

Chinese General Practice ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (33): 4125-4131.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0071
Special Issue: 老年人群健康最新文章合辑; 老年问题最新文章合辑
• Original Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-02-23
Revised:2024-07-11
Published:2024-11-20
Online:2024-08-08
Contact:
CHEN Qiuyu, ZHANG Yue
通讯作者:
陈秋雨, 张越
作者简介:作者贡献:
贾高鹏提出主要研究目标,负责研究的构思与设计,研究的实施,撰写论文;曲泽、李桂梅、赵子豪、闫爽、陈秋雨进行数据的收集与整理,统计学处理,图、表的绘制与展示;皇甫卫忠、张越负责文章的质量控制与审查,对文章整体负责,监督管理。
基金资助:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0071
| 项目 | 药物涂层球囊 | 药物洗脱支架 | 生物可吸收支架 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | 紫杉醇药物涂层球囊 | 唑他莫司药物洗脱支架/依维莫司药物洗脱支架 | 生物可吸收冠状动脉 雷帕霉素洗脱支架 |
| 承载物 | 无聚合物球囊 | 钴合金/铂铬合金 | 聚左旋乳酸 |
| 药物 | 紫杉醇 | 唑他莫司/依维莫司 | 西罗莫司 |
| 传输基质 | 碘普罗胺 | BioLink/聚甲基丙烯酸正丁酯 | 聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物 |
| 药物释放 | 瞬时释放 | 缓慢释放 | 缓慢释放 |
| 药物分布 | 均匀 | 不均匀 | 不均匀 |
Table 1 Research equipment information
| 项目 | 药物涂层球囊 | 药物洗脱支架 | 生物可吸收支架 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | 紫杉醇药物涂层球囊 | 唑他莫司药物洗脱支架/依维莫司药物洗脱支架 | 生物可吸收冠状动脉 雷帕霉素洗脱支架 |
| 承载物 | 无聚合物球囊 | 钴合金/铂铬合金 | 聚左旋乳酸 |
| 药物 | 紫杉醇 | 唑他莫司/依维莫司 | 西罗莫司 |
| 传输基质 | 碘普罗胺 | BioLink/聚甲基丙烯酸正丁酯 | 聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物 |
| 药物释放 | 瞬时释放 | 缓慢释放 | 缓慢释放 |
| 药物分布 | 均匀 | 不均匀 | 不均匀 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄[M(P25,P75),岁] | 性别(男/女) | 吸烟[例(%)] | 糖尿病[例(%)] | 高血压[例(%)] | 介入治疗史[例(%)] | 心肌梗死病史[例(%)] | TC(mmol/L) | TG(mmol/L) | LDL-C(mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCB组 | 30 | 71.5(65.5,75.5) | 20/10 | 14(46.7) | 15(50.0) | 23(76.7) | 8(26.7) | 5(16.7) | 4.32±0.65 | 1.50±0.20 | 2.24±0.48 |
| DES组 | 64 | 69.0(64.0,74.5) | 41/23 | 29(45.3) | 31(48.4) | 48(75.0) | 16(25.0) | 7(10.9) | 4.18±0.80 | 1.55±0.25 | 2.30±0.42 |
| BVS组 | 34 | 71.0(64.8,75.0) | 21/13 | 16(47.1) | 16(47.1) | 26(76.5) | 9(26.5) | 4(11.8) | 4.28±0.70 | 1.50±0.23 | 2.41±0.49 |
| 检验统计量值 | 3.449a | 0.166 | 8.817 | 0.055 | 0.043 | 0.041 | 0.636 | 0.436b | 0.871b | 1.129b | |
| P值 | 0.178 | 0.920 | 0.066 | 0.973 | 0.979 | 0.980 | 0.728 | 0.647 | 0.421 | 0.327 | |
| 组别 | 肌酐[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 糖化血红蛋白(%) | LVEF(%) | 氯吡格雷[例(%)] | 冠状动脉病变情况[例(%)] | 靶血管病变部位[例(%)] | 靶病变长度(mm) | ||||
| 单支 | 双支 | 三支 | LAD | LCX | RCA | ||||||
| DCB组 | 75.50(84.25,67.75) | 6.05±0.57 | 59.00±6.24 | 24(80.0) | 4(13.3) | 5(16.7) | 21(70.0) | 19(63.3) | 37(26.7) | 18(10.0) | 16.24±1.43 |
| DES组 | 74.50(66.25,87.00) | 6.18±0.68 | 59.28±5.46 | 53(82.8) | 16(25.0) | 15(23.4) | 33(51.6) | 8(57.8) | 17(26.6) | 10(15.6) | 16.47±1.22 |
