

Chinese General Practice ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (06): 760-768.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0461
Special Issue: 肿瘤最新文章合辑; 消化系统疾病最新文章合辑; 数智医疗最新文章合辑
• Medical Information Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2022-05-20
Revised:2022-08-21
Published:2023-02-20
Online:2022-08-25
Contact:
WU Lei
About author:
通讯作者:
吴磊
作者简介:基金资助:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0461
| 检索步骤 | 检索式 | 文献数量(篇) |
|---|---|---|
| 1# | esophag* (Topic) or oesophag* (Topic) or gullet (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 103 423 |
| 2# | cancer* (Topic) or tumour* (Topic) or tumor* (Topic) or neoplas* (Topic) or onco* (Topic) or carcinoma* (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 3 272 272 |
| 3# | 1# AND 2# | 54 077 |
| 4# | "artificial intelligen*" (Topic) or computational NEAR/5 intelligence (Topic) or expert* system* (Topic) or intelligent learning (Topic) or feature* extraction (Topic) or feature* mining (Topic) or feature* learning (Topic) or machine learning (Topic) or feature* selection (Topic) or unsupervised clustering (Topic) or image* segmentation (Topic) or supervised learning (Topic) or semantic segmentation (Topic) or deep network* (Topic) or bayes* network (Topic) or deep learning (Topic) or neural network* (Topic) or neural learning (Topic) or neural nets model (Topic) or artificial neural network (Topic) or data mining (Topic) or graph mining (Topic) or data clustering (Topic) or big data (Topic) or knowledge graph (Topic) or AI (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 1 068 667 |
| 5# | 3# AND 4# | 1 074 |
Table 1 List of esophageal cancer studies using AI published from 2000 to 2022
| 检索步骤 | 检索式 | 文献数量(篇) |
|---|---|---|
| 1# | esophag* (Topic) or oesophag* (Topic) or gullet (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 103 423 |
| 2# | cancer* (Topic) or tumour* (Topic) or tumor* (Topic) or neoplas* (Topic) or onco* (Topic) or carcinoma* (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 3 272 272 |
