

Chinese General Practice ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (14): 1742-1749.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0709
• Article·Epidemiological Study • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2023-10-19
Revised:2023-12-21
Published:2024-05-15
Online:2024-03-22
Contact:
YU Xiaohui, DANG Zheng
通讯作者:
于晓辉, 党政
作者简介:基金资助:CLC Number:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0709
| 性别 | 发病率 | 患病率 | 死亡率 | DALYs率 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粗率(95%UI) | 标化率(95%UI) | 粗率(95%UI) | 标化率(95%UI) | 粗率(95%UI) | 标化率(95%UI) | 粗率(95%UI) | 标化率(95%UI) | |
| 男性 | ||||||||
| 1990年 | 0.93(0.72~1.55) | 1.56(1.25~2.51) | 1.04(0.81~1.73) | 1.60(1.27~2.60) | 0.89(0.71~1.50) | 1.62(1.33~2.59) | 24.05(39.50~18.93) | 34.26(27.38~56.37) |
| 2019年 | 2.73(1.83~3.44) | 2.25(1.52~2.79) | 3.33(2.18~4.23) | 2.63(1.74~3.30) | 2.45(1.78~3.09) | 2.09(1.53~2.60) | 56.65(40.45~72.06) | 42.60(30.64~53.79) |
| 女性 | ||||||||
| 1990年 | 1.18(0.92~2.02) | 1.64(1.27~2.82) | 1.28(0.99~2.15) | 1.70(1.31~2.88) | 1.16(0.90~2.00) | 1.66(1.29~2.84) | 28.30(21.50~48.73) | 36.46(27.95~62.67) |
| 2019年 | 2.71(1.62~3.54) | 1.84(1.10~2.41) | 3.32(1.95~4.36) | 2.23(1.31~2.93) | 2.39(1.48~3.05) | 1.64(1.01~2.09) | 50.60(31.61~65.08) | 33.57(20.96~43.23) |
| 总体 | ||||||||
| 1990年 | 1.05(0.87~1.69) | 1.58(1.32~2.51) | 1.16(0.96~1.83) | 1.64(1.37~2.59) | 1.02(0.84~1.65) | 1.61(1.35~2.54) | 26.11(21.47~41.07) | 35.18(29.16~56.02) |
| 2019年 | 2.72(1.92~3.27) | 2.01(1.41~2.41) | 3.32(2.31~4.02) | 2.40(1.66~2.91) | 2.42(1.77~2.90) | 1.82(1.32~2.17) | 53.68(38.85~64.72) | 37.71(27.91~45.35) |
Table 1 Disease burden of gallbladder cancer per 100 000 individuals in Chinese population and males and females from 1990 to 2019
| 性别 | 发病率 | 患病率 | 死亡率 | DALYs率 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粗率(95%UI) | 标化率(95%UI) | 粗率(95%UI) | 标化率(95%UI) | 粗率(95%UI) | 标化率(95%UI) | 粗率(95%UI) | 标化率(95%UI) | |
| 男性 | ||||||||
| 1990年 | 0.93(0.72~1.55) | 1.56(1.25~2.51) | 1.04(0.81~1.73) | 1.60(1.27~2.60) | 0.89(0.71~1.50) | 1.62(1.33~2.59) | 24.05(39.50~18.93) | 34.26(27.38~56.37) |
| 2019年 | 2.73(1.83~3.44) | 2.25(1.52~2.79) | 3.33(2.18~4.23) | 2.63(1.74~3.30) | 2.45(1.78~3.09) | 2.09(1.53~2.60) | 56.65(40.45~72.06) | 42.60(30.64~53.79) |
| 女性 | ||||||||
| 1990年 | 1.18(0.92~2.02) | 1.64(1.27~2.82) | 1.28(0.99~2.15) | 1.70(1.31~2.88) | 1.16(0.90~2.00) | 1.66(1.29~2.84) | 28.30(21.50~48.73) | 36.46(27.95~62.67) |
| 2019年 | 2.71(1.62~3.54) | 1.84(1.10~2.41) | 3.32(1.95~4.36) | 2.23(1.31~2.93) | 2.39(1.48~3.05) | 1.64(1.01~2.09) | 50.60(31.61~65.08) | 33.57(20.96~43.23) |
| 总体 | ||||||||
