

Chinese General Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (34): 4371-4377.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0220
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2025-04-15
Revised:2025-08-21
Published:2025-12-05
Online:2025-10-21
Contact:
GAO Yi
通讯作者:
高怡
作者简介:作者贡献:
姚世华、谢燕清、黄锐波、郑劲平、高怡负责提出研究思路,设计研究方案,包括观察指标制定、纳入及排除标准制定以及试验分组方法;姚世华负责与受试者沟通、知情同意书签署,负责论文起草;吴仲平、陈树冰、谢燕清、沈北兰、钟丽萍、安嘉颖、王旭东、刘文婷、虞欣欣负责研究过程的实施,包括肺弥散功能测试、纳入对象的筛选;姚世华、黄锐波负责数据收集、采集、清洗;姚世华、符土平负责数据统计学分析;姚世华、郑劲平、高怡负责最终版本修订,对论文负责。
基金资助:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0220
| 观察指标 | 间质肺病(n=67) | 慢阻肺病(n=66) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验组 | 对照组 | 差值绝对值 | 实验组 | 对照组 | 差值绝对值 | |
| DLCO(mmol·min-1·kPa-1) | 4.97±1.53 | 4.92±1.50 | 0.05 | 5.39±2.07 | 5.25±1.96 | 0.14 |
| VA(L) | 3.62±0.93 | 3.89±0.90 | 0.26 | 4.49±1.13 | 4.89±1.21 | 0.40 |
| DLCO/VA(mmol·min-1·kPa-1·L-1) | 1.39±0.34 | 1.28±0.31 | 0.12 | 1.21±0.14 | 1.08±0.34 | 0.13 |
| IVC(L) | 2.62±0.72 | 2.51±0.70 | 0.11 | 2.70±0.90 | 2.61±0.82 | 0.09 |
| FVC(L) | 2.67±0.71 | 2.66±0.70 | 0.01 | 2.81±0.92 | 2.82±0.88 | 0.01 |
| FEV1(L) | 2.23±0.57 | 2.18±0.55 | 0.05 | 1.47±0.81 | 1.41±0.76 | 0.06 |
Table 1 Distribution of diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide and spirometry in the experimental group and control group among interstitial lung disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease groups
| 观察指标 | 间质肺病(n=67) | 慢阻肺病(n=66) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验组 | 对照组 | 差值绝对值 | 实验组 | 对照组 | 差值绝对值 | |
| DLCO(mmol·min-1·kPa-1) | 4.97±1.53 | 4.92±1.50 | 0.05 | 5.39±2.07 | 5.25±1.96 | 0.14 |
| VA(L) | 3.62±0.93 | 3.89±0.90 | 0.26 | 4.49±1.13 | 4.89±1.21 | 0.40 |
| DLCO/VA(mmol·min-1·kPa-1·L-1) | 1.39±0.34 | 1.28±0.31 | 0.12 | 1.21±0.14 | 1.08±0.34 | 0.13 |
| IVC(L) | 2.62±0.72 | 2.51±0.70 | 0.11 | 2.70±0.90 | 2.61±0.82 | 0.09 |
| FVC(L) | 2.67±0.71 | 2.66±0.70 | 0.01 | 2.81±0.92 | 2.82±0.88 | 0.01 |
| FEV1(L) | 2.23±0.57 | 2.18±0.55 | 0.05 | 1.47±0.81 | 1.41±0.76 | 0.06 |
| 观察指标 | ICC | 95%CI | 一致性 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLCO | 0.981 6 | 0.970 7~0.988 6 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| VA | 0.944 9 | 0208 7~0.985 5 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| DLCO/VA | 0.916 8 | 0.109 9~0.977 7 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| IVC | 0.969 8 | 0.867 9~0.988 1 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| FVC | 0.984 4 | 0.974 8~0.990 4 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| FEV1 | 0.982 4 | 0.963 5~0.990 5 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