| 3# | 1# AND 2# | 54 077 |
| 4# | "artificial intelligen*" (Topic) or computational NEAR/5 intelligence (Topic) or expert* system* (Topic) or intelligent learning (Topic) or feature* extraction (Topic) or feature* mining (Topic) or feature* learning (Topic) or machine learning (Topic) or feature* selection (Topic) or unsupervised clustering (Topic) or image* segmentation (Topic) or supervised learning (Topic) or semantic segmentation (Topic) or deep network* (Topic) or bayes* network (Topic) or deep learning (Topic) or neural network* (Topic) or neural learning (Topic) or neural nets model (Topic) or artificial neural network (Topic) or data mining (Topic) or graph mining (Topic) or data clustering (Topic) or big data (Topic) or knowledge graph (Topic) or AI (Topic) and Article OR Review (Document Type) and English (Language) | 1 068 667 |
| 5# | 3# AND 4# | 1 074 |
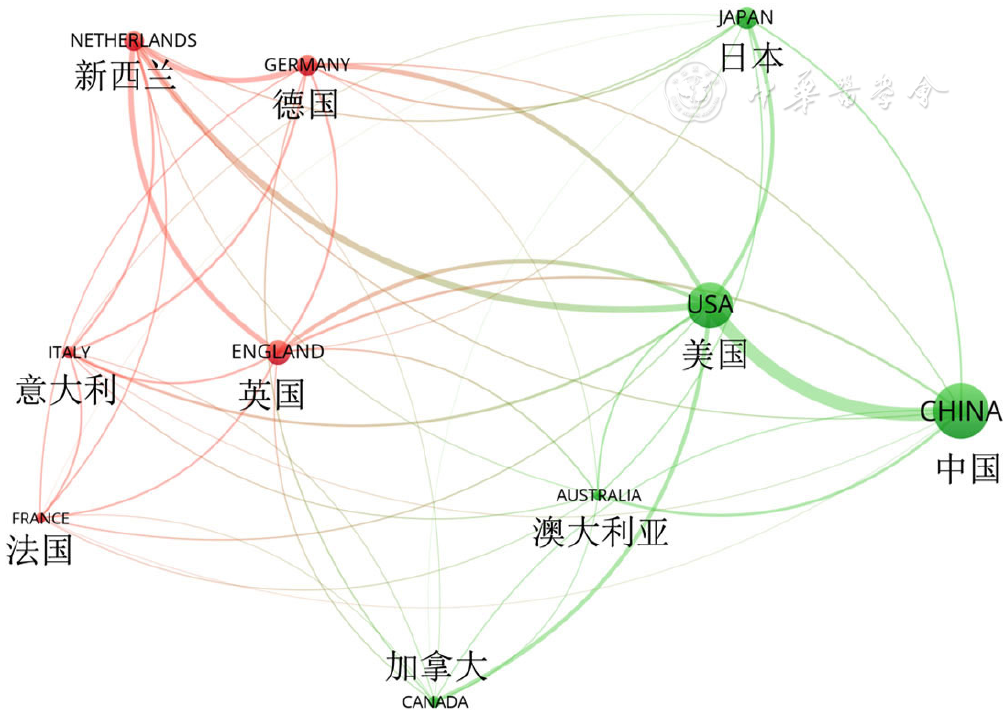
Figure 2 VOSviewer-generated collaboration map of top 10 research countries related to esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022
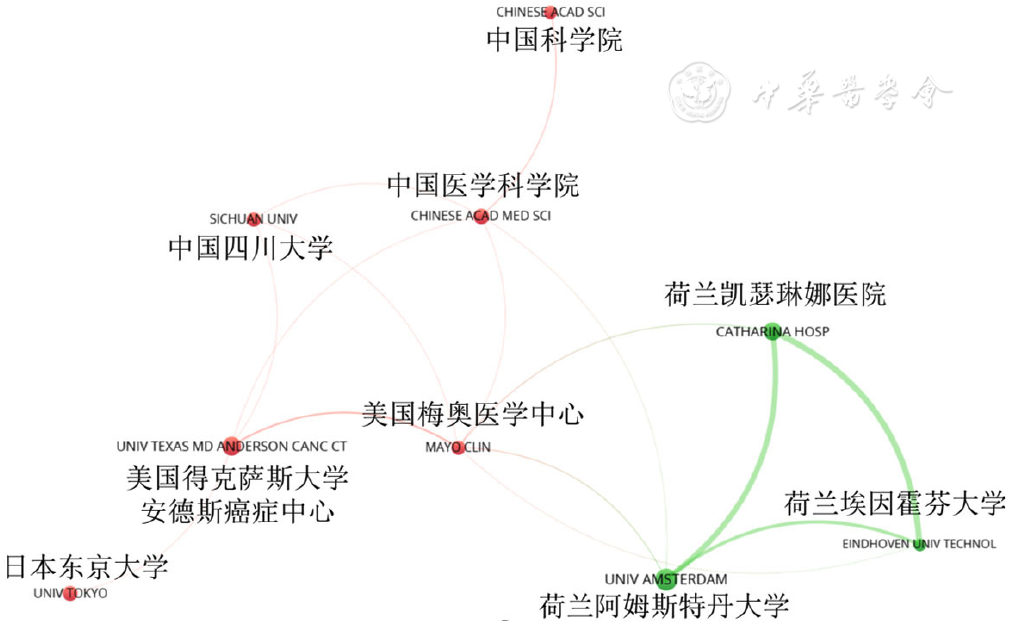
Figure 3 VOSviewer-generated collaboration map of institutions published more than 15 esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022
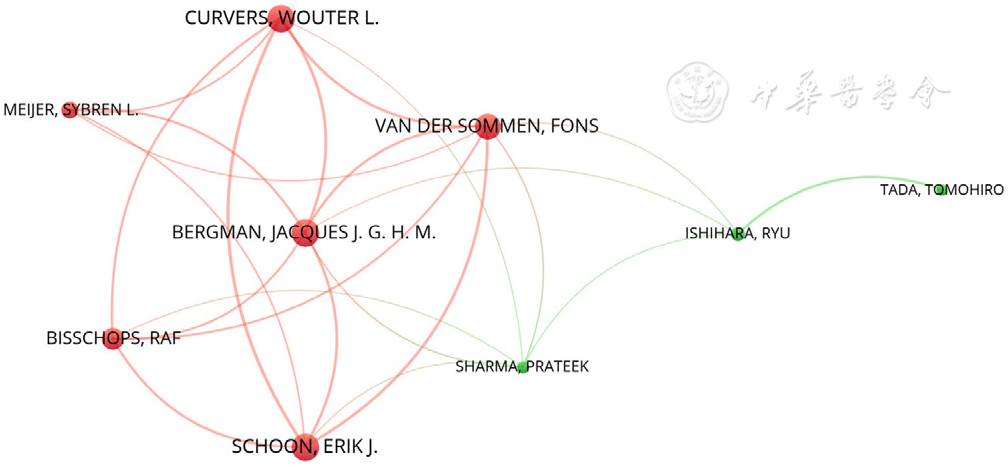
Figure 4 VOSviewer-generated collaboration map of authors published more than 10 esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022
| 序号 | 共被引作者 | 地区 | 共被引次数(次) | 总被引次数(次) | 中介中心性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Freddie Ian Bray | 法国 | 89 | 304 | 0 |
| 2 | Prateek Sharma | 美国 | 87 | 1 907 | 0.04 |
| 3 | Yoshimasa Horie | 日本 | 56 | 691 | 0.04 |
| 4 | Jacques Ferlay | 法国 | 53 | 748 | 0.01 |
| 5 | Jesper Lagergren | 瑞典 | 52 | 1 591 | 0.15 |
| 6 | Lambin Philippe | 比利时 | 46 | 562 | 0.04 |
| 7 | Rebecca L Siegel | 美国 | 46 | 417 | 0 |
| 8 | Hirasawa Toshiaki | 日本 | 45 | 1 025 | 0.06 |