| 1990年 | 1.05(0.87~1.69) | 1.58(1.32~2.51) | 1.16(0.96~1.83) | 1.64(1.37~2.59) | 1.02(0.84~1.65) | 1.61(1.35~2.54) | 26.11(21.47~41.07) | 35.18(29.16~56.02) |
| 2019年 | 2.72(1.92~3.27) | 2.01(1.41~2.41) | 3.32(2.31~4.02) | 2.40(1.66~2.91) | 2.42(1.77~2.90) | 1.82(1.32~2.17) | 53.68(38.85~64.72) | 37.71(27.91~45.35) |
| 分类 | 指标 | 时间 | 变化值(95%CI)(%) | t值 | P值 | 分类 | 指标 | 时间 | 变化值(95%CI)(%) | t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标化发病率 | 标化死亡率 | ||||||||||
| 男性 | APC | 1990—1996年 | -1.16(-1.49~0.83) | -7.36 | <0.001 | 男性 | APC | 1990—1996年 | -1.30(-1.60~-0.99) | -9.00 | <0.001 |
| 1996—1999年 | 1.37(-0.72~3.31) | 1.35 | 0.203 | 1996—1999年 | 0.85(-0.97~2.70) | 0.99 | 0.348 | ||||
| 1999—2005年 | 7.20(6.72~7.67) | 33.10 | <0.001 | 1999—2005年 | 6.61(6.17~7.04) | 33.32 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2005—2011年 | 1.05(0.60~1.50) | 4.99 | <0.001 | 2005—2011年 | 0.65(0.24~1.06) | 3.37 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2011—2019年 | -1.14(-1.36~-0.93) | -11.22 | <0.001 | 2011—2019年 | -1.52(-1.72~-1.33) | -16.37 | <0.001 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 1.23(0.99~1.48) | 9.99 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.86(0.63~1.08) | 7.58 | <0.001 | ||
| 女性 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -1.72(-1.93~-1.51) | -17.42 | <0.001 | 女性 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -2.00(-2.21~-1.79) | -20.26 | <0.001 |
| 1998—2001年 | 5.00(2.95~7.09) | 5.35 | <0.001 | 1998—2001年 | 4.50(2.46~6.58) | 4.82 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2001—2004年 | 9.15(7.02~11.32) | 9.60 | <0.001 | 2001—2004年 | 8.34(6.22~10.49) | 8.77 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2004—2010年 | -0.07(-0.51~0.37) | -0.35 | 0.734 | 2004—2010年 | -0.68(-1.12~-0.24) | -3.33 | 0.012 | ||||
| 2010—2015年 | -2.71(-3.32~-2.11) | -9.54 | <0.001 | 2010—2015年 | -3.07(-3.67~-2.46) | -10.79 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2015—2019年 | -0.38(-1.00~0.24) | -1.33 | <0.001 | 2015—2019年 | -0.79(-1.41~-0.17) | -2.76 | 0.016 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.39(0.08~0.70) | 2.50 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | -0.06(-0.37~0.25) | -0.39 | 0.692 | ||
| 总体 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -1.25(-1.37~-1.13) | -22.46 | <0.001 | 总体 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -1.48(-1.59~-1.37) | -28.71 | <0.001 |
