中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (08): 923-932.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0364
• 论著 • 上一篇
范佳宁1,2, 陈洁婷3, 王梓琪1,2, 范津赫1,2, 井明霞1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-17
修回日期:2024-11-06
出版日期:2025-03-15
发布日期:2025-01-02
通讯作者:
井明霞
作者贡献:
范佳宁负责数据分析,文章撰写,并对文章整体负责;陈洁婷进行研究设计指导,论文指导与修改;王梓琪、范津赫进行数据的收集与整理;井明霞负责文章的质量控制,论文修改与审校。
FAN Jianing1,2, CHEN Jieting3, WANG Ziqi1,2, FAN Jinhe1,2, JING Mingxia1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-17
Revised:2024-11-06
Published:2025-03-15
Online:2025-01-02
Contact:
JING Mingxia
摘要: 背景 随着人口老龄化程度进一步加深,我国慢性病负担明显加剧,其中大部分患者患有高血压、糖尿病等心血管代谢性疾病。健康相关生命质量(HRQoL)作为主观评价指标,能够反映慢性病患者生理健康水平与心理健康状态。目前有关心血管代谢性疾病患者的HRQoL研究主要集中在影响因素及其现状评估,然而,相较于对HRQoL静态现状的研究,对其随时间变化的动态趋势的研究稍显不足。 目的 分析中老年心血管代谢性疾病患者HRQoL的发展轨迹及其影响因素,并探讨各影响因素的贡献程度,为提高心血管代谢性疾病患者HRQoL提供科学依据。 方法 利用现场调查的时间序列数据,本研究于2016年(T0)采用典型抽样方法选取新疆生产建设兵团某师3个城市社区和周边的2个团场社区进行基线调查,随机抽取符合纳入标准的原发性高血压病或2型糖尿病患者进行调查。并分别在2017年(T1)、2018年(T2)、2019年(T3)和2021年(T4)进行4轮随访调查。基线时期共调查1 599例,完成后期4轮随访过程的共有565例,其中高血压389例、糖尿病176例。在排除HRQoL和人口学特征等关键指标缺失的样本后,最终有563例研究对象的数据纳入分析。采用自行设计的问卷进行调查,问卷内容主要包括个人基本情况、社会心理状况、生活方式、疾病情况以及卫生服务利用5部分内容。采用五级的欧洲五维健康量表(EQ-5D-5L)对患者的HRQoL进行测量。运用增长混合模型探索异质化HRQoL发展轨迹,通过Logistic回归模型分析和Shapley值分解进行发展轨迹的影响因素分析和评估。 结果 本研究共识别3类异质化发展轨迹:显著增长组452例(80.28%)、适度下降组81例(14.39%)和显著衰减组30例(5.33%)。多元Logistic回归分析结果显示,以显著增长组为参照,不进行体育锻炼、生活自理能力受损、健康状况恶化、非城镇职工医保以及对门诊慢性病政策不满意的患者更容易进入适度下降组(P<0.05);不进行体育锻炼以及对门诊慢性病政策满意程度一般的患者更容易进入显著衰减组(P<0.05)。Shapley值分解结果显示,各影响因素对患者HRQoL的预测贡献程度在各类别轨迹组间不同。在显著增长组中,贡献程度较大的影响因素为健康状况变化和生活自理能力;在适度下降组中,贡献程度较大的影响因素为体育锻炼和生活自理能力;在显著衰减组中,对门诊慢性病政策的满意程度在贡献程度分析中排名第一,其次则是体育锻炼。 结论 心血管代谢性疾病患者HRQoL存在不同的变化轨迹,且不同轨迹的影响因素不尽相同。可根据心血管代谢性疾病患者HRQoL变化轨迹及影响因素动态调整干预措施,为其提供更为精准的医疗卫生服务。应重点关注健康状况恶化、生活自理能力受损以及不进行体育锻炼的CMD患者。同时,应开展有关慢性病政策和医疗保险等养老政策的宣传,持续提高门诊慢性病医疗服务质量,提升患者对门诊慢性病政策的满意度,从而进一步改善HRQoL。
| 特征 | 例数 | 健康效用值 | 特征 | 例数 | 健康效用值 | 特征 | 例数 | 健康效用值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | BMI | 并发症 | ||||||
| 男 | 213 | 0.952(0.842,1.000) | 偏低 | 19 | 0.942(0.703,1.000) | 是 | 316 | 0.942(0.784,1.000) |
| 女 | 350 | 0.942(0.876,1.000) | 正常 | 152 | 0.942(0.876,1.000) | 否 | 247 | 1.000(0.942,1.000) |
| 年龄(岁) | 超重或肥胖 | 392 | 0.951(0.833,1.000) | 家庭患相同病情况(人) | ||||
| 45~59 | 14 | 1.000(0.942,1.000) | 社会支持 | 1 | 318 | 0.942(0.842,1.000) | ||
| 60~79 | 367 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) | 低支持程度 | 4 | 0.938(0.747,1.000) | 2 | 221 | 0.942(0.876,1.000) |
| ≥80 | 182 | 0.942(0.810,1.000) | 中支持程度 | 487 | 0.942(0.828,1.000) | ≥3 | 24 | 0.942(0.701,1.000) |
| 婚姻状况 | 高支持程度 | 72 | 1.000(0.936,1.000) | 健康状况变化 | ||||
| 有配偶 | 425 | 0.942(0.839,1.000) | 吸烟 | 没变化 | 218 | 1.000(0.940,1.000) | ||
| 无配偶 | 138 | 0.975(0.893,1.000) | 是 | 37 | 0.942(0.842,1.000) | 变好 | 80 | 1.000(0.942,1.000) |
| 民族 | 否 | 526 | 0.951(0.862,1.000) | 变坏 | 249 | 0.893(0.734,1.000) | ||
| 汉族 | 554 | 0.942(0.862,1.000) | 饮酒 | 不确定 | 16 | 0.942(0.842,1.000) | ||
| 其他 | 9 | 0.942(0.543,1.000) | 是 | 23 | 0.942(0.842,1.000) | 医保类型 | ||
| 居住地 | 否 | 540 | 0.942(0.862,1.000) | 公费医疗 | 2 | 0.971(0.942,—) | ||