| 9 | Nicholas James Shaheen | 美国 | 45 | 136 | 0.04 |
| 10 | Thomas William Rice | 美国 | 43 | 1 107 | 0.12 |
Table 2 Total co-citations of esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022 by author (top 10)
| 序号 | 共被引作者 | 地区 | 共被引次数(次) | 总被引次数(次) | 中介中心性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Freddie Ian Bray | 法国 | 89 | 304 | 0 |
| 2 | Prateek Sharma | 美国 | 87 | 1 907 | 0.04 |
| 3 | Yoshimasa Horie | 日本 | 56 | 691 | 0.04 |
| 4 | Jacques Ferlay | 法国 | 53 | 748 | 0.01 |
| 5 | Jesper Lagergren | 瑞典 | 52 | 1 591 | 0.15 |
| 6 | Lambin Philippe | 比利时 | 46 | 562 | 0.04 |
| 7 | Rebecca L Siegel | 美国 | 46 | 417 | 0 |
| 8 | Hirasawa Toshiaki | 日本 | 45 | 1 025 | 0.06 |
| 9 | Nicholas James Shaheen | 美国 | 45 | 136 | 0.04 |
| 10 | Thomas William Rice | 美国 | 43 | 1 107 | 0.12 |
| 序号 | 文章题目 | 期刊名称 | 第一作者 | 出版年份(年) | 共被引次数(次) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Global cancer statistics 2018:Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries | Ca-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians | BRAY | 2018 | 87 |
| 2 | Diagnostic outcomes of esophageal cancer by artificial intelligence using convolutional neural networks | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | HORIE | 2019 | 56 |
| 3 | Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for detecting gastric cancer in endoscopic images | Gastric Cancer | HIRASAWA | 2018 | 43 |
| 4 | Real-time automated diagnosis of precancerous lesions and early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using a deep learning model (with videos) | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | GUO | 2019 | 37 |
| 5 | Deep-learning system detects neoplasia in patients with barrett's esophagus with higher accuracy than endoscopists in a multistep training and validation study with benchmarking | Gastroenterology | DE GROOF | 2020 | 32 |
| 6 | Endoscopic detection and differentiation of esophageal lesions using a deep neural network | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | OHMORI | 2020 | 32 |