| 1998—2001年 | 5.31(4.15~6.49) | 10.08 | <0.001 | 1998—2001年 | 4.80(3.73~5.88) | 9.86 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2001—2004年 | 9.00(7.79~10.21) | 16.78 | <0.001 | 2001—2004年 | 8.25(7.14~9.37) | 16.68 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2004—2010年 | 0.78(0.53~1.03) | 6.78 | <0.001 | 2004—2010年 | 0.24(0.01~0.47) | 2.25 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2010—2015年 | -1.99(-2.33~-1.64) | -12.35 | <0.001 | 2010—2015年 | -2.34(-2.66~-2.02) | -15.76 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2015—2019年 | -0.55(-0.90~-0.20) | -3.41 | <0.001 | 2015—2019年 | -0.96(-1.29~-0.64) | -6.45 | <0.001 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.82(0.65~1.00) | 9.31 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.40(0.24~0.56) | 4.93 | <0.001 | ||
| 标化患病率 | 标化DALYs率 | ||||||||||
| 男性 | APC | 1990—1996年 | -0.94(-1.29~-0.59) | -5.71 | <0.001 | 男性 | APC | 1990—1996年 | -1.86(-2.02~-1.34) | -10.37 | <0.001 |
| 1996—1999年 | 1.78(-0.31~3.92) | 1.80 | 0.093 | 1996—1999年 | 1.02(-1.03~3.12) | 1.05 | 0.314 | ||||
| 1999—2005年 | 7.89(7.39~8.39) | 34.64 | <0.001 | 1999—2005年 | 6.76(6.28~7.26) | 30.22 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2005—2011年 | 1.54(1.07~2.02) | 6.99 | <0.001 | 2005—2011年 | 0.06(-0.40~0.52) | 0.26 | 0.792 | ||||
| 2011—2019年 | -0.67(-0.89~-0.44) | -6.27 | <0.001 | 2011—2019年 | -1.45(-1.67~-1.22) | -13.78 | <0.001 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 1.70(1.45~1.96) | 13.18 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.72(0.47~0.97) | 5.67 | <0.001 | ||
| 女性 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -1.31(-1.52~-1.10) | -13.71 | <0.001 | 女性 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -2.18(-2.35~-2.02) | -28.46 | <0.001 |
| 1998—2001年 | 5.59(3.61~7.62) | 6.19 | <0.001 | 1998—2001年 | 4.25(2.67~5.87) | 5.86 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2001—2004年 | 10.07(8.00~12.18) | 10.91 | <0.001 | 2001—2004年 | 7.93(6.29~9.60) | 10.74 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2004—2010年 | 0.62(0.20~1.05) | 3.15 | <0.001 | 2004—2010年 | -1.20(-1.54~-0.86) | -7.60 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2010—2015年 | -2.33(-2.92~-1.75) | -8.50 | <0.001 | 2010—2015年 | -3.06(-3.53~-2.59) | -13.85 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2015—2019年 | 0.16(-0.44~0.77) | 0.59 | 0.569 | 2015~2019年 | -0.80(-1.28~-0.31) | -3.56 | <0.001 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.94(0.64~1.24) | 6.22 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | -0.28(-0.52~-0.05) | -2.34 | 0.016 | ||
| 总体 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -0.91(-1.04~-0.77) | -14.53 | <0.001 | 总体 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -1.75(-1.84~-1.65) | -41.08 | <0.001 |
| 1998—2001年 | 5.93(4.62~7.26) | 10.00 | <0.001 | 1998—2001年 | 4.86(3.97~5.75) | 12.08 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2001—2004年 | 9.85(8.49~11.22) | 16.31 | <0.001 | 2001—2004年 | 8.15(7.23~9.07) | 19.94 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2004—2010年 | 1.43(1.15~1.71) | 11.01 | <0.001 | 2004—2010年 | -0.16(-0.35~0.03) | -1.83 | 0.092 | ||||