| 城市 | 264 | 0.942(0.827,1.000) | 体育锻炼 | 城镇职工基本医疗保险 | 411 | 0.942(0.848,1.000) | ||
| 城郊 | 98 | 1.000(0.868,1.000) | 是 | 505 | 0.951(0.885,1.000) | 城镇居民基本医疗保险 | 145 | 1.000(0.859,1.000) |
| 农村 | 201 | 0.951(0.893,1.000) | 否 | 58 | 0.697(0.257,0.942) | 新型农村合作医疗保险 | 5 | 1.000(0.893,1.000) |
| 受教育程度 | 体检 | 门诊慢性病政策的了解程度 | ||||||
| 不识字 | 181 | 0.942(0.784,1.000) | 是 | 547 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) | 了解 | 242 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) |
| 高中及以下 | 369 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) | 否 | 16 | 0.259(0.062,0.937) | 一般 | 173 | 0.942(0.876,1.000) |
| 大专及以上 | 13 | 1.000(0.843,1.000) | 生活自理能力 | 不了解 | 148 | 0.942(0.783,1.000) | ||
| 家庭规模(人) | 正常 | 428 | 1.000(0.942,1.000) | 门诊慢性病政策的满意程度 | ||||
| 1 | 81 | 1.000(0.893,1.000) | 受损 | 135 | 0.734(0.481,0.893) | 满意 | 493 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) |
| 2 | 370 | 0.942(0.841,1.000) | 疾病数量(种) | 一般 | 44 | 0.895(0.735,1.000) | ||
| ≥3 | 112 | 0.942(0.827,1.000) | 1 | 25 | 1.000(0.876,1.000) | 不满意 | 26 | 0.883(0.742,0.963) |
| 贫困情况 | 2 | 74 | 0.942(0.868,1.000) | 定点医疗机构的满意程度 | ||||
| 是 | 35 | 0.893(0.734,1.000) | ≥3 | 464 | 0.942(0.852,1.000) | 满意 | 474 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) |
| 否 | 528 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) | 一般 | 56 | 0.942(0.783,1.000) | |||
| 不满意 | 33 | 0.824(0.592,1.000) | ||||||
表1 不同基本特征的研究对象健康效用值[M(P25,P75),n=563]
Table 1 Basic characteristic and health utility value of subjects
| 特征 | 例数 | 健康效用值 | 特征 | 例数 | 健康效用值 | 特征 | 例数 | 健康效用值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | BMI | 并发症 | ||||||
| 男 | 213 | 0.952(0.842,1.000) | 偏低 | 19 | 0.942(0.703,1.000) | 是 | 316 | 0.942(0.784,1.000) |
| 女 | 350 | 0.942(0.876,1.000) | 正常 | 152 | 0.942(0.876,1.000) | 否 | 247 | 1.000(0.942,1.000) |
| 年龄(岁) | 超重或肥胖 | 392 | 0.951(0.833,1.000) | 家庭患相同病情况(人) | ||||
| 45~59 | 14 | 1.000(0.942,1.000) | 社会支持 | 1 | 318 | 0.942(0.842,1.000) | ||
| 60~79 | 367 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) | 低支持程度 | 4 | 0.938(0.747,1.000) | 2 | 221 | 0.942(0.876,1.000) |
| ≥80 | 182 | 0.942(0.810,1.000) | 中支持程度 | 487 | 0.942(0.828,1.000) | ≥3 | 24 | 0.942(0.701,1.000) |
| 婚姻状况 | 高支持程度 | 72 | 1.000(0.936,1.000) | 健康状况变化 | ||||
| 有配偶 | 425 | 0.942(0.839,1.000) | 吸烟 | 没变化 | 218 | 1.000(0.940,1.000) | ||
| 无配偶 | 138 | 0.975(0.893,1.000) | 是 | 37 | 0.942(0.842,1.000) | 变好 | 80 | 1.000(0.942,1.000) |
| 民族 | 否 | 526 | 0.951(0.862,1.000) | 变坏 | 249 | 0.893(0.734,1.000) | ||
| 汉族 | 554 | 0.942(0.862,1.000) | 饮酒 | 不确定 | 16 | 0.942(0.842,1.000) | ||
| 其他 | 9 | 0.942(0.543,1.000) | 是 | 23 | 0.942(0.842,1.000) | 医保类型 | ||
| 居住地 | 否 | 540 | 0.942(0.862,1.000) | 公费医疗 | 2 | 0.971(0.942,—) | ||
| 城市 | 264 | 0.942(0.827,1.000) | 体育锻炼 | 城镇职工基本医疗保险 | 411 | 0.942(0.848,1.000) | ||
| 城郊 | 98 | 1.000(0.868,1.000) | 是 | 505 | 0.951(0.885,1.000) | 城镇居民基本医疗保险 | 145 | 1.000(0.859,1.000) |
| 农村 | 201 | 0.951(0.893,1.000) | 否 | 58 | 0.697(0.257,0.942) | 新型农村合作医疗保险 | 5 | 1.000(0.893,1.000) |