Table 2 Numerical ICC analysis of test index parameters in the experimental group and the control group with interstitial lung disease
| 观察指标 | ICC | 95%CI | 一致性 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLCO | 0.981 6 | 0.970 7~0.988 6 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| VA | 0.944 9 | 0208 7~0.985 5 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| DLCO/VA | 0.916 8 | 0.109 9~0.977 7 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| IVC | 0.969 8 | 0.867 9~0.988 1 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| FVC | 0.984 4 | 0.974 8~0.990 4 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| FEV1 | 0.982 4 | 0.963 5~0.990 5 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| 观察指标 | ICC | 95%CI | 一致性 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLCO | 0.990 7 | 0.976 1~0.995 5 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| VA | 0.917 9 | 0.089 9~0.978 4 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| DLCO/VA | 0.920 9 | 0.083 1~0.979 5 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| IVC | 0.960 2 | 0.926 1~0.977 4 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| FVC | 0.979 8 | 0.967 3~0.987 6 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| FEV1 | 0.989 7 | 0.967 1~0.995 5 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
Table 3 Numerical ICC analysis of test index parameters in experimental group and control group of COPD group
| 观察指标 | ICC | 95%CI | 一致性 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLCO | 0.990 7 | 0.976 1~0.995 5 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| VA | 0.917 9 | 0.089 9~0.978 4 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| DLCO/VA | 0.920 9 | 0.083 1~0.979 5 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| IVC | 0.960 2 | 0.926 1~0.977 4 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| FVC | 0.979 8 | 0.967 3~0.987 6 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
| FEV1 | 0.989 7 | 0.967 1~0.995 5 | 一致性较高 | <0.001 |
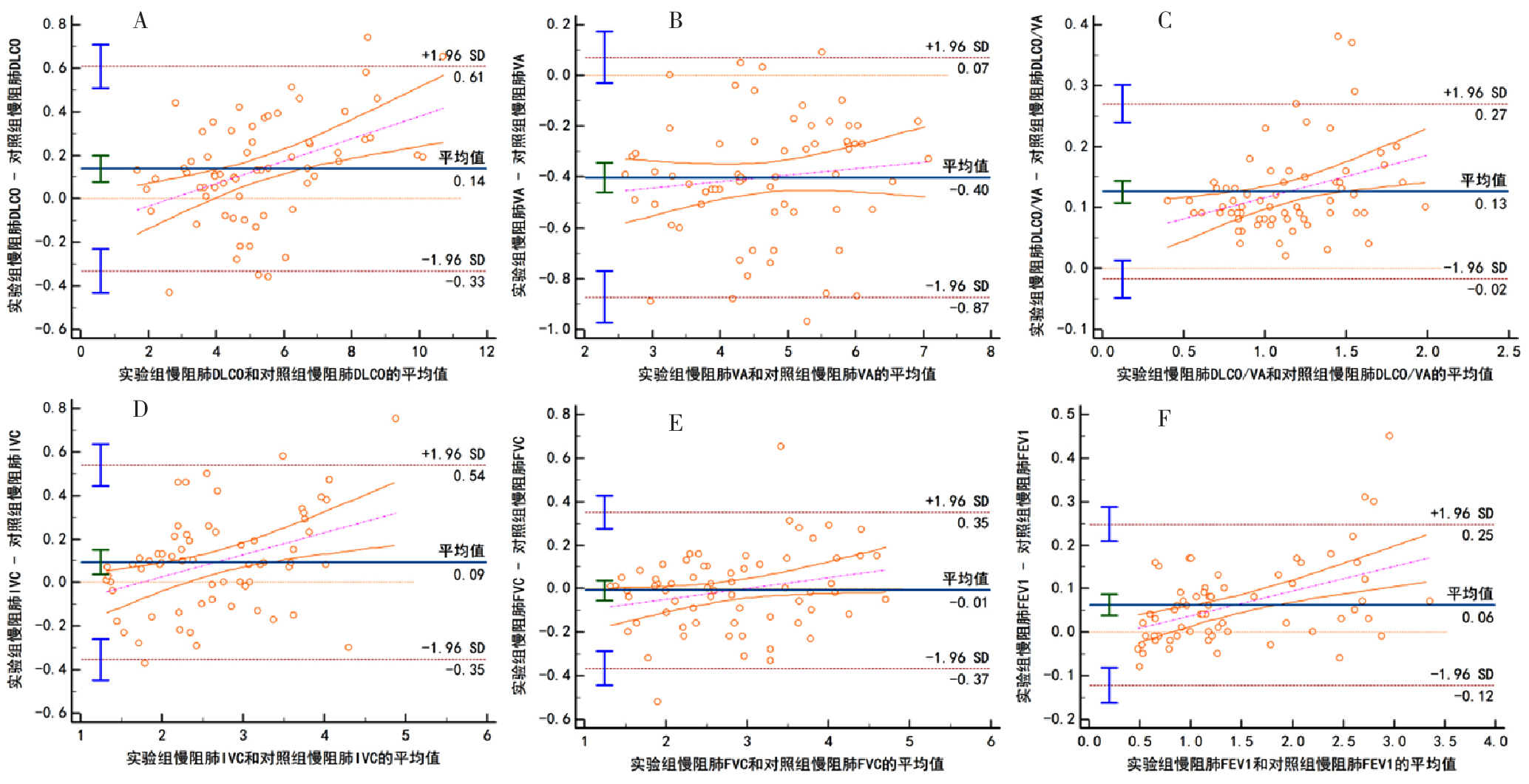
Figure 3 Bland-Altman scatter plots of each analysis index between the experimental group and the control group in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