| 2010—2015年 | -1.57(-1.96~-1.18) | -8.68 | <0.001 | 2010—2015年 | -2.34(-2.60~-2.07) | -19.04 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2015—2019年 | -0.04(-0.44~0.35) | -0.23 | 0.825 | 2015—2019年 | -0.90(-1.17~-0.63) | -7.28 | <0.001 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 1.34(1.14~1.54) | 13.49 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.25(0.12~0.38) | 3.71 | <0.001 | ||
Table 2 Annual changes in the disease burden of gallbladder cancer in Chinese population and males and females from 1990 to 2019
| 分类 | 指标 | 时间 | 变化值(95%CI)(%) | t值 | P值 | 分类 | 指标 | 时间 | 变化值(95%CI)(%) | t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标化发病率 | 标化死亡率 | ||||||||||
| 男性 | APC | 1990—1996年 | -1.16(-1.49~0.83) | -7.36 | <0.001 | 男性 | APC | 1990—1996年 | -1.30(-1.60~-0.99) | -9.00 | <0.001 |
| 1996—1999年 | 1.37(-0.72~3.31) | 1.35 | 0.203 | 1996—1999年 | 0.85(-0.97~2.70) | 0.99 | 0.348 | ||||
| 1999—2005年 | 7.20(6.72~7.67) | 33.10 | <0.001 | 1999—2005年 | 6.61(6.17~7.04) | 33.32 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2005—2011年 | 1.05(0.60~1.50) | 4.99 | <0.001 | 2005—2011年 | 0.65(0.24~1.06) | 3.37 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2011—2019年 | -1.14(-1.36~-0.93) | -11.22 | <0.001 | 2011—2019年 | -1.52(-1.72~-1.33) | -16.37 | <0.001 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 1.23(0.99~1.48) | 9.99 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.86(0.63~1.08) | 7.58 | <0.001 | ||
| 女性 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -1.72(-1.93~-1.51) | -17.42 | <0.001 | 女性 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -2.00(-2.21~-1.79) | -20.26 | <0.001 |
| 1998—2001年 | 5.00(2.95~7.09) | 5.35 | <0.001 | 1998—2001年 | 4.50(2.46~6.58) | 4.82 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2001—2004年 | 9.15(7.02~11.32) | 9.60 | <0.001 | 2001—2004年 | 8.34(6.22~10.49) | 8.77 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2004—2010年 | -0.07(-0.51~0.37) | -0.35 | 0.734 | 2004—2010年 | -0.68(-1.12~-0.24) | -3.33 | 0.012 | ||||
| 2010—2015年 | -2.71(-3.32~-2.11) | -9.54 | <0.001 | 2010—2015年 | -3.07(-3.67~-2.46) | -10.79 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2015—2019年 | -0.38(-1.00~0.24) | -1.33 | <0.001 | 2015—2019年 | -0.79(-1.41~-0.17) | -2.76 | 0.016 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.39(0.08~0.70) | 2.50 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | -0.06(-0.37~0.25) | -0.39 | 0.692 | ||
| 总体 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -1.25(-1.37~-1.13) | -22.46 | <0.001 | 总体 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -1.48(-1.59~-1.37) | -28.71 | <0.001 |