| 受教育程度 | 体检 | 门诊慢性病政策的了解程度 | ||||||
| 不识字 | 181 | 0.942(0.784,1.000) | 是 | 547 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) | 了解 | 242 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) |
| 高中及以下 | 369 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) | 否 | 16 | 0.259(0.062,0.937) | 一般 | 173 | 0.942(0.876,1.000) |
| 大专及以上 | 13 | 1.000(0.843,1.000) | 生活自理能力 | 不了解 | 148 | 0.942(0.783,1.000) | ||
| 家庭规模(人) | 正常 | 428 | 1.000(0.942,1.000) | 门诊慢性病政策的满意程度 | ||||
| 1 | 81 | 1.000(0.893,1.000) | 受损 | 135 | 0.734(0.481,0.893) | 满意 | 493 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) |
| 2 | 370 | 0.942(0.841,1.000) | 疾病数量(种) | 一般 | 44 | 0.895(0.735,1.000) | ||
| ≥3 | 112 | 0.942(0.827,1.000) | 1 | 25 | 1.000(0.876,1.000) | 不满意 | 26 | 0.883(0.742,0.963) |
| 贫困情况 | 2 | 74 | 0.942(0.868,1.000) | 定点医疗机构的满意程度 | ||||
| 是 | 35 | 0.893(0.734,1.000) | ≥3 | 464 | 0.942(0.852,1.000) | 满意 | 474 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) |
| 否 | 528 | 0.951(0.876,1.000) | 一般 | 56 | 0.942(0.783,1.000) | |||
| 不满意 | 33 | 0.824(0.592,1.000) | ||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 行动能力 | 自我照顾 | 日常活动 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 没有困难 | 有一点困难 | 中等困难 | 严重困难 | 无法进行/有非常严重的困难 | 没有困难 | 有一点困难 | 中等困难 | 严重困难 | 无法进行/有非常严重的困难 | 没有困难 | 有一点困难 | 中等困难 | 严重困难 | 无法进行/有非常严重的困难 | ||
| 显著增长组 | 452 | 377(83.41) | 62(13.72) | 13(2.88) | 0 | 0 | 423(93.58) | 29(6.42) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 415(91.81) | 34(7.52) | 3(0.66) | 0 | 0 |
| 适度下降组 | 81 | 24(29.63) | 21(25.93) | 30(37.04) | 5(6.17) | 1(1.23) | 49(60.49) | 21(25.93) | 8(9.88) | 2(2.47) | 1(1.23) | 40(49.38) | 27(33.33) | 11(13.58) | 2(2.47) | 1(1.23) |
| 显著衰减组 | 30 | 1(3.33) | 11(36.67) | 9(30.00) | 9(30.00) | 0 | 1(3.33) | 3(10.00) | 12(40.00) | 6(20.00) | 8(26.67) | 1(3.33) | 3(10.00) | 12(40.00) | 4(13.33) | 10(33.33) |
| 组别 | 疼痛/不适 | 焦虑/抑郁 | ||||||||||||||
| 没有困难 | 有一点困难 | 中等困难 | 严重困难 | 无法进行/有非常严重的困难 | 没有困难 | 有一点困难 | 中等困难 | 严重困难 | 无法进行/有非常严重的困难 | |||||||
| 显著增长组 | 292(64.60) | 140(30.97) | 19(4.20) | 1(0.22) | 0 | 371(82.08) | 76(16.81) | 5(1.11) | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| 适度下降组 | 15(18.52) | 39(48.15) | 23(28.40) | 4(4.94) | 0 | 43(53.09) | 33(40.74) | 3(3.70) | 2(2.47) | 0 | ||||||
| 显著衰减组 | 5(16.67) | 6(20.00) | 9(30.00) | 9(30.00) | 1(3.33) | 10(33.33) | 9(30.00) | 8(26.67) | 3(10.00) | 0 | ||||||
表2 不同异质化发展轨迹的中老年CMD患者HRQoL的分布情况[例(%)]
Table 2 Distribution of HRQoL among middle-aged and elderly patients with different heterogeneous development trajectories
| 组别 | 例数 | 行动能力 | 自我照顾 | 日常活动 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 没有困难 | 有一点困难 | 中等困难 | 严重困难 | 无法进行/有非常严重的困难 | 没有困难 | 有一点困难 | 中等困难 | 严重困难 | 无法进行/有非常严重的困难 | 没有困难 | 有一点困难 | 中等困难 | 严重困难 | 无法进行/有非常严重的困难 | ||
| 显著增长组 | 452 | 377(83.41) | 62(13.72) | 13(2.88) | 0 | 0 | 423(93.58) | 29(6.42) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 415(91.81) | 34(7.52) | 3(0.66) | 0 | 0 |