| 7 | Using a deep learning system in endoscopy for screening of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (with video) | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | CAI | 2019 | 31 |
| 8 | Computer-assisted diagnosis of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using narrow-band imaging magnifying endoscopy | Endoscopy | ZHAO | 2019 | 30 |
| 9 | Integrated genomic characterization of oesophageal carcinoma | Nature | KIM | 2017 | 30 |
| 10 | Cancer statistics in China,2015 | Ca-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians | CHEN | 2016 | 30 |
Table 3 The analysis of co-cited esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022(top 10)
| 序号 | 文章题目 | 期刊名称 | 第一作者 | 出版年份(年) | 共被引次数(次) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Global cancer statistics 2018:Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries | Ca-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians | BRAY | 2018 | 87 |
| 2 | Diagnostic outcomes of esophageal cancer by artificial intelligence using convolutional neural networks | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | HORIE | 2019 | 56 |
| 3 | Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for detecting gastric cancer in endoscopic images | Gastric Cancer | HIRASAWA | 2018 | 43 |
| 4 | Real-time automated diagnosis of precancerous lesions and early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using a deep learning model (with videos) | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | GUO | 2019 | 37 |
| 5 | Deep-learning system detects neoplasia in patients with barrett's esophagus with higher accuracy than endoscopists in a multistep training and validation study with benchmarking | Gastroenterology | DE GROOF | 2020 | 32 |
| 6 | Endoscopic detection and differentiation of esophageal lesions using a deep neural network | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | OHMORI | 2020 | 32 |