| 1998—2001年 | 5.31(4.15~6.49) | 10.08 | <0.001 | 1998—2001年 | 4.80(3.73~5.88) | 9.86 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2001—2004年 | 9.00(7.79~10.21) | 16.78 | <0.001 | 2001—2004年 | 8.25(7.14~9.37) | 16.68 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2004—2010年 | 0.78(0.53~1.03) | 6.78 | <0.001 | 2004—2010年 | 0.24(0.01~0.47) | 2.25 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2010—2015年 | -1.99(-2.33~-1.64) | -12.35 | <0.001 | 2010—2015年 | -2.34(-2.66~-2.02) | -15.76 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2015—2019年 | -0.55(-0.90~-0.20) | -3.41 | <0.001 | 2015—2019年 | -0.96(-1.29~-0.64) | -6.45 | <0.001 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.82(0.65~1.00) | 9.31 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.40(0.24~0.56) | 4.93 | <0.001 | ||
| 标化患病率 | 标化DALYs率 | ||||||||||
| 男性 | APC | 1990—1996年 | -0.94(-1.29~-0.59) | -5.71 | <0.001 | 男性 | APC | 1990—1996年 | -1.86(-2.02~-1.34) | -10.37 | <0.001 |
| 1996—1999年 | 1.78(-0.31~3.92) | 1.80 | 0.093 | 1996—1999年 | 1.02(-1.03~3.12) | 1.05 | 0.314 | ||||
| 1999—2005年 | 7.89(7.39~8.39) | 34.64 | <0.001 | 1999—2005年 | 6.76(6.28~7.26) | 30.22 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2005—2011年 | 1.54(1.07~2.02) | 6.99 | <0.001 | 2005—2011年 | 0.06(-0.40~0.52) | 0.26 | 0.792 | ||||
| 2011—2019年 | -0.67(-0.89~-0.44) | -6.27 | <0.001 | 2011—2019年 | -1.45(-1.67~-1.22) | -13.78 | <0.001 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 1.70(1.45~1.96) | 13.18 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.72(0.47~0.97) | 5.67 | <0.001 | ||
| 女性 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -1.31(-1.52~-1.10) | -13.71 | <0.001 | 女性 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -2.18(-2.35~-2.02) | -28.46 | <0.001 |
| 1998—2001年 | 5.59(3.61~7.62) | 6.19 | <0.001 | 1998—2001年 | 4.25(2.67~5.87) | 5.86 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2001—2004年 | 10.07(8.00~12.18) | 10.91 | <0.001 | 2001—2004年 | 7.93(6.29~9.60) | 10.74 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2004—2010年 | 0.62(0.20~1.05) | 3.15 | <0.001 | 2004—2010年 | -1.20(-1.54~-0.86) | -7.60 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2010—2015年 | -2.33(-2.92~-1.75) | -8.50 | <0.001 | 2010—2015年 | -3.06(-3.53~-2.59) | -13.85 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2015—2019年 | 0.16(-0.44~0.77) | 0.59 | 0.569 | 2015~2019年 | -0.80(-1.28~-0.31) | -3.56 | <0.001 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.94(0.64~1.24) | 6.22 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | -0.28(-0.52~-0.05) | -2.34 | 0.016 | ||
