORMAZABAL V,NAIR S,ELFEKY O,et al. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2018,17(1):122. DOI:10.1186/s12933-018-0762-4. |
| [24] | MARKUS M R P,ROSPLESZCZ S,ITTERMANN T,et al. Glucose and insulin levels are associated with arterial stiffness and concentric remodeling of the heart[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2019,18(1):145. DOI:10.1186/s12933-019-0948-4. |
| [25] | KOZAKOVA M,MORIZZO C,GONCALVES I,et al. Cardiovascular organ damage in type 2 diabetes mellitus:the role of lipids and inflammation[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2019,18(1):61. DOI:10.1186/s12933-019-0865-6. |
| [26] | AROOR A R,JIA G H,SOWERS J R. Cellular mechanisms underlying obesity-induced arterial stiffness[J]. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol,2018,314(3):R387-398. DOI:10.1152/ajpregu.00235.2016. |
| [27] | TANAKA M. Improving obesity and blood pressure[J]. Hypertens Res,2020,43(2):79-89. DOI:10.1038/s41440-019-0348-x. |
| [28] | IVANOVA E A,MYASOEDOVA V A,MELNICHENKO A A,et al. Small dense low-density lipoprotein as biomarker for atherosclerotic diseases[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev,2017,2017:1273042. DOI:10.1155/2017/1273042. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||