| 7 | Using a deep learning system in endoscopy for screening of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (with video) | Gastrointestinal Endoscopy | CAI | 2019 | 31 |
| 8 | Computer-assisted diagnosis of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using narrow-band imaging magnifying endoscopy | Endoscopy | ZHAO | 2019 | 30 |
| 9 | Integrated genomic characterization of oesophageal carcinoma | Nature | KIM | 2017 | 30 |
| 10 | Cancer statistics in China,2015 | Ca-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians | CHEN | 2016 | 30 |
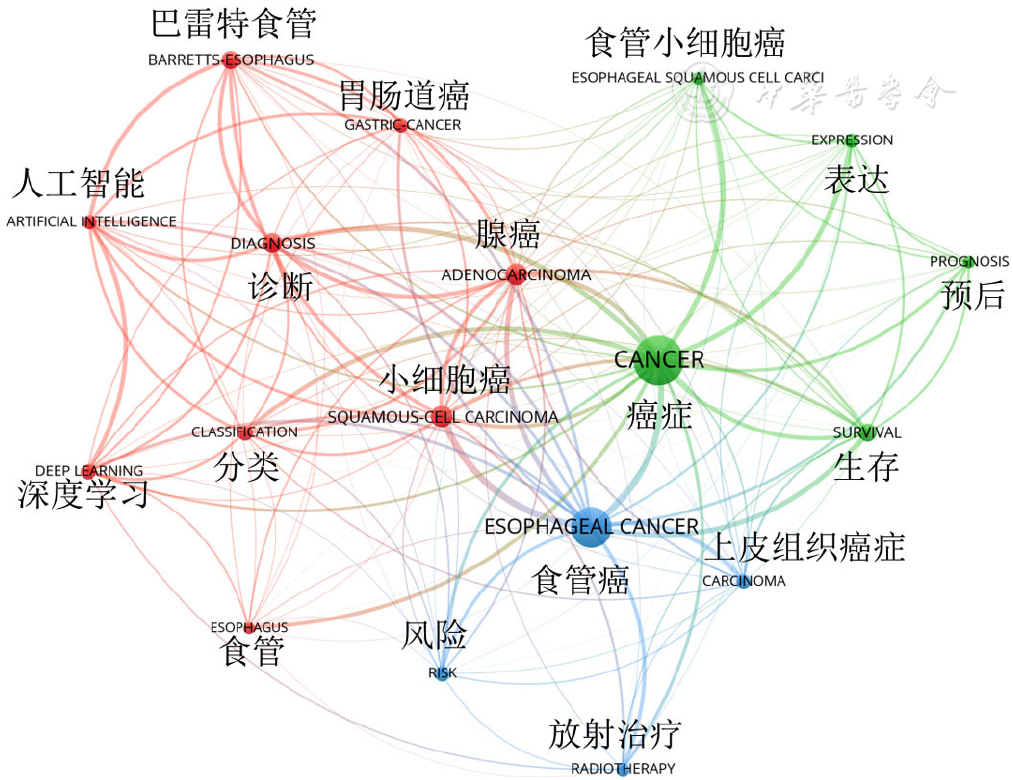
Figure 7 VOSviewer network visualization of the collinear map of keywords (frequency ≥ 50) in esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2022
| 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.31 | 16 | 2000 | 结直肠癌 |
| 2 | 0.23 | 71 | 2000 | 癌症 |
| 3 | 0.23 | 41 | 2000 | 上皮小细胞癌 |
| 4 | 0.19 | 49 | 2000 | 小细胞癌 |
| 5 | 0.19 | 6 | 2005 | 突变 |
| 6 | 0.18 | 47 | 2003 | 巴雷特食管癌 |
| 7 | 0.17 | 48 | 2000 | 食管癌 |
| 8 | 0.17 | 21 | 2001 | 乳腺癌 |
| 9 | 0.17 | 6 | 2001 | p53 |
| 10 | 0.13 | 25 | 2001 | 上皮组织癌 |
| 11 | 0.12 | 10 | 2003 | 肿瘤 |
| 12 | 0.11 | 23 | 2007 | 风险 |
| 13 | 0.11 | 8 | 2015 | 食管腺癌 |
Table 4 Keywords with centrality greater than 0.10 in esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2000 to 2016
| 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.31 | 16 | 2000 | 结直肠癌 |
| 2 | 0.23 | 71 | 2000 | 癌症 |
| 3 | 0.23 | 41 | 2000 | 上皮小细胞癌 |
| 4 | 0.19 | 49 | 2000 | 小细胞癌 |
| 5 | 0.19 | 6 | 2005 | 突变 |
| 6 | 0.18 | 47 | 2003 | 巴雷特食管癌 |
| 7 | 0.17 | 48 | 2000 | 食管癌 |
| 8 | 0.17 | 21 | 2001 | 乳腺癌 |
| 9 | 0.17 | 6 | 2001 | p53 |
| 10 | 0.13 | 25 | 2001 | 上皮组织癌 |
| 11 | 0.12 | 10 | 2003 | 肿瘤 |
| 12 | 0.11 | 23 | 2007 | 风险 |
| 13 | 0.11 | 8 | 2015 | 食管腺癌 |
| 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 | 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.24 | 11 | 2017 | 生物学标志物 | 14 | 0.14 | 20 | 2017 | 验证 |