| 总体 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -0.91(-1.04~-0.77) | -14.53 | <0.001 | 总体 | APC | 1990—1998年 | -1.75(-1.84~-1.65) | -41.08 | <0.001 |
| 1998—2001年 | 5.93(4.62~7.26) | 10.00 | <0.001 | 1998—2001年 | 4.86(3.97~5.75) | 12.08 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2001—2004年 | 9.85(8.49~11.22) | 16.31 | <0.001 | 2001—2004年 | 8.15(7.23~9.07) | 19.94 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2004—2010年 | 1.43(1.15~1.71) | 11.01 | <0.001 | 2004—2010年 | -0.16(-0.35~0.03) | -1.83 | 0.092 | ||||
| 2010—2015年 | -1.57(-1.96~-1.18) | -8.68 | <0.001 | 2010—2015年 | -2.34(-2.60~-2.07) | -19.04 | <0.001 | ||||
| 2015—2019年 | -0.04(-0.44~0.35) | -0.23 | 0.825 | 2015—2019年 | -0.90(-1.17~-0.63) | -7.28 | <0.001 | ||||
| AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 1.34(1.14~1.54) | 13.49 | <0.001 | AAPC | 1990—2019年 | 0.25(0.12~0.38) | 3.71 | <0.001 | ||
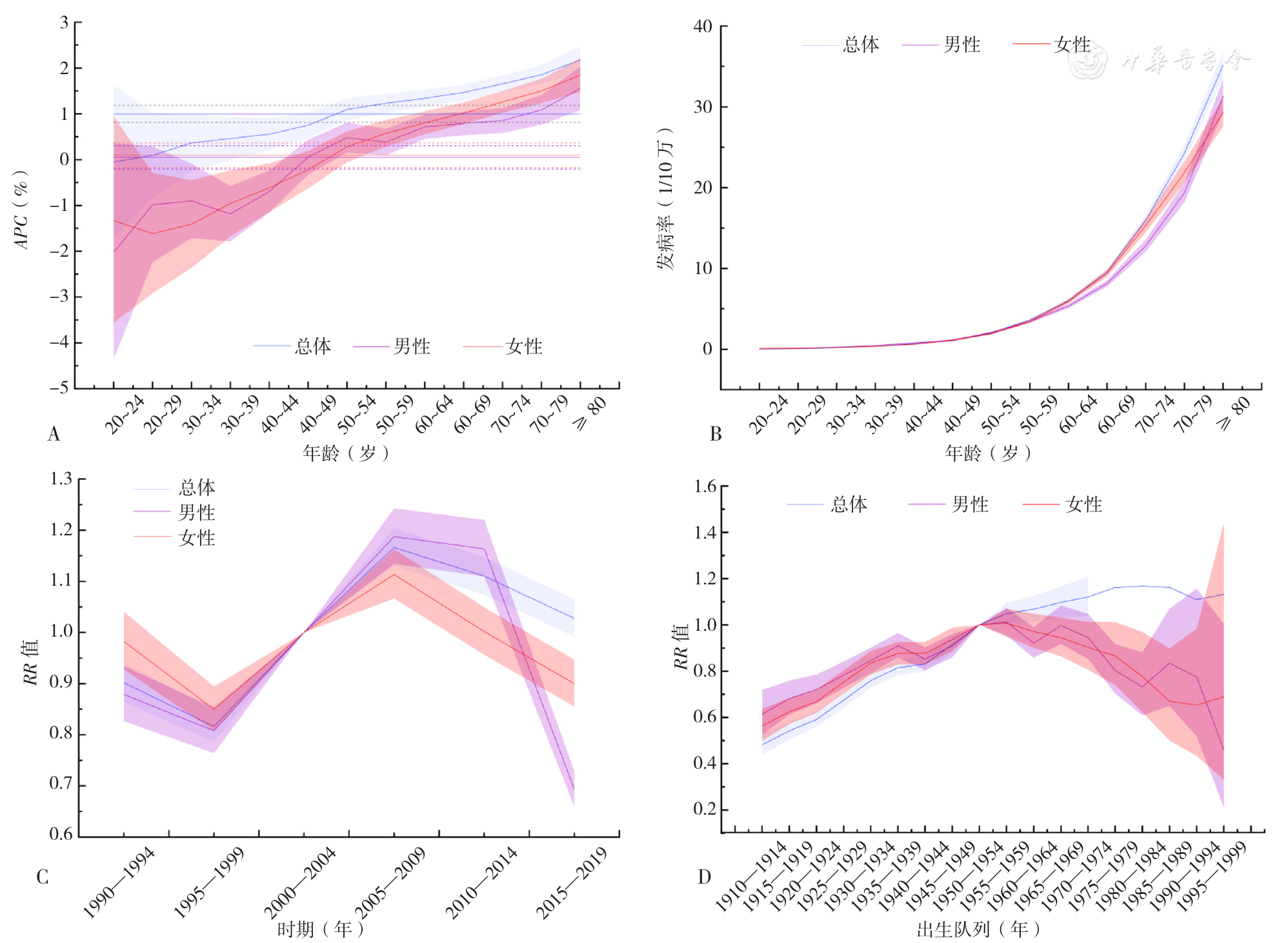
Figure 2 Bayesian age-period-cohort analysis model visualizing the incidence of gallbladder cancer in Chinese population and males and females from 1990 to 2019
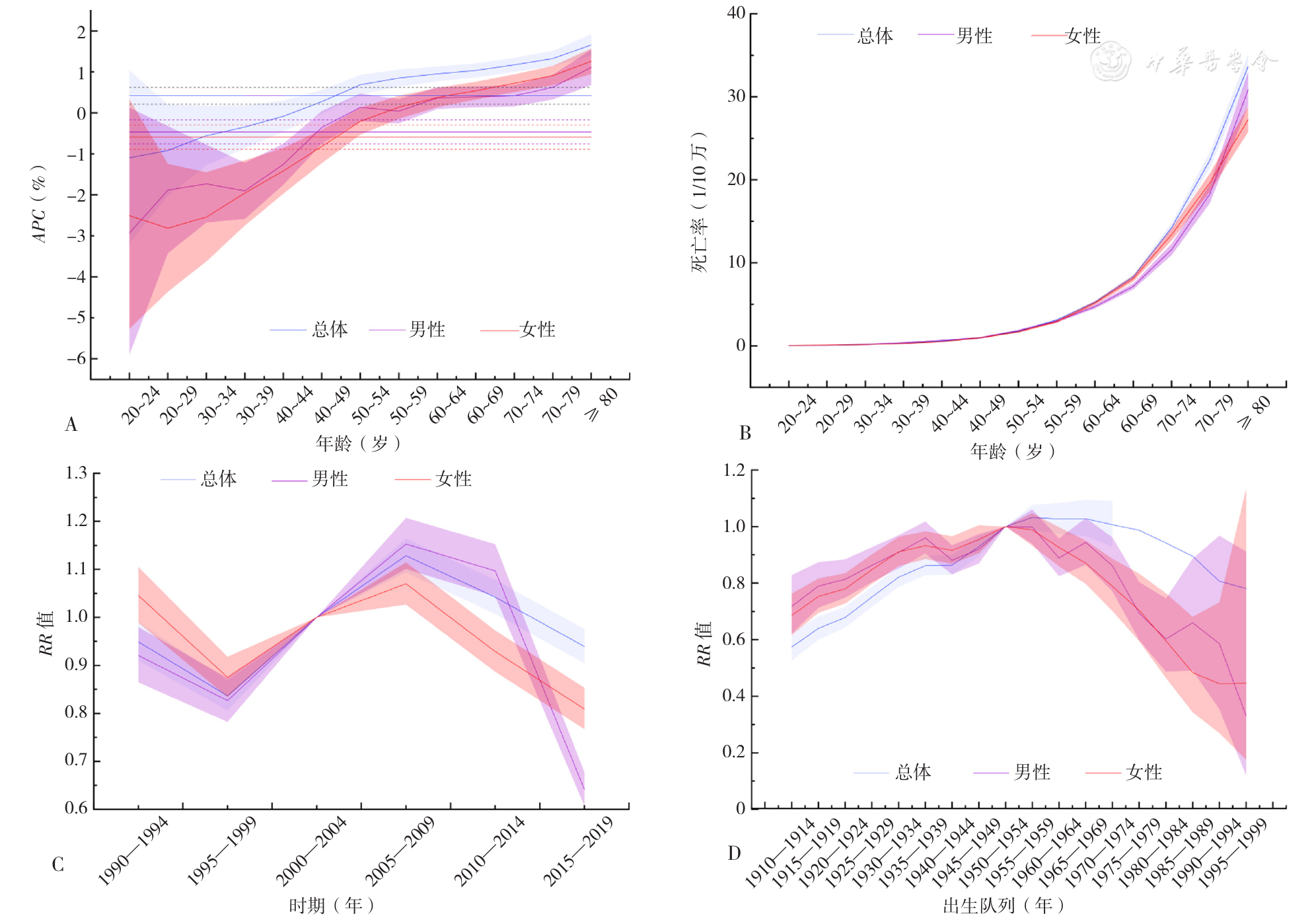
Figure 3 Bayesian age-period-cohort analysis model visualizing the mortality of gallbladder cancer in Chinese population and males and females from 1990 to 2019
| 指标 | MSE | MAE | MAPE(%) | 拟合精度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标化发病率 | 0.000 4 | 0.015 8 | 0.748 8 | 99.251 2 |
| 标化患病率 | 0.000 5 | 0.017 6 | 0.713 9 | 99.286 1 |
| 标化死亡率 | 0.000 4 | 0.015 0 | 0.775 5 | 99.224 5 |
| 标化DALYs率 | 0.107 7 | 0.267 7 | 0.665 8 | 99.334 2 |
Table 3 Prediction model fitting of disease burden of gallbladder cancer in China from 1990 to 2019
| 指标 | MSE | MAE | MAPE(%) | 拟合精度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标化发病率 | 0.000 4 | 0.015 8 | 0.748 8 | 99.251 2 |
| 标化患病率 | 0.000 5 | 0.017 6 | 0.713 9 | 99.286 1 |
| 标化死亡率 | 0.000 4 | 0.015 0 | 0.775 5 | 99.224 5 |
| 标化DALYs率 | 0.107 7 | 0.267 7 | 0.665 8 | 99.334 2 |
| 年份(年) | 标化发病率(95%CI) | 标化患病率(95%CI) | 标化死亡率(95%CI) | 标化DALYs率(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 2.00(1.95~2.06) | 2.41(2.35~2.47) | 1.81(1.76~1.86) | 37.58(36.52~38.65) |
| 2021 | 2.01(1.88~2.13) | 2.42(2.28~2.56) | 1.82(1.69~1.94) | 37.54(34.98~40.09) |
| 2022 | 2.01(1.80~2.22) | 2.43(2.20~2.66) | 1.82(1.62~2.02) | 37.53(33.29~41.78) |
| 2023 | 2.01(1.72~2.31) | 2.45(2.12~2.77) | 1.82(1.54~2.11) | 37.56(31.59~43.53) |
| 2024 | 2.02(1.65~2.39) | 2.46(2.05~2.88) | 1.83(1.47~2.19) | 37.59(29.98~45.21) |
| 2025 | 2.03(1.58~2.47) | 2.48(1.98~2.98) | 1.84(1.40~2.27) | 37.63(28.49~46.77) |
| 2026 | 2.04(1.52~2.56) | 2.50(1.91~3.08) | 1.84(1.34~2.34) | 37.67(27.13~48.21) |