| BVS组 | 80.50(65.75,88.25) | 6.18±0.75 | 59.03±4.86 | 27(79.4) | 7(20.6) | 9(26.5) | 18(52.9) | 3(52.9) | 10(29.4) | 6(17.6) | 16.14±1.32 |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.553a | 0.471b | 0.038b | 0.209 | 3.359 | 0.331 | 0.849 | ||||
| P值 | 0.758 | 0.625 | 0.963 | 0.901 | 0.500 | 0.847 | 0.430 | ||||
Table 2 The comparison outcomes of the baseline data of patients in the DCB group,the DES group and the BVS group
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄[M(P25,P75),岁] | 性别(男/女) | 吸烟[例(%)] | 糖尿病[例(%)] | 高血压[例(%)] | 介入治疗史[例(%)] | 心肌梗死病史[例(%)] | TC(mmol/L) | TG(mmol/L) | LDL-C(mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCB组 | 30 | 71.5(65.5,75.5) | 20/10 | 14(46.7) | 15(50.0) | 23(76.7) | 8(26.7) | 5(16.7) | 4.32±0.65 | 1.50±0.20 | 2.24±0.48 |
| DES组 | 64 | 69.0(64.0,74.5) | 41/23 | 29(45.3) | 31(48.4) | 48(75.0) | 16(25.0) | 7(10.9) | 4.18±0.80 | 1.55±0.25 | 2.30±0.42 |
| BVS组 | 34 | 71.0(64.8,75.0) | 21/13 | 16(47.1) | 16(47.1) | 26(76.5) | 9(26.5) | 4(11.8) | 4.28±0.70 | 1.50±0.23 | 2.41±0.49 |
| 检验统计量值 | 3.449a | 0.166 | 8.817 | 0.055 | 0.043 | 0.041 | 0.636 | 0.436b | 0.871b | 1.129b | |
| P值 | 0.178 | 0.920 | 0.066 | 0.973 | 0.979 | 0.980 | 0.728 | 0.647 | 0.421 | 0.327 | |
| 组别 | 肌酐[M(P25,P75),μmol/L] | 糖化血红蛋白(%) | LVEF(%) | 氯吡格雷[例(%)] | 冠状动脉病变情况[例(%)] | 靶血管病变部位[例(%)] | 靶病变长度(mm) | ||||
| 单支 | 双支 | 三支 | LAD | LCX | RCA | ||||||
| DCB组 | 75.50(84.25,67.75) | 6.05±0.57 | 59.00±6.24 | 24(80.0) | 4(13.3) | 5(16.7) | 21(70.0) | 19(63.3) | 37(26.7) | 18(10.0) | 16.24±1.43 |
| DES组 | 74.50(66.25,87.00) | 6.18±0.68 | 59.28±5.46 | 53(82.8) | 16(25.0) | 15(23.4) | 33(51.6) | 8(57.8) | 17(26.6) | 10(15.6) | 16.47±1.22 |
| BVS组 | 80.50(65.75,88.25) | 6.18±0.75 | 59.03±4.86 | 27(79.4) | 7(20.6) | 9(26.5) | 18(52.9) | 3(52.9) | 10(29.4) | 6(17.6) | 16.14±1.32 |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.553a | 0.471b | 0.038b | 0.209 | 3.359 | 0.331 | 0.849 | ||||
| P值 | 0.758 | 0.625 | 0.963 | 0.901 | 0.500 | 0.847 | 0.430 | ||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 术前 | 术后即刻 | 术后1年 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RVD(mm) | MLD(mm) | DS(%) | MLD(mm) | RDS[M(P25,P75),%] | AG(mm) | MLD(mm) | RDS(%) | LLL(mm) | ||
| DCB组 | 30 | 3.36±0.17 | 0.60±0.13 | 81.82±3.77 | 3.06±0.11 | 9.80(6.40,13.52) | 2.42±0.21 | 2.83±0.06 | 17.31±3.89 | 0.24±0.14 |
| DES组 | 64 | 3.36±0.18 | 0.59±0.10 | 82.75±3.32 | 3.13±0.11 | 5.45(1.72,9.00) | 2.57±0.17 | 2.88±0.08 | 13.76±4.98b | 0.26±0.12 |
| BVS组 | 34 | 3.40±0.17 | 0.57±0.10 | 82.44±3.02 | 3.18±0.14bc | 3.10(1.24,11.17)bc | 2.61±0.17bc | 2.88±0.09 | 14.75±4.98 | 0.31±0.14 |
| F(H)值 | 0.441 | 0.623 | 0.774 | 8.809 | 16.018a | 9.618 | 2.791 | 4.250 | 1.794 | |
| P值 | 0.664 | 0.538 | 0.464 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.066 | 0.017 | 0.172 | |