| 2 | 0.22 | 18 | 2017 | 基因 | 15 | 0.13 | 36 | 2017 | 上皮组织癌 |
| 3 | 0.20 | 38 | 2017 | 表达 | 16 | 0.13 | 4 | 2020 | 计算机辅助诊断 |
| 4 | 0.19 | 19 | 2017 | 发育不良 | 17 | 0.13 | 26 | 2017 | 肺癌 |
| 5 | 0.18 | 15 | 2017 | 协助 | 18 | 0.13 | 13 | 2017 | 食管癌 |
| 6 | 0.18 | 6 | 2020 | 计算机辅助检测 | 19 | 0.13 | 2 | 2020 | CPR |
| 7 | 0.17 | 8 | 2019 | 准确度 | 20 | 0.13 | 4 | 2018 | 术前放化疗 |
| 8 | 0.17 | 10 | 2017 | 氟-18FDG断层扫描 | 21 | 0.12 | 4 | 2020 | 食管上皮小细胞癌 |
| 9 | 0.17 | 4 | 2017 | 肿瘤抑制因子 | 22 | 0.11 | 5 | 2021 | 生物信息学分析 |
| 10 | 0.16 | 11 | 2017 | 数据 | 23 | 0.11 | 42 | 2017 | CT检查 |
| 11 | 0.15 | 22 | 2017 | 结肠癌 | 24 | 0.11 | 4 | 2018 | 标志物 |
| 12 | 0.14 | 6 | 2017 | FDG断层扫描 | 25 | 0.11 | 41 | 2017 | 风险 |
| 13 | 0.14 | 11 | 2017 | 鉴别 | 26 | 0.11 | 2 | 2017 | 纹理特征 |
Table 5 Keywords with centrality over 0.10 in esophageal cancer studies using artificial intelligence from 2017 to 2022
| 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 | 序号 | 中心性 | 频率 | 年份(年) | 关键词 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.24 | 11 | 2017 | 生物学标志物 | 14 | 0.14 | 20 | 2017 | 验证 |
| 2 | 0.22 | 18 | 2017 | 基因 | 15 | 0.13 | 36 | 2017 | 上皮组织癌 |
| 3 | 0.20 | 38 | 2017 | 表达 | 16 | 0.13 | 4 | 2020 | 计算机辅助诊断 |
| 4 | 0.19 | 19 | 2017 | 发育不良 | 17 | 0.13 | 26 | 2017 | 肺癌 |
| 5 | 0.18 | 15 | 2017 | 协助 | 18 | 0.13 | 13 | 2017 | 食管癌 |
| 6 | 0.18 | 6 | 2020 | 计算机辅助检测 | 19 | 0.13 | 2 | 2020 | CPR |
| 7 | 0.17 | 8 | 2019 | 准确度 | 20 | 0.13 | 4 | 2018 | 术前放化疗 |
| 8 | 0.17 | 10 | 2017 | 氟-18FDG断层扫描 | 21 | 0.12 | 4 | 2020 | 食管上皮小细胞癌 |
| 9 | 0.17 | 4 | 2017 | 肿瘤抑制因子 | 22 | 0.11 | 5 | 2021 | 生物信息学分析 |
| 10 | 0.16 | 11 | 2017 | 数据 | 23 | 0.11 | 42 | 2017 | CT检查 |
| 11 | 0.15 | 22 | 2017 | 结肠癌 | 24 | 0.11 | 4 | 2018 | 标志物 |
| 12 | 0.14 | 6 | 2017 | FDG断层扫描 | 25 | 0.11 | 41 | 2017 | 风险 |
| 13 | 0.14 | 11 | 2017 | 鉴别 | 26 | 0.11 | 2 | 2017 | 纹理特征 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
中共中央办公厅 国务院办公厅印发《关于进一步加强科研诚信建设的若干意见》[EB/OL].(2018-05-30)[2022-04-30].