| 2027 | 2.04(1.46~2.63) | 2.51(1.85~3.18) | 1.85(1.29~2.40) | 37.70(25.89~49.52) |
| 2028 | 2.05(1.40~2.71) | 2.53(1.80~3.27) | 1.85(1.24~2.46) | 37.74(24.75~50.73) |
| 2029 | 2.06(1.35~2.78) | 2.55(1.74~3.36) | 1.86(1.20~2.52) | 37.77(23.70~51.84) |
| 2030 | 2.07(1.30~2.85) | 2.57(1.69~3.45) | 1.86(1.15~2.57) | 37.81(22.74~52.88) |
Table 4 Prediction of disease burden of gallbladder cancer per 100 000 individuals in China from 2020 to 2030
| 年份(年) | 标化发病率(95%CI) | 标化患病率(95%CI) | 标化死亡率(95%CI) | 标化DALYs率(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 2.00(1.95~2.06) | 2.41(2.35~2.47) | 1.81(1.76~1.86) | 37.58(36.52~38.65) |
| 2021 | 2.01(1.88~2.13) | 2.42(2.28~2.56) | 1.82(1.69~1.94) | 37.54(34.98~40.09) |
| 2022 | 2.01(1.80~2.22) | 2.43(2.20~2.66) | 1.82(1.62~2.02) | 37.53(33.29~41.78) |
| 2023 | 2.01(1.72~2.31) | 2.45(2.12~2.77) | 1.82(1.54~2.11) | 37.56(31.59~43.53) |
| 2024 | 2.02(1.65~2.39) | 2.46(2.05~2.88) | 1.83(1.47~2.19) | 37.59(29.98~45.21) |
| 2025 | 2.03(1.58~2.47) | 2.48(1.98~2.98) | 1.84(1.40~2.27) | 37.63(28.49~46.77) |
| 2026 | 2.04(1.52~2.56) | 2.50(1.91~3.08) | 1.84(1.34~2.34) | 37.67(27.13~48.21) |
| 2027 | 2.04(1.46~2.63) | 2.51(1.85~3.18) | 1.85(1.29~2.40) | 37.70(25.89~49.52) |
| 2028 | 2.05(1.40~2.71) | 2.53(1.80~3.27) | 1.85(1.24~2.46) | 37.74(24.75~50.73) |
| 2029 | 2.06(1.35~2.78) | 2.55(1.74~3.36) | 1.86(1.20~2.52) | 37.77(23.70~51.84) |
| 2030 | 2.07(1.30~2.85) | 2.57(1.69~3.45) | 1.86(1.15~2.57) | 37.81(22.74~52.88) |
| [1] |
李永盛,李茂岚,刘颖斌. 胆囊癌相关基础研究现状与展望[J]. 中国实用外科杂志,2021,41(1):52-55. DOI:10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2021.01.08.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
任泰,李永盛,耿亚军,等. 中国2010—2017年胆囊癌治疗模式及预后分析[J]. 中华外科杂志,2020,58(9):697-706.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
郑荣寿,张思维,孙可欣,等. 2016年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志,2023,45(3):212-220.
|
| [6] |
GBD 2019 Viewpoint Collaborators. Five insights from the global burden of disease study 2019[J]. Lancet,2020,396(10258):1135-1159. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31404-5.
|
| [7] |
GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories,1990-2019:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet,2020,396(10258):1223-1249. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30752-2.
|
| [8] |
李辉章,杜灵彬. Joinpoint回归模型在肿瘤流行病学时间趋势分析中的应用[J]. 中华预防医学杂志,2020,54(8):908-912. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20200616-00889.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
郑荣寿,陈万青. 基于贝叶斯方法的年龄-时期-队列预测模型的介绍[J]. 中华预防医学杂志,2012,46(7):648-650.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
黄瑜,刘玉琴,丁高恒,等. 2009—2015年甘肃省肿瘤登记地区胆囊癌流行特征及变化趋势分析[J]. 实用肿瘤学杂志,2021,35(3):193-199.