| DLCO%pred分级 | 间质肺病组 | 慢阻肺病组 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验组(n=67) | 对照组(n=67) | 实验组(n=66) | 对照组(n=66) | |
| 正常 | 12(17.9) | 13(19.4) | 16(24.2) | 15(22.7) |
| 轻度 | 23(34.3) | 22(32.8) | 22(33.3) | 24(36.4) |
| 中度 | 24(35.8) | 24(35.8) | 22(33.3) | 20(30.3) |
| 重度 | 8(11.9) | 8(11.9) | 6(9.1) | 77(10.6) |
Table 4 The degree of pulmonary dispersion dysfunction in the experimental group and the control group of interstitial lung disease and COPD lung disease
| DLCO%pred分级 | 间质肺病组 | 慢阻肺病组 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验组(n=67) | 对照组(n=67) | 实验组(n=66) | 对照组(n=66) | |
| 正常 | 12(17.9) | 13(19.4) | 16(24.2) | 15(22.7) |
| 轻度 | 23(34.3) | 22(32.8) | 22(33.3) | 24(36.4) |
| 中度 | 24(35.8) | 24(35.8) | 22(33.3) | 20(30.3) |
| 重度 | 8(11.9) | 8(11.9) | 6(9.1) | 77(10.6) |
| 组别 | ICC | 95%CI | P值 | 一致性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 间质肺病组 | 0.939 7 | 0.903 9~0.962 5 | <0.001 | 一致性较高 |
| 慢阻肺病组 | 0.975 0 | 0.953 9~0.985 8 | <0.001 | 一致性较高 |
Table 5 ICC analysis of the degree of pulmonary dispersion dysfunction in interstitial lung and COPD lung disease groups
| 组别 | ICC | 95%CI | P值 | 一致性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 间质肺病组 | 0.939 7 | 0.903 9~0.962 5 | <0.001 | 一致性较高 |
| 慢阻肺病组 | 0.975 0 | 0.953 9~0.985 8 | <0.001 | 一致性较高 |
| 组别 | 加权kappa | 95%CI | P值 | 一致性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 间质肺病组 | 0.896 86 | 0.823 6~0.970 1 | <0.001 | 一致性极好 |
| 慢阻肺病组 | 0.837 15 | 0.746 4~0.927 9 | <0.001 | 一致性极好 |
Table 6 Analysis results of Cohen's weighted kappa consistency strength test on the severity of dispersion dysfunction in interstitial lung and COPD groups
| 组别 | 加权kappa | 95%CI | P值 | 一致性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 间质肺病组 | 0.896 86 | 0.823 6~0.970 1 | <0.001 | 一致性极好 |
| 慢阻肺病组 | 0.837 15 | 0.746 4~0.927 9 | <0.001 | 一致性极好 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
钟丽萍,吴仲平,黄锐波,等. 国产新型压差式肺量计优呼吸PF680的测量值评价[J]. 中国全科医学,2021,24(29):3664-3670.
|
| [10] |
方伟,陈焱焱,王远,等. 肺弥散功能检测系统设计与验证[J]. 中国医疗器械杂志,2022,46(4):408-412.
|
| [11] |
汤宁,成其新,温宇标,等. 大型肺功能系统通气模块与弥散模块的关键技术[J]. 中国医学装备,2020,17(8):202-205.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
王柳盛,李惠萍. 中国大陆间质性肺疾病流行病学资料及研究进展[J].中华内科杂志,2014,53(8):652-654.
|
| [15] |
廖清,陶玉坚. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病流行病学及危险因素研究现状[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2018,12(8):468-471.