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
科技部办公厅. 科技部办公厅关于加强新型冠状病毒肺炎科技攻关项目管理有关事项的通知[J]. 现代养生,2020,20(S1):6.
|
| [1] | NIU Ben, ZHU Xiaoqian, YANG Chen, LIANG Wannian, LIU Jue. Evolution and Trends of Domestic and International Research Hotspots in the Field of Large Language Models in Medicine Based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3200-3208. |
| [2] | WANG Hui, HU Yinhuan, FENG Xiandong, LIU Sha, WANG Yangfan. The Application of Artificial Intelligence in Psychological Interventions: Effectiveness, Challenges, and Prospects [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3209-3216. |
| [3] | PAN Qi, REN Jingjing, MA Fanghui, HU Mengjie. Survey of General Practitioners' Cognition and Needs for AI Assisted Diagnosis and Treatment Systems [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3127-3136. |
| [4] | ZHAO Yali, LU Xiaoqin, LIU Jue, ZHANG Yifan, ZHU Zuyi, CHEN Kaiyuan, LIU Min, LIANG Wannian. The Construction of Assessment Index System of Artificial Intelligence General Practitioner [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2705-2711. |
| [5] | WANG Songzhu, YAO Yi, ZHOU Yiheng, ZHAO Jiaxi, YANG Rong, ZHAO Qian, ZHANG Rui, DAI Hua, LI Dongze, LIAO Xiaoyang, YANG Hui. Analysis of Research Hotspots and Development Trends of General Practice in the Last Five Years: a Visualization Analysis Based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2330-2337. |
| [6] | YAN Wenxin, LIU Jue, LIANG Wannian. DeepSeek Empowers General Medicine: Potential Application and Prospect [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2065-2069. |
| [7] | LI Yiting, TU Wenjing, YIN Tingting, MEI Ziqi, ZHANG Sumin, WANG Meng, XU Guihua. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Nutritional Management of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: a Scoping Review [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(14): 1709-1716. |
| [8] | GE Qiong, HU Jiakang, YU Yuqi, LAI Wenwen, LUO Shiwen, LU Quqin. Bibliometric Analysis of RNA-seq Technology in Liver Cancer Research [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(12): 1473-1478. |
| [9] | ZHANG Yushuang, WU Zhongbing, HUANG Ming, JIA Lei, GAO Shuang, ZHAO Weipeng, LI Jing. Study on Metabolic Characteristics in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients with TCM Differentiation of Deficiency of Fluid and Blood Based on Non Target Metabolomics [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(12): 1513-1519. |
| [10] | WANG Ganhong, ZHANG Zihao, XI Meijuan, XIA Kaijian, ZHOU Yanting, CHEN Jian. Construction of an Artificial Intelligence Model and Application for an Automatic Recognition of Traditional Chinese Medicine Herbals Based on Convolutional Neural Networks [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(09): 1128-1136. |
| [11] | CHENG Qi, YU Wenbing, LI Keke, ZUO You, JIAO Qianxin, LIU Xinhao, GAO Lili. A CiteSpace-based Analysis of Hotspots and Cutting-edge Trends in Mental Health among Middle School Students Research [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(07): 853-862. |
| [12] | Tsinghua University Vanke School of Public Health, Peking University School of Public Health, Chinese Association of General Practitioners of Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Chinese Expert Consensus on Artificial Intelligence General Practitioner (AIGP) [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(02): 135-142. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xuan, ZHANG Fei, LI Minglin, WANG Jiahe. Application and Challenges of Intelligent Robots in Grassroots Chronic Disease Management [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(01): 7-12. |
| [14] | WANG Zhenni, XU Yueping, XIA Kaijian, XU Xiaodan, GU Lihua. Construction of an Artificial Intelligence-assisted System for Automatic Detection of Pressure Injury Based on the YOLO Neural Network [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(36): 4582-4590. |
| [15] | ZHOU Yiheng, YANG Ziyu, LYU Yao, LIU Lidi, SHEN Can, LIAO Xiaoyang, JIA Yu. Interpretation of the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Improving Outcomes in Heart Disease:a Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(35): 4353-4357. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||