| 适度下降组 | 81 | 24(29.63) | 21(25.93) | 30(37.04) | 5(6.17) | 1(1.23) | 49(60.49) | 21(25.93) | 8(9.88) | 2(2.47) | 1(1.23) | 40(49.38) | 27(33.33) | 11(13.58) | 2(2.47) | 1(1.23) |
| 显著衰减组 | 30 | 1(3.33) | 11(36.67) | 9(30.00) | 9(30.00) | 0 | 1(3.33) | 3(10.00) | 12(40.00) | 6(20.00) | 8(26.67) | 1(3.33) | 3(10.00) | 12(40.00) | 4(13.33) | 10(33.33) |
| 组别 | 疼痛/不适 | 焦虑/抑郁 | ||||||||||||||
| 没有困难 | 有一点困难 | 中等困难 | 严重困难 | 无法进行/有非常严重的困难 | 没有困难 | 有一点困难 | 中等困难 | 严重困难 | 无法进行/有非常严重的困难 | |||||||
| 显著增长组 | 292(64.60) | 140(30.97) | 19(4.20) | 1(0.22) | 0 | 371(82.08) | 76(16.81) | 5(1.11) | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| 适度下降组 | 15(18.52) | 39(48.15) | 23(28.40) | 4(4.94) | 0 | 43(53.09) | 33(40.74) | 3(3.70) | 2(2.47) | 0 | ||||||
| 显著衰减组 | 5(16.67) | 6(20.00) | 9(30.00) | 9(30.00) | 1(3.33) | 10(33.33) | 9(30.00) | 8(26.67) | 3(10.00) | 0 | ||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别 | 年龄(岁) | 婚姻状况 | 民族 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 45~59 | 60~79 | ≥80 | 有配偶 | 无配偶 | 汉族 | 其他 | |||
| 显著增长组 | 452 | 169(37.39) | 283(62.61) | 14(3.10) | 305(67.48) | 133(29.42) | 336(74.34) | 116(25.66) | 446(98.67) | 6(1.33) | |
| 适度下降组 | 81 | 29(35.80) | 52(64.20) | 0 | 46(56.79) | 35(43.21) | 62(76.54) | 19(23.46) | 78(96.30) | 3(3.70) | |
| 显著衰减组 | 30 | 15(50.00) | 15(50.00) | 0 | 16(53.33) | 14(46.67) | 27(90.00) | 3(10.00) | 30(100.00) | 0 | |
| χ2值 | 2.068 | 10.106a | 3.787 | 2.472a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.356 | 0.029 | 0.149 | 0.199 | |||||||
| 组别 | 居住地 | 受教育程度 | 家庭规模(人) | 贫困情况 | |||||||
| 城市 | 城郊 | 农村 | 不识字 | 高中及以下 | 大专及以上 | 1 | 2 | ≥3 | 是 | 否 | |
| 显著增长组 | 204(45.13) | 81(17.92) | 167(36.95) | 141(31.19) | 299(66.15) | 12(2.66) | 70(15.49) | 301(66.59) | 81(17.92) | 25(5.53) | 427(94.47) |
| 适度下降组 | 42(51.85) | 12(14.81) | 27(33.33) | 27(33.33) | 53(65.43) | 1(1.23) | 11(13.58) | 50(61.73) | 20(24.69) | 7(8.64) | 74(91.36) |
| 显著衰减组 | 18(60.00) | 5(16.67) | 7(23.33) | 13(43.33) | 17(56.77) | 0 | 19(63.33) | 11(36.67) | 0 | 3(10.00) | 27(90.00) |
| χ2值 | 3.822 | 2.114a | 48.647 | 1.918 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.434 | 0.677 | <0.001 | 0.421 | |||||||
| 组别 | BMI | 社会支持 | 吸烟 | 饮酒 | |||||||
| 偏低 | 正常 | 超重或肥胖 | 低支持程度 | 中支持程度 | 高支持程度 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | ||
| 显著增长组 | 15(3.32) | 116(25.66) | 321(71.02) | 2(0.44) | 383(84.74) | 67(14.82) | 31(6.86) | 421(93.14) | 20(4.42) | 432(95.58) | |
| 适度下降组 | 2(2.47) | 29(35.80) | 50(61.73) | 2(2.47) | 75(92.59) | 4(4.94) | 4(4.94) | 77(95.96) | 3(3.70) | 78(96.30) | |
| 显著衰减组 | 2(6.67) | 7(23.33) | 21(70.00) | 0 | 29(96.67) | 1(3.33) | 2(6.67) | 28(93.33) | 0 | 30(100.00) | |
| χ2值 | 4.96a | 12.236a | 0.413 | 0.702a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.257 | 0.011 | 0.894 | 0.760 | |||||||
| 组别 | 体育锻炼 | 体检 | 生活自理能力 | 疾病数量(种) | 并发症 | ||||||
| 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 正常 | 受损 | 1 | 2 | ≥3 | 是 | 否 | |
| 显著增长组 | 428(94.69) | 24(5.31) | 446(98.67) | 6(1.33) | 392(86.73) | 60(13.27) | 22(4.87) | 60(13.27) | 370(81.86) | 235(51.99) | 217(48.01) |