Table 3 The comparison results of coronary angiography among the DCB group,the DES group and the BVS group
| 组别 | 例数 | 术前 | 术后即刻 | 术后1年 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RVD(mm) | MLD(mm) | DS(%) | MLD(mm) | RDS[M(P25,P75),%] | AG(mm) | MLD(mm) | RDS(%) | LLL(mm) | ||
| DCB组 | 30 | 3.36±0.17 | 0.60±0.13 | 81.82±3.77 | 3.06±0.11 | 9.80(6.40,13.52) | 2.42±0.21 | 2.83±0.06 | 17.31±3.89 | 0.24±0.14 |
| DES组 | 64 | 3.36±0.18 | 0.59±0.10 | 82.75±3.32 | 3.13±0.11 | 5.45(1.72,9.00) | 2.57±0.17 | 2.88±0.08 | 13.76±4.98b | 0.26±0.12 |
| BVS组 | 34 | 3.40±0.17 | 0.57±0.10 | 82.44±3.02 | 3.18±0.14bc | 3.10(1.24,11.17)bc | 2.61±0.17bc | 2.88±0.09 | 14.75±4.98 | 0.31±0.14 |
| F(H)值 | 0.441 | 0.623 | 0.774 | 8.809 | 16.018a | 9.618 | 2.791 | 4.250 | 1.794 | |
| P值 | 0.664 | 0.538 | 0.464 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.066 | 0.017 | 0.172 | |
| 组别 | 例数 | MACE事件总数 | 复发性心绞痛 | 靶病变血运重建 | 出血事件 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCB组 | 30 | 7(23.3) | 6(20.0) | 1(3.3) | 0 |
| DES组 | 64 | 18(26.6) | 14(21.9) | 1(1.6) | 3(4.7) |
| BVS组 | 34 | 13(38.2) | 9(26.5) | 1(2.9) | 3(8.8) |
| χ2值 | 1.845 | 0.425 | 0.953 | 2.466 | |
| P值 | 0.397 | 0.808 | 0.799 | 0.249 |
Table 4 Comparison of the incidence of MACEs between the hospital and 6 months
| 组别 | 例数 | MACE事件总数 | 复发性心绞痛 | 靶病变血运重建 | 出血事件 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCB组 | 30 | 7(23.3) | 6(20.0) | 1(3.3) | 0 |
| DES组 | 64 | 18(26.6) | 14(21.9) | 1(1.6) | 3(4.7) |
| BVS组 | 34 | 13(38.2) | 9(26.5) | 1(2.9) | 3(8.8) |
| χ2值 | 1.845 | 0.425 | 0.953 | 2.466 | |
| P值 | 0.397 | 0.808 | 0.799 | 0.249 |
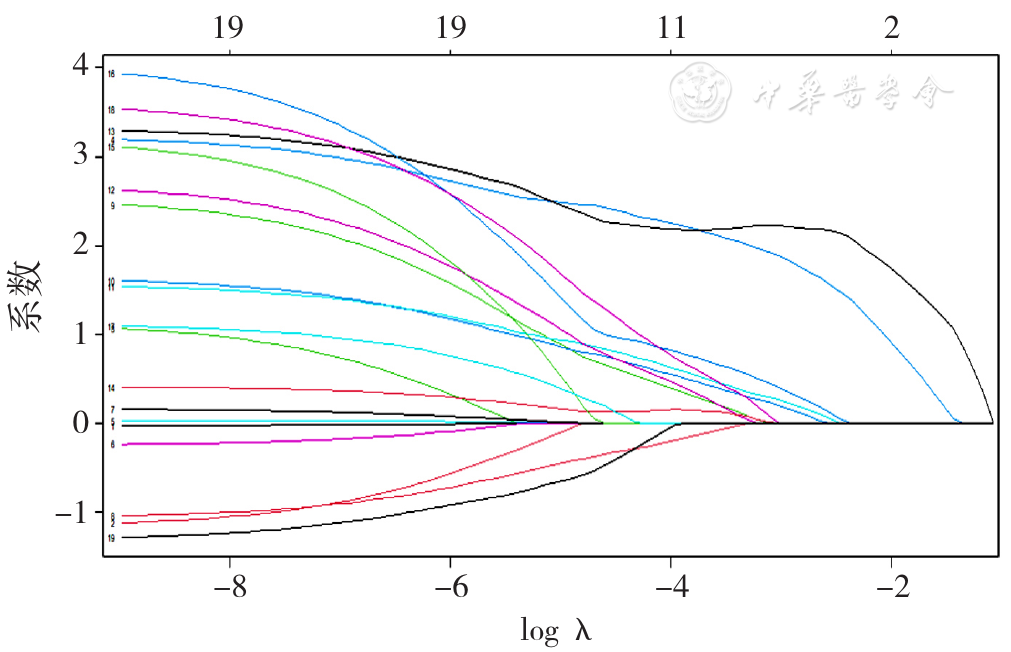
Figure 2 The trajectory diagrams of the regression coefficients of the occurrence of MACE in patients of the DCB group,the DES group and the BVS group
| 变量 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDL-C | 2.502 | 0.651 | 14.770 | <0.001 | 12.204(3.403~43.768) |
| 介入治疗史 | -3.194 | 0.710 | 20.180 | <0.001 | 0.041(0.010~0.162) |
Table 5 The results of multifactorial Logistic regression analysis of MACE in patients
| 变量 | β | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDL-C | 2.502 | 0.651 | 14.770 | <0.001 | 12.204(3.403~43.768) |
| 介入治疗史 | -3.194 | 0.710 | 20.180 | <0.001 | 0.041(0.010~0.162) |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
陈韵岱,邱春光,唐强,等. 药物涂层球囊临床应用中国专家共识(第二版)[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志,2023,31(6):413-426.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
刘睿方,徐方兴,周玉杰,等. 冠状动脉植入金属裸支架适应证的研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(17):2036-2041. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.142.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||