|
| [16] |
中华医学会呼吸病学分会肺功能专业组.肺功能检查指南——肺弥散功能检查[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志,2015,38(3):164-169. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2015.03.003.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
孙广浩,刘薇,邵润霞. 现症吸烟者肺弥散功能变化对慢性阻塞性肺疾病发病风险的影响[J]. 临床研究,2022,30(6):46-48.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
2024 GOLD Report - Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease - GOLD[EB/OL]. [2024-03-17].
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
郭娥. 我国肺功能应用现状调查[D]. 广州:广州医科大学,2014.
|
| [1] | WU Zhongping, HUANG Ruibo, LIN Kuiqing, YU Xinxin, ZHONG Liping, CHEN Shubing, ZHENG Jinping, GAO Yi. Application of a Standard Diffusion Simulator in Quality Evaluation of DLCO Instruments [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(35): 4494-4500. |
| [2] | TAN Huihui, MAO Wei, YANG Zihan. Research Progress of Annexin A1 in Respiratory Diseases [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(13): 1668-1673. |
| [3] | YANG Jianuo, WANG Guanli, YANG Jiafu, HE Jiahao, CHEN Shumin, SHEN Yi, LI Juan, REN Ni, LIU Chunli, DENG Fangge. New Progress in the Application of Infrared Thermal Imaging in Pulmonary Diseases [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(08): 1012-1016. |
| [4] | ZHANG Dongying, YE Peitao, LI Qiasheng, JIAN Wenhua, LIANG Zhenyu, ZHENG Jinping. Study of Techniques and Methods for Building a Database of Lung Auscultation Sounds [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(36): 4598-4608. |
| [5] | LI Chunyang, WANG Jiajia, WEI Mengyu, LI Jiansheng. Research Status of Patient-reported Outcome Measurements for Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(31): 3896-3904. |
| [6] | YANG Can, LI Ning, LI Xuefei, ZHAO Li, XU Hao, SHI Qi, WANG Yongjun, LIANG Qianqian. Efficacy of Zang Bi Formula in Treating Arthritis and Its Pulmonary Complications in Rheumatoid Arthritis Interstitial Lung Disease Mice [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(24): 3015-3022. |
| [7] | YUAN Quan, LU Haiying, WANG Yi, LIU Yunxiao, YU Jiaqin, TIAN Fengzhao, LI Yao. Telemedicine Management in Stabilized Respiratory Rehabilitation of Elderly Patients with Moderate-to-severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: a Randomized Controlled Trial [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(06): 711-716. |
| [8] | LIANG Xuan, NA Feiyang, QIN Mengyao, YANG Hui, GUO Li, GUO Qi, REN Lei, CHEN De, LIU Donghai, ZHANG Rongfang. Clinical Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Bronchial Asthma Combined with Obstructive Sleep Apnea-hypopnea Syndrome in Children [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(33): 4225-4230. |
| [9] | WEI Mengyu, WANG Jiajia, ZHANG Yingying, LI Chunyang, LI Jiansheng. Research Status of Patient-reported Outcome Assessment Tools for Obstructive Sleep Apnea [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(30): 3725-3733. |
| [10] | FENG Jia, WANG Jie, YU Dan, LIU Yongheng, ZHAO Weidong, TIAN Hongyuan. Analysis of Research Hotspots of Multiple Chronic Conditions in the Elderly in 2010-2021 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(21): 2574-2580. |
| [11] | LI Jingbo, PANG Gaofeng, REN Yanling, SHA Xixue, NI Huiping. Executive Function of GO/NOGO Paradigm Experiment in Children with Bronchial Asthma and Its Relationship with Pulmonary Function [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(20): 2503-2507. |
| [12] | HU Yiqing, FANG Jiwei, LIU Huanbing. Attaching Importance to the Application of Lung Function Examination Technology in Grassroots Medical and Health Institutions——Expert Answers to Key Questions [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(05): 532-540. |
| [13] | HUANG Tao, LUO Na, LUO Song, XU Qin. Clinical Application of a Novel Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation Face Mask with Two Channels and Constant Leakage for Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Carbon Dioxide Retention [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(03): 343-347. |
| [14] | XU Lili, HONG Yunzhe, LI Zhihui, YU Ningxia, DI Jiaqi, YANG Shuguang, LIN Qingqing, YU Xueqing. Prognostic Biomarkers in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: a Recent Review [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(03): 372-379. |
| [15] | WANG Jun, ZHANG Dong, FENG Zhenzhen, ZHANG Shujuan, ZHAO Guixiang, ZHANG Hailong, LI Jiansheng. Literature-based Research on Common Syndromes of Cough Variant Asthma [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(03): 321-328. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||