| 适度下降组 | 66(81.48) | 15(18.52) | 78(96.30) | 3(3.70) | 36(44.44) | 45(55.66) | 2(2.47) | 12(14.81) | 67(82.72) | 55(67.90) | 26(32.10) |
| 显著衰减组 | 11(36.67) | 19(63.33) | 23(76.67) | 7(23.33) | 0 | 30(100.00) | 1(3.33) | 2(6.67) | 27(90.00) | 26(86.67) | 4(13.33) |
| χ2值 | 109.411 | 24.918a | 167.829 | 1.777a | 19.063 | ||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.767 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 组别 | 家庭患此病情况(人) | 健康状况变化 | 医保类型 | ||||||||
| 1 | 2 | ≥3 | 没变化 | 变好 | 变坏 | 不确定 | 公费医疗 | 城镇职工基本医疗保险 | 城镇居民基本医疗保险 | 新型农村合作医疗 | |
| 显著增长组 | 257(56.86) | 177(39.16) | 18(3.98) | 193(42.70) | 72(15.93) | 173(38.27) | 14(3.10) | 1(0.22) | 330(73.01) | 116(25.66) | 5(1.11) |
| 适度下降组 | 47(58.02) | 32(39.51) | 2(2.47) | 19(23.46) | 7(8.64) | 53(65.43) | 2(2.47) | 1(1.23) | 53(65.43) | 27(33.33) | 0 |
| 显著衰减组 | 14(46.67) | 12(40.00) | 4(13.33) | 6(20.00) | 1(3.33) | 23(76.67) | 0 | 0 | 28(93.33) | 2(6.67) | 0 |
| χ2值 | 5.629a | 32.49a | 12.399a | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.207 | <0.001 | 0.041 | ||||||||
| 组别 | 门诊慢性病政策的了解程度 | 门诊慢性病政策的满意程度 | 定点医疗机构的满意程度 | ||||||||
| 了解 | 一般 | 不了解 | 满意 | 一般 | 不满意 | 满意 | 一般 | 不满意 | |||
| 显著增长组 | 195(43.14) | 143(31.64) | 114(25.22) | 408(90.26) | 30(6.64) | 14(3.10) | 394(87.17) | 40(8.85) | 18(3.98) | ||
| 适度下降组 | 34(41.97) | 26(32.10) | 21(25.93) | 62(76.54) | 10(12.35) | 9(11.11) | 59(72.84) | 10(12.35) | 12(14.81) | ||
| 显著衰减组 | 13(43.33) | 4(13.33) | 13(43.33) | 23(76.67) | 4(13.33) | 3(10.00) | 21(70.00) | 6(20.00) | 3(10.00) | ||
| χ2值 | 6.663 | 16.824a | 19.128a | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.154 | 0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
表3 不同HRQoL异质化发展轨迹组调查资料比较[例(%)]
Table 3 Comparison of characteristics among heterogeneous development trajectories of HRQoL
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别 | 年龄(岁) | 婚姻状况 | 民族 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 45~59 | 60~79 | ≥80 | 有配偶 | 无配偶 | 汉族 | 其他 | |||
| 显著增长组 | 452 | 169(37.39) | 283(62.61) | 14(3.10) | 305(67.48) | 133(29.42) | 336(74.34) | 116(25.66) | 446(98.67) | 6(1.33) | |
| 适度下降组 | 81 | 29(35.80) | 52(64.20) | 0 | 46(56.79) | 35(43.21) | 62(76.54) | 19(23.46) | 78(96.30) | 3(3.70) | |
| 显著衰减组 | 30 | 15(50.00) | 15(50.00) | 0 | 16(53.33) | 14(46.67) | 27(90.00) | 3(10.00) | 30(100.00) | 0 | |
| χ2值 | 2.068 | 10.106a | 3.787 | 2.472a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.356 | 0.029 | 0.149 | 0.199 | |||||||
| 组别 | 居住地 | 受教育程度 | 家庭规模(人) | 贫困情况 | |||||||
| 城市 | 城郊 | 农村 | 不识字 | 高中及以下 | 大专及以上 | 1 | 2 | ≥3 | 是 | 否 | |
| 显著增长组 | 204(45.13) | 81(17.92) | 167(36.95) | 141(31.19) | 299(66.15) | 12(2.66) | 70(15.49) | 301(66.59) | 81(17.92) | 25(5.53) | 427(94.47) |
| 适度下降组 | 42(51.85) | 12(14.81) | 27(33.33) | 27(33.33) | 53(65.43) | 1(1.23) | 11(13.58) | 50(61.73) | 20(24.69) | 7(8.64) | 74(91.36) |
| 显著衰减组 | 18(60.00) | 5(16.67) | 7(23.33) | 13(43.33) | 17(56.77) | 0 | 19(63.33) | 11(36.67) | 0 | 3(10.00) | 27(90.00) |