|
| [22] |
张明迪,龚伟,郑莹,等. 上海市胆囊癌流行状况和趋势分析[J]. 中国实用外科杂志,2013,33(8):691-694. DOI:08.2208/j.issn.1005-2208.2013.08.004.
|
| [23] |
单天昊,安澜,徐梦圆,等. 2020年全球肝癌和胆囊癌发病死亡分析[J]. 肝癌电子杂志,2022,9(4):46-51. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-7815.2022.04.008.
|
| [24] |
胡霄,李丽,欧阳一非,等. 2000—2018年中国十六省(自治区、直辖市)7~17岁儿童青少年超重与肥胖流行趋势[J]. 卫生研究,2022,51(4):568-573.
|
| [25] |
费太安. 健康中国 百年求索——党领导下的我国医疗卫生事业发展历程及经验[J]. 管理世界,2021,37(11):26-40,3.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [1] | XIAN Lihong, LI Juan, XUE Chao, ZHAO Xuejiao, LU Ting, YAN Huan. Prevalence for Cerebral Microbleeds in China: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(20): 2527-2533. |
| [2] | MIAO Lipeng, REN Kehao, LI Mengdie, LYU Juncheng. Trend Analysis and Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease Mortality in China from 2009 to 2021 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(18): 2260-2264. |
| [3] | MA Xuefeng, HUANG Jun, LI Na, SHAO Huijuan, LU Lixia, YU Xiaohui, ZHANG Jiucong. Analysis of Disease Burden and Annual Change Trends of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in China from 1990 to 2019 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(18): 2265-2271. |
| [4] | YIN Qiuguo, QIN Xintong, ZHANG Yidan, JIANG Peng, GUO Ping, JIA Xingtai, JIAN Liguo. Correlation between Insulin Resistance Metabolic Score and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(18): 2179-2185. |
| [5] | XU Su, CAI Wenwei, LI Chenyi, WANG Guanghui, XU Youduan. Current Status and Influencing Factors of Dysphagia among the Elderly in Communities: a Cross-sectional Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(17): 2083-2090. |
| [6] | ZHOU Zitong, JIA Yu, YAN Hong, XU Jialan, WEN Jun, WANG Siyu. The Prevalence of Dyslipidemia in Chinese Children and Adolescents: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(17): 2145-2154. |
| [7] | HONG Ling, LU Liping, CHENG Ning, SUN Qin, JIANG Jianhong, ZHU Liangfeng. Prevalence and Epidemiological Characteristics of Venous Thromboembolism in Jiaxing City [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(15): 1837-1842. |
| [8] | HUANG Gang, CAO Guiying, LIU Min. Current Situation and Trends in the Disease Burden of Dental Caries in China, 1990-2019 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(14): 1735-1741. |
| [9] | QU Yuanyuan, CAO Miao, WANG Jing, CHENG Li, HE Xiaoshuang. Trends in Prevalence and Burden of Asthma and Its Risk Factors in China, 1990-2019 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(13): 1594-1600. |
| [10] | ZHANG Yuan, HOU Qiqi, QI Qi, JIANG Yue, WANG Nan, YUE Bocheng, CHEN Shuohua, HAN Quanle, WU Shouling, LI Kangbo. Relationship between Cardiovascular Health Score of Life's Essential 8 and New-onset Atrial Fibrillation: a Large Sample, Long-Term Follow-up Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(12): 1431-1437. |
| [11] | ZHANG Shengnan, XU Shihua, HUANG Rongchao, CHEN Jian, ZHAO Chunru, MENG Minglyu, MA Yingjiao. Trend and Forecast Analysis of Premature Mortality Probability by Four Major Non-communicable Diseases in Baise from 2015 to 2021 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(11): 1387-1394. |
| [12] | XU Li, GE Jing, YU Peng, YU Ying. Shifts in Chronic Disease and Comorbidity Patterns among Chinese Older Adults: an Analysis Based on the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(11): 1296-1302. |
| [13] | LIANG Dong, YANG Chenglin, LIN Xiaoru, ZHAO Yang, OUYANG Jiang, LIN Xiuquan. Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases Attributable to Diabetes among Chinese Adults from 1990 to 2019 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(11): 1380-1386. |
| [14] | HE Haiyang, YANG Jialing, LEI Xun. Prevalence and Influencing Factors of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(11): 1370-1379. |
| [15] | CHEN Dan, WANG Yawei, HUANG Fang, XU Yifan, ZHANG Yiying, SHAO Yueqin. Epidemic Trend Analysis of Colorectal Cancer in Jiading District, Shanghai from 2003 to 2019 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(10): 1261-1266. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||