| χ2值 | 3.822 | 2.114a | 48.647 | 1.918 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.434 | 0.677 | <0.001 | 0.421 | |||||||
| 组别 | BMI | 社会支持 | 吸烟 | 饮酒 | |||||||
| 偏低 | 正常 | 超重或肥胖 | 低支持程度 | 中支持程度 | 高支持程度 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | ||
| 显著增长组 | 15(3.32) | 116(25.66) | 321(71.02) | 2(0.44) | 383(84.74) | 67(14.82) | 31(6.86) | 421(93.14) | 20(4.42) | 432(95.58) | |
| 适度下降组 | 2(2.47) | 29(35.80) | 50(61.73) | 2(2.47) | 75(92.59) | 4(4.94) | 4(4.94) | 77(95.96) | 3(3.70) | 78(96.30) | |
| 显著衰减组 | 2(6.67) | 7(23.33) | 21(70.00) | 0 | 29(96.67) | 1(3.33) | 2(6.67) | 28(93.33) | 0 | 30(100.00) | |
| χ2值 | 4.96a | 12.236a | 0.413 | 0.702a | |||||||
| P值 | 0.257 | 0.011 | 0.894 | 0.760 | |||||||
| 组别 | 体育锻炼 | 体检 | 生活自理能力 | 疾病数量(种) | 并发症 | ||||||
| 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 正常 | 受损 | 1 | 2 | ≥3 | 是 | 否 | |
| 显著增长组 | 428(94.69) | 24(5.31) | 446(98.67) | 6(1.33) | 392(86.73) | 60(13.27) | 22(4.87) | 60(13.27) | 370(81.86) | 235(51.99) | 217(48.01) |
| 适度下降组 | 66(81.48) | 15(18.52) | 78(96.30) | 3(3.70) | 36(44.44) | 45(55.66) | 2(2.47) | 12(14.81) | 67(82.72) | 55(67.90) | 26(32.10) |
| 显著衰减组 | 11(36.67) | 19(63.33) | 23(76.67) | 7(23.33) | 0 | 30(100.00) | 1(3.33) | 2(6.67) | 27(90.00) | 26(86.67) | 4(13.33) |
| χ2值 | 109.411 | 24.918a | 167.829 | 1.777a | 19.063 | ||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.767 | <0.001 | ||||||
| 组别 | 家庭患此病情况(人) | 健康状况变化 | 医保类型 | ||||||||
| 1 | 2 | ≥3 | 没变化 | 变好 | 变坏 | 不确定 | 公费医疗 | 城镇职工基本医疗保险 | 城镇居民基本医疗保险 | 新型农村合作医疗 | |
| 显著增长组 | 257(56.86) | 177(39.16) | 18(3.98) | 193(42.70) | 72(15.93) | 173(38.27) | 14(3.10) | 1(0.22) | 330(73.01) | 116(25.66) | 5(1.11) |
| 适度下降组 | 47(58.02) | 32(39.51) | 2(2.47) | 19(23.46) | 7(8.64) | 53(65.43) | 2(2.47) | 1(1.23) | 53(65.43) | 27(33.33) | 0 |
| 显著衰减组 | 14(46.67) | 12(40.00) | 4(13.33) | 6(20.00) | 1(3.33) | 23(76.67) | 0 | 0 | 28(93.33) | 2(6.67) | 0 |
| χ2值 | 5.629a | 32.49a | 12.399a | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.207 | <0.001 | 0.041 | ||||||||
| 组别 | 门诊慢性病政策的了解程度 | 门诊慢性病政策的满意程度 | 定点医疗机构的满意程度 | ||||||||
| 了解 | 一般 | 不了解 | 满意 | 一般 | 不满意 | 满意 | 一般 | 不满意 | |||
| 显著增长组 | 195(43.14) | 143(31.64) | 114(25.22) | 408(90.26) | 30(6.64) | 14(3.10) | 394(87.17) | 40(8.85) | 18(3.98) | ||
| 适度下降组 | 34(41.97) | 26(32.10) | 21(25.93) | 62(76.54) | 10(12.35) | 9(11.11) | 59(72.84) | 10(12.35) | 12(14.81) | ||
| 显著衰减组 | 13(43.33) | 4(13.33) | 13(43.33) | 23(76.67) | 4(13.33) | 3(10.00) | 21(70.00) | 6(20.00) | 3(10.00) | ||
| χ2值 | 6.663 | 16.824a | 19.128a | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.154 | 0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| 类别 | 变量 | β | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 适度下降组 | 体育锻炼(以是为参照) | |||||
| 否 | 0.923 | 0.444 | 2.076 | 0.038 | 2.516(1.053~6.011) | |
| 生活自理能力(以正常为参照) | ||||||
| 受损 | 1.987 | 0.302 | 6.579 | <0.001 | 7.297(4.036~13.191) | |
| 健康状况变化(以没变化为参照) | ||||||
| 变好 | -0.035 | 0.518 | -0.068 | 0.946 | 0.965(0.350~2.665) | |
| 变坏 | 0.921 | 0.333 | 2.769 | 0.006 | 2.512(1.309~4.821) | |
| 不确定 | -0.041 | 0.914 | -0.044 | 0.965 | 0.960(0.160~5.764) | |
| 医保类型(以公费医疗为参照) | ||||||
| 城镇职工基本医疗保险 | -3.175 | 1.523 | -2.085 | 0.037 | 0.042(0.002~0.827) | |
| 城镇居民基本医疗保险 | -2.638 | 1.535 | -1.719 | 0.086 | 0.071(0.004~1.448) | |
| 新型农村合作医疗保险 | -19.123 | 5 725.303 | 0.003 | 0.997 | 4.95×10-9(0~—) | |
| 门诊慢性病政策的满意程度(以满意为参照) | ||||||
| 一般 | 0.832 | 0.510 | 1.630 | 0.103 | 2.298(0.845~6.250) | |
| 不满意 | 1.501 | 0.594 | 2.525 | 0.012 | 4.485(1.399~14.378) | |
| 显著衰减组 | 体育锻炼(以是为参照) | |||||
| 否 | 2.688 | 0.706 | 3.807 | <0.001 | 14.704(3.685~58.672) | |
| 门诊慢性病政策的满意程度(以满意为参照) | ||||||
| 一般 | 1.899 | 0.904 | 2.101 | 0.036 | 6.677(1.136~39.242) | |
| 不满意 | 1.843 | 1.206 | 1.529 | 0.126 | 6.318(0.595~67.135) | |
表4 中老年心血管代谢性疾病患者HRQoL异质化发展轨迹多元Logistic回归分析
Table 4 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of heterogeneous development trajectories of HRQoL in middle-aged and elderly patients with CMD
| 类别 | 变量 | β | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 适度下降组 | 体育锻炼(以是为参照) | |||||
| 否 | 0.923 | 0.444 | 2.076 | 0.038 | 2.516(1.053~6.011) | |
| 生活自理能力(以正常为参照) | ||||||
| 受损 | 1.987 | 0.302 | 6.579 | <0.001 | 7.297(4.036~13.191) | |
| 健康状况变化(以没变化为参照) | ||||||
| 变好 | -0.035 | 0.518 | -0.068 | 0.946 | 0.965(0.350~2.665) | |
| 变坏 | 0.921 | 0.333 | 2.769 | 0.006 | 2.512(1.309~4.821) | |
| 不确定 | -0.041 | 0.914 | -0.044 | 0.965 | 0.960(0.160~5.764) | |
| 医保类型(以公费医疗为参照) | ||||||
| 城镇职工基本医疗保险 | -3.175 | 1.523 | -2.085 | 0.037 | 0.042(0.002~0.827) | |
| 城镇居民基本医疗保险 | -2.638 | 1.535 | -1.719 | 0.086 | 0.071(0.004~1.448) | |
| 新型农村合作医疗保险 | -19.123 | 5 725.303 | 0.003 | 0.997 | 4.95×10-9(0~—) | |
| 门诊慢性病政策的满意程度(以满意为参照) | ||||||
| 一般 | 0.832 | 0.510 | 1.630 | 0.103 | 2.298(0.845~6.250) | |
| 不满意 | 1.501 | 0.594 | 2.525 | 0.012 | 4.485(1.399~14.378) | |
| 显著衰减组 | 体育锻炼(以是为参照) | |||||
| 否 | 2.688 | 0.706 | 3.807 | <0.001 | 14.704(3.685~58.672) | |
| 门诊慢性病政策的满意程度(以满意为参照) | ||||||
| 一般 | 1.899 | 0.904 | 2.101 | 0.036 | 6.677(1.136~39.242) | |
| 不满意 | 1.843 | 1.206 | 1.529 | 0.126 | 6.318(0.595~67.135) | |
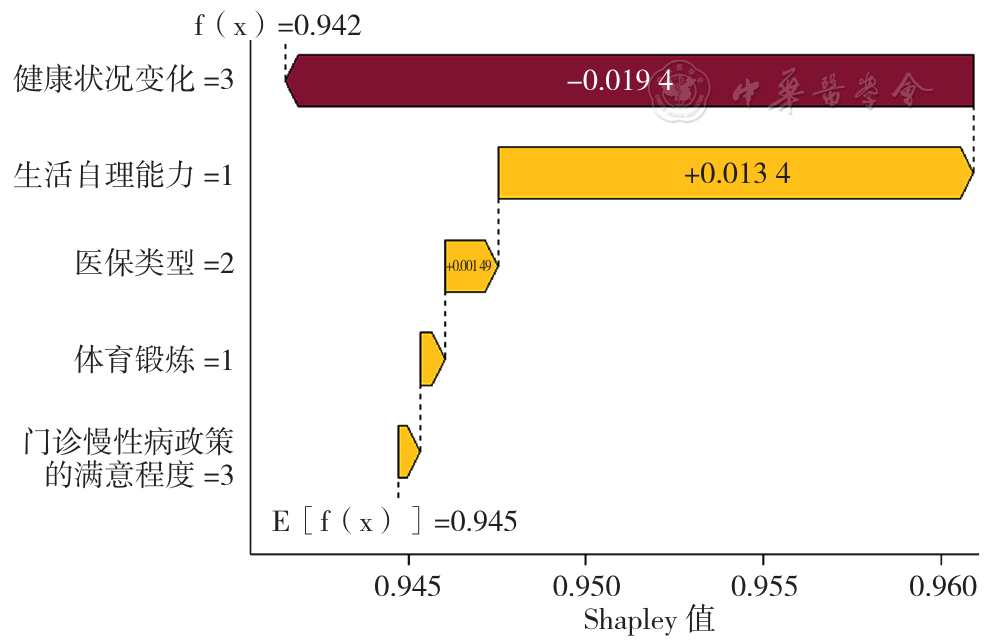
图2 显著增长组的影响因素Shapley值分解瀑布图
Figure 2 The waterfall chart visualizing the Shapley value decomposition of influencing factors in the significant growth group
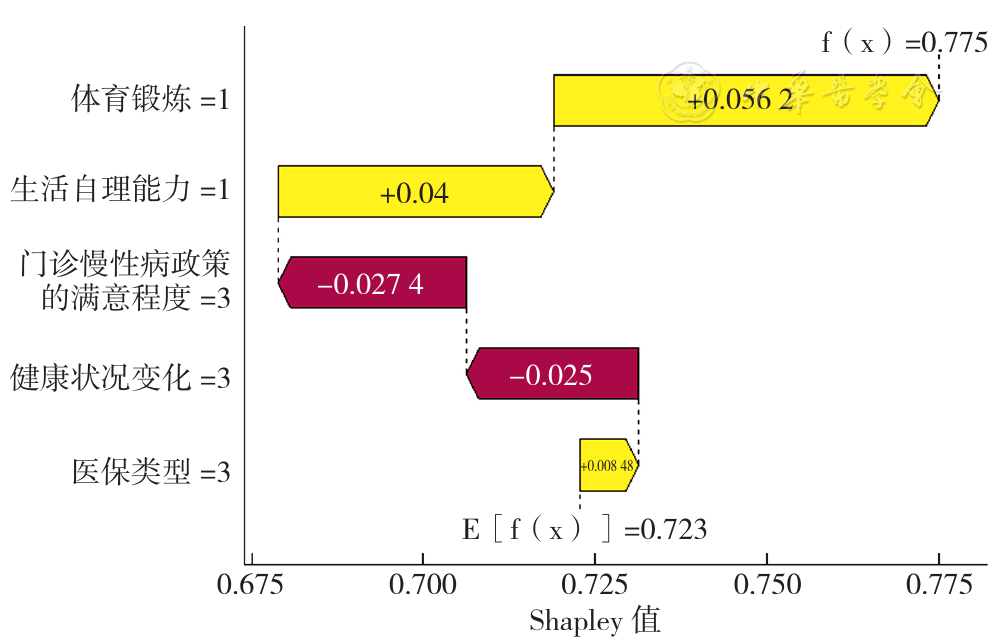
图3 适度下降组的影响因素Shapley值分解瀑布图
Figure 3 The waterfall chart visualizing the Shapley value decomposition of influencing factors in the moderate decline group
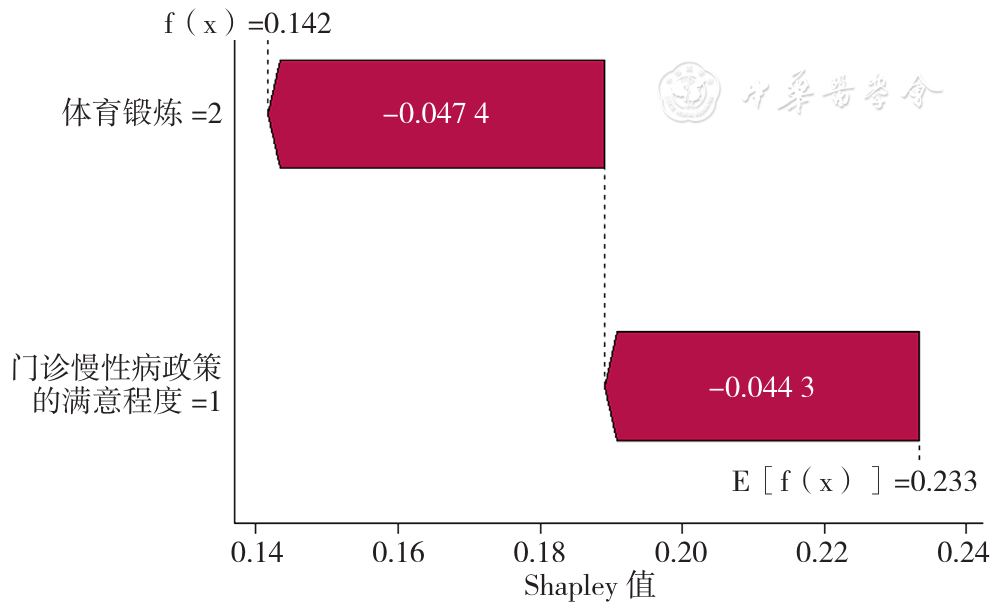
图4 显著衰减组的影响因素Shapley值分解瀑布图
Figure 4 The waterfall chart visualizing the Shapley value decomposition of influencing factors in the significant attenuation group
| [1] |
The World Health Organization quality of life assessment(WHOQOL):position paper from the World Health Organization[J]. Soc Sci Med,1995,41(10):1403-1409.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
施博文,熊巨洋. 慢性病共病对中国老年人健康相关生命质量的影响研究[J]. 人口与发展,2024,30(1):120-128.
|
| [6] |
新疆维吾尔自治区第七次全国人口普查公报(第三号)[EB/OL]. [2024-03-25].
|
| [7] |
旷南岳,李辉,林娟,等. 新疆生产建设兵团60 699例成年居民身体质量指数与高血压、糖尿病和血脂异常患病率的相关分析[J]. 安徽医药,2023,27(12):2425-2428. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6469.2023.12.020.
|
| [8] |
中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022概要[J]. 中国循环杂志,2023,38(6):583-612. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2023.06.001.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
GBD 2021 Diabetes Collaborators. Global,regional,and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021,with projections of prevalence to 2050:a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021[J]. Lancet,2023,402(10397):203-234.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
朱敬丽,刘梦莹,沈冲,等. 心脑血管疾病患者健康相关生命质量与卫生服务利用的关系分析[J]. 中国卫生经济,2023,42(2):62-68.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
刘新雨. 山东省农村老年高血压患者社会经济地位与生命质量的关系:社会资本的中介作用[D]. 济南:山东大学,2022.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
张新洲. 健康生态学视角下癌症患者生命质量及影响因素研究[D]. 合肥:安徽医科大学,2023.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
肖水源. 《社会支持评定量表》的理论基础与研究应用[J]. 临床精神医学杂志,1994,4(2):98-100.
|
| [22] |
秦廷廷,任德宇,孙晓杰,等. 基于EQ-5D-5L量表的住院肺癌患者健康相关生命质量及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国预防医学杂志,2022,23(12):904-908. DOI:10.16506/j.1009-6639.2022.12.004.
|
| [23] |
李培雯,贺嘉慧,马喜民,等. 基于EQ-5D-3L的宁夏回族自治区农村居民健康相关生命质量与卫生服务利用的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2023,26(19):2361-2368. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0770.
|
| [24] |
肖健,叶玲珑,方亚. 增长混合模型在健康轨迹研究中的应用进展[J]. 中国卫生统计,2020,37(4):637-640.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
万广华. 不平等的度量与分解[J]. 经济学(季刊),2009,9(1):347-368.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
杨帆,田利民,余静,等. 骨质疏松患者EQ-5D-5L量表健康相关影响因素分析[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(3):341-347.
|
| [29] |
王真,孙婧,张悠扬,等. 老年患者慢性病负担对焦虑和抑郁的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2020,23(23):2923-2926,2932. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.664.
|
| [30] | |
| [31] |
周玉兰. 哈密市老年人日常活动能力和健康期望寿命及其影响因素的研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2019.
|
| [1] | 张萍淑, 薛晶, 邢爱君, 王连辉, 马倩, 符永山, 元小冬. 急性后循环缺血性脑卒中患者睡眠状态变化与预后影响因素的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(05): 548-553. |
| [2] | 朱露, 艾军, 廖生武, 黄淑婷, 龚妮容, 孔耀中, 刘德慧, 窦献蕊, 张广清. 预后营养指数对腹膜透析患者心血管疾病死亡的影响:一项多中心回顾性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(05): 568-574. |
| [3] | 张家鸣, 王欣宇, 王道荣, 孙晓芳. 17~45岁肥胖门诊患者的6分钟步行试验距离参考方程研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(03): 330-334. |
| [4] | 高焱, 杨淑显, 范雷, 常亮, 高莉, 张寒雪, 李卉, 康锴. 老年人群骨关节疾病流行特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(03): 280-284. |
| [5] | 齐鸣瑞, 王文娟, 田利民. 中国西北地区老年高血压人群的健康相关生命质量研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 199-207. |
| [6] | 卢静, 孙国珍, 王洁, 高敏, 于甜栖, 孙姝怡, 王琴, 温高芹. 慢性心力衰竭患者社会衰弱现状及其影响因素可解释性分析研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 220-227. |
| [7] | 刘庆平, 柯居中, 宋家慧, 高娇娇, 李智韬, 王小楠, 邱桦, 周弋, 阮晓楠, 吴抗. 糖尿病发病时间趋势及其与中国内脏脂肪指数的关系:一项前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 183-192. |
| [8] | 舒婷, 兰志鹏, 巫霞, 罗映娟, 杨柳. 宫颈癌筛查妇女高危型人乳头瘤病毒感染现状及影响因素研究:基于成都市45万人群[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 213-219. |
| [9] | 安然, 唐昕, 齐士格, 王志会, 崔露, 张晗, 郭浩岩. 社区老年人照护需求现状及影响因素研究:基于三省的基线调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(01): 59-64. |
| [10] | 贾佳, 刘嘉慧, 季文君, 郑博, 王新刚, 范芳芳, 李寅, 张龙, 张岩. 急性心肌梗死患者血浆前蛋白转化酶枯草溶菌素9水平的影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(36): 4568-4574. |
| [11] | 高澜, 张祥凝, 谢昊泰, 范芳芳, 贾佳, 李建平, 马为, 张岩. 社区人群心内膜下心肌活力率的影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(36): 4554-4560. |
| [12] | 柴梅梅, 包信娟, 曾梅, 李芙兰, 汉瑞娟. 肺癌术后患者持续性咳嗽发生率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(34): 4350-4352. |
| [13] | 张亚琳, 刘力滴, 陈正勇, 刘长明, 杨梓钰, 曹毅, 廖晓阳. 医联体背景下基层医疗卫生机构服务能力及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(34): 4302-4307. |
| [14] | 施译楠, 周驰. 不同年龄段就诊居民社区卫生服务的反应性评价现状与影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(31): 3877-3883. |
| [15] | 郑传雷, 丁睿聪, 王琪, 郭逸星, 李剑, 黄争春, 董明华, 罗晓婷, 吴清锋. ≥35岁居民膳食模式与血脂异常相关性研究:基于赣南慢病队列调查数据[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(30): 3739-